What is the primary effect of cardiomyopathies on the heart?
Affecting the shape and function of the ventricular walls
What heart rate characterizes sinus bradycardia?
- Below 60 bpm
What mitral valve mean valve gradient, what would be considered moderate stenosis
- 5-10
What grade of diastolic dysfunction is also referred to as pseudo normal?
Grade II
What peak tricuspid regurgitation velocity would be considered an indication for pulmonary hypertension.
>2.8
Severe Aortic Insufficiency jet in the LVOT is characterized by:
Occupying more than half the LVOT area
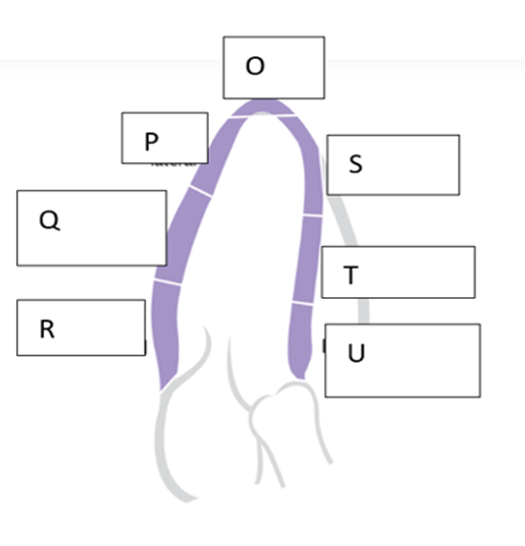
What is the name of the wall segment labeled “U”?
- Basal anteroseptum
What would be considered a normal diastolic wall thickness for a female patient?
0.6 - 0.9 cm
During Isovolumic Relaxation Time what is happening to the ventricular pressures?
Decrease
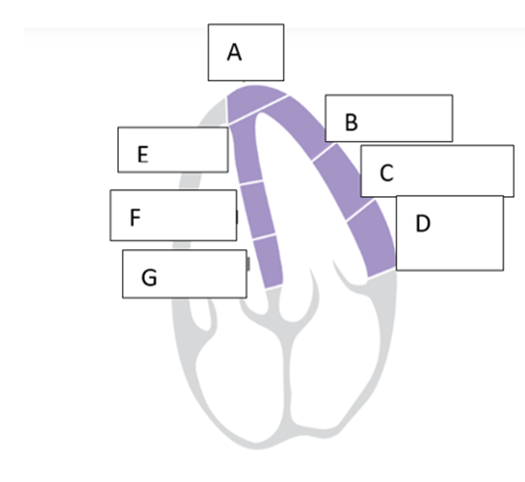
what is the name of the wall segment labeled “E”?
Apical septum
Dilated Cardiomyopathy is characterized by:
Dilated chambers and decreased function
What heart rate characterizes sinus tachycardia?
- Heart rate is above 100 bpm
What procedure can be performed in the CATH lab for severe mitral regurgitation?
- Mitral Valve Clip
What grade of diastolic dysfunction is also referred to as restrictive?
- Grade III
What TAPSE (mm) measurement would be considered abnormal, indicated reduced RV systolic function?
< 17
Classify the aortic valve pathology with a AV Vmax of 4.58 m/s, and AV meanPG of 52.84 mmHg:
- Severe Aortic Stenosis
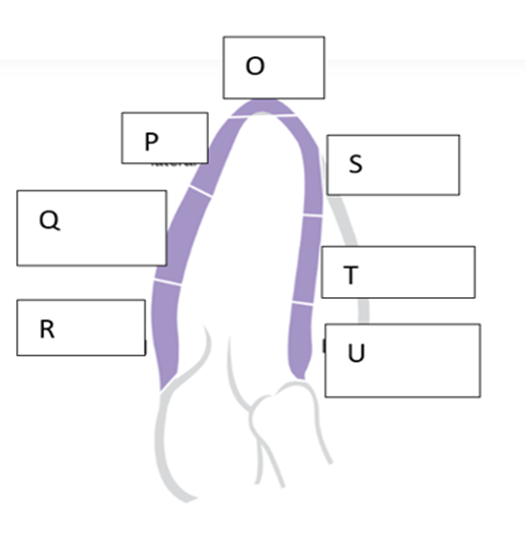
What is the name of the wall segment labeled “R”?
- Basal inferolateral
What would be considered a normal diastolic wall thickness for a male patient?
0.6 - 1.0 cm
Which of the following accurately describes the progression of cardiac phases?
- IVRT, Systole, IVCT, Diastole
- Diastole, IVRT, Systole, IVCT
- IVCT, IVRT, Systole, Diastole
- IVCT, Systole, IVRT, Diastole
IVCT, Systole, IVRT, Diastole
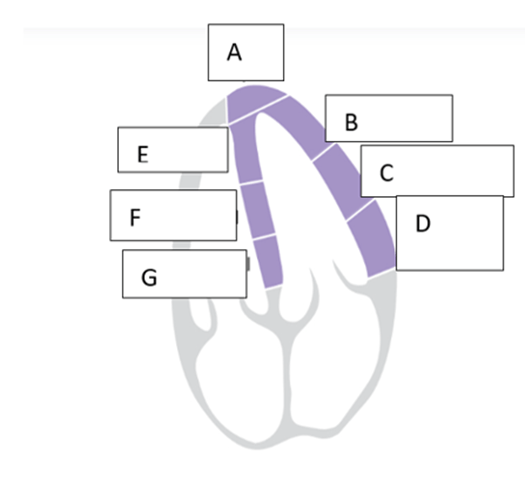
what is the name of the wall segment labeled “C”?
- Mid anterolateral
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy is mainly characterized by:
Increased muscle mass in one or more wall segments
Which cells have the lowest automaticity threshold in the heart?
- SA node pacemaker cells
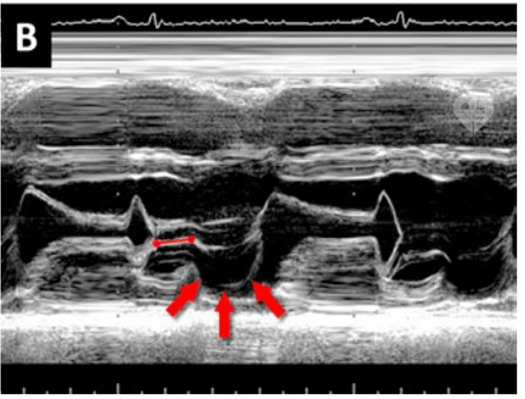
What would the most likely diagnosis be on the above image
Mitral valve prolapse
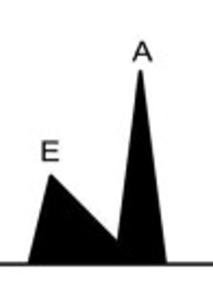
What grade of diastolic dysfunction would be expected with the above mitral inflow pattern, with normal LV systolic function?
- Grade I
What RV S’ (cm/s) would consider abnormal indicated reduced RV systolic function?
< 10
Your patient with Aortic Stenosis has an Aortic Valve Maximum Velocity (V-max) of 2.7 m/s. How would you classify this, based on velocity alone?
Mild
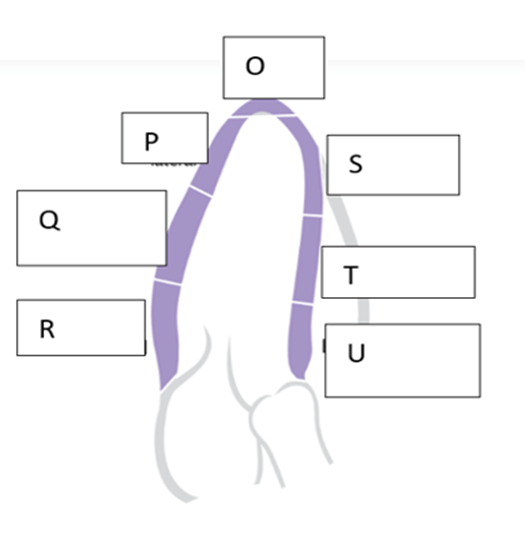
What is the name of the wall segment labeled “S”?
Apical septal
What would be considered a normal LVIDd for a female patient?
3.8 - 5.2 cm
What would be considered a normal EF for a female patient?
54 - 74%
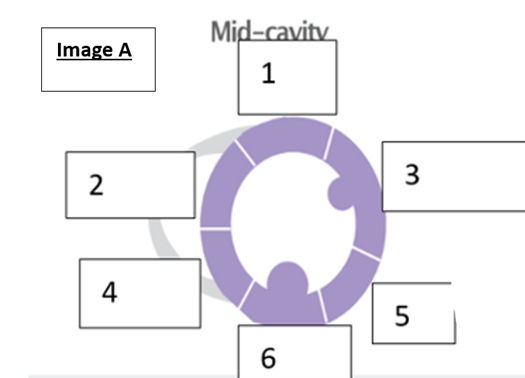
what is the name of the wall segment labeled “4’?
- Inferoseptum
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy is characterized by:
Decreased compliance
What on the EKG represents ventricular depolarization phase?
- QRS complex
Patient Jone Johnson has an LA volume of 40 ml/m2 what would the most likely classification of these chamber be.
Mildly increased
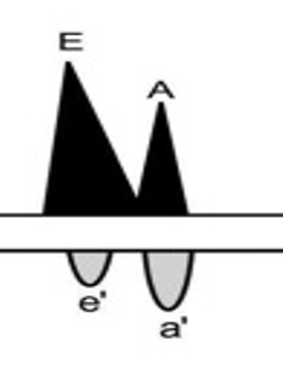
- What grade of diastolic dysfunction would be expected with the above mitral inflow pattern (flow noted on top), and the bottom flow pattern obtained from tissue Doppler?
Grade II
What TR velocity and RVSP is an indication for possible pulmonary hypertension in a younger adult?
>2.8, >35
Aortic Valve Stenosis with an Aortic Valve Maximum Velocity (AoV Vmax) of 3.2 m/s is classified as:
Moderate
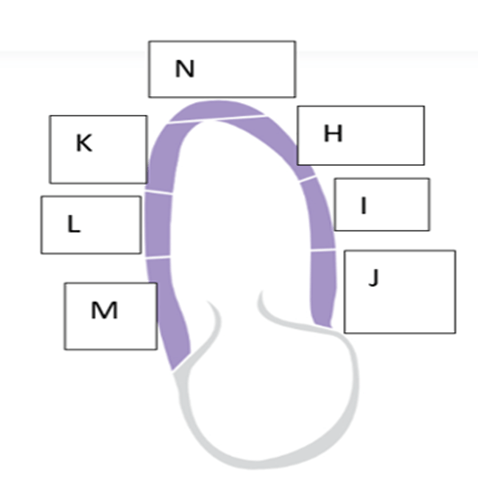
what is the name of the wall segment labeled “I”?
- Mid anterior
What would be considered a normal LVIDd for a male patient?
4.2 - 5.8 cm
What would be considered a normal EF for a male patient?
52 - 72%
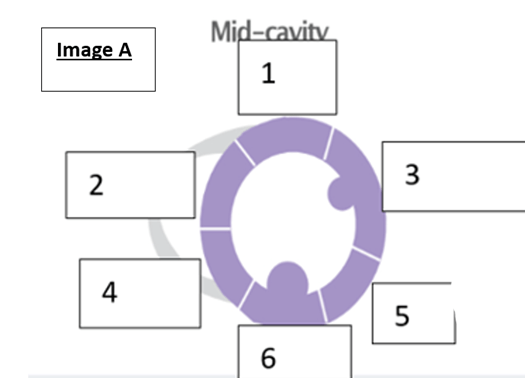
what is the name of the wall segment labeled ‘5”?
- Inferolateral
What type of cardiomyopathy is SAM "systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve" associated with:
Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
What is the purpose of the AV Node delaying conduction?
To provide adequate time for blood to move from the atrium into the ventricle
Mitral valve mean gradient would be considered severe MV stenosis?
> 10 mmHg
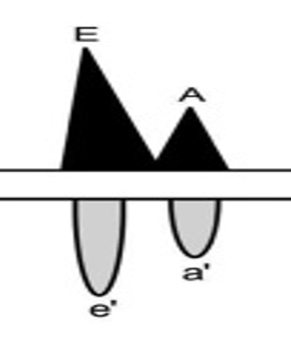
What grade of diastolic dysfunction would be expected with the above mitral inflow pattern, with normal LV systolic function, and the bottom flow pattern obtained from tissue Doppler?
Normal diastolic function
What number would be used to calculate the RVSP from the TR velocity, with a IVC diameter of greater than 2.1 and less than 50% collapse with inspiration.
- 15
What aortic valve area is considered severe aortic stenosis?
< 1.0 cm2
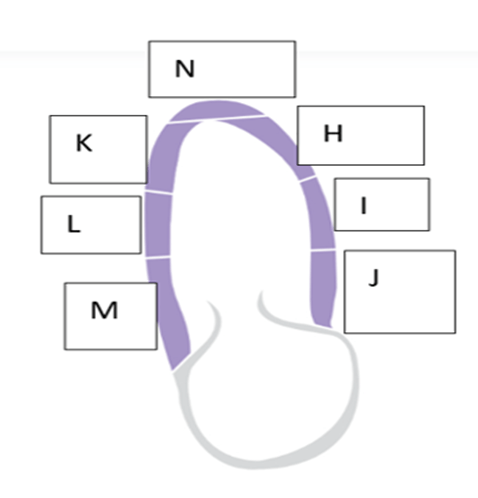
what is the name of the wall segment labeled “L”?
- Mid inferior
What would be considered a normal LAVI (LA volume index)?
16 - 34 ml/m2
What is considered a normal diameter for mid chamber of the right ventricle form the apical 4-ch view?
1.9 - 3.5 cm
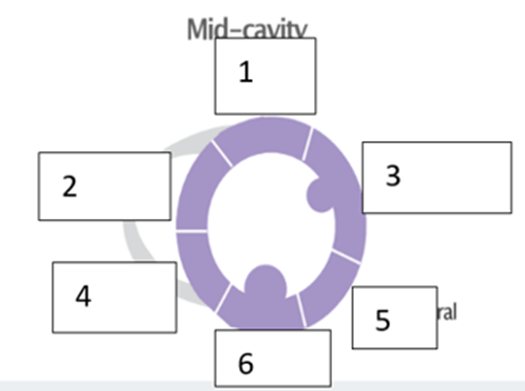
what is the name of the wall segment labeled “1”?
Anterior