These elements make up 98% of the human body except for:
A. Iron
B. Carbon
C. Phosphorus
D. Oxygen
E. Hydrogen
A. Iron
Tell me the four major classes of macromolecules and their polymers.
Carbohydrates-
Monomer: monosaccharides Polymer: Polysaccharides
Proteins:
Monomer: Amino acid Polymer: polypeptides
Nucleic Acid
Monomer: Nucleotides Polymer: Polynucleotides
Lipids: Not really no monomers but the types are triglycerides, phospholipids, and Steroids
Input and outputs of glycolysis?
Input: Glucose
Output: 2 pyruvates, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
What is the central dogma or molecular biology
DNA to RNA using trancripion
RNA to protein using translation
Difference between phenotype and genotype?
Phenotype- Physical appearance
Genotype- Organism genetic information.
Tell me all of the bonds: Covalent bonds, Ionic bonds, Hydrogen bonds.
Covalent - Share electrons & can have polar covalent (unequal) or nonpolar covalent bonds (equally)
Ionic - Transfer electrons & opposite charges attract
Hydrogen - The partial positive hydrogen from a polar molecule attracts to the partial negative atom of another polar molecule
Is this amino acid polar or nonpolar? Is it hydrophilic or hydrophobic? How can you tell?
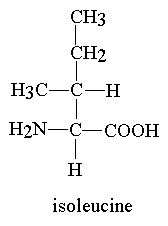
Nonpolar, hydrophobic, You look at the R group (at the top)
Input and outputs of Pyruvate oxidation?
Input: 2 pyruvates
Output: 2 Acetyl CoA, 2 CO2, 2 NADH
Explain briefly DNA replication.
DNA gets unwinded using a helicase.
Single stranded binding protein keeps it in place.
Primase makes a short strand of RNA.
DNA polymerase makes a new strand of DNA.
Which of these are referring to traits & which are referring to characteristics?
A. Purple hair
B.Height
C. Brown hair
D.Short
E.Flower Color
A, B, D are Traits
B,E are characters
Tell me the four properties of water fundamental for life.
Cohesion & Adhesion - Water can stick to itself (cohesion) and water can stick to anything else (adhesion)
Moderation of temperature - Water can resist temperature changes. Water has high heat capacity.
Expansion upon freezing - Molecules are more spread when water is in ice form
Versatility as a solvent - A lot of substances can dissolve in water
Types of carbs (polysaccharides)? Types of lipids? Nucleic acids make?
Carbs: Glycogen, Starch, Glucose
Lipids: Tryglycerides, Phospholipids, and Steroids
Nucleic Acid make DNA/RNA
What is the main point of the ETC/oxdative phosphorylation?
To make A LOT of ATP
Explain mitosis!
1. Prophase - Nuclear membrane & nucleolus starts to break down, chromatin begins to condense, & centrosomes begin moving to opposite poles
2. Metaphase - Sister chromatids are now aligned at the equatorial plate & line up parallel
3. Anaphase - Sister chromatids are separated from each other & become daughter chromosomes
4. Telophase - Nuclear envelope & nucleolus start to come back. Chromosomes start to decondense to chromatin. Dont need spindle anymore
Briefly describe translation
Small subunit of ribosome binds to the mRNA & scans until it finds the start codon, then the large subunit attaches
The polypeptide keeps growing by breaking the bond in the polypeptide and the tRNA at the P site to make a new peptide bond with the next amino acid
Ribosome reaches stop codon on mRNA
Define acid and bases. Using the terms H+ OH- and ph.
Acid is increase number of hydrogen ion pH would go down.
Base is decrease number of hydrogen ions and increase number of hydroxide ions pH would go up.
Which of these structures is not surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer?
A. Mitochondria
B. Endoplasmic Reticulum
C. Golgi Apparatus
D. Ribosomes
D. Ribosomes
Input and outputs of Citric Acid Cycle?
Explain the cell cycle.
1. Interphase
G1- Cell stay and do what they need to do
S- DNA replication
G2- Preparing for M phase
2. Mitosis/meiosis
3. Cytokinesis
Cell plate
Cleavage furrow
Explain Incomplete dominance, codominance, polygenic inheritance, epistasis.
Incomplete dominance: "Blending" of genes. Creates a new phenotype.
Codominance: Both allels will be expressed 100%.
Polygenic inheritance: More than one gene make up a single phenotype.
Epistatsis: where the expression of one gene is modified that can either be expressed or inhibited.
Tell me why a molecule would be classified as polar vs non-polar.
Polar have unequal sharing of electrons and Nonpolar have equal sharing of electrons.
Tell me the four levels of protein synthesis and the bonds of each.
Primary- Peptide bonds, long polypeptide chain not a functional protein
Secondary- Hydrogen bonds between the polypeptide. Not a functional protein yet.
Tertiary- Many bonds within the R group. Can be a functional protein.
Quaternary- 2 or more polypeptide.
Briefly explain fermentation and outputs for both humans and yeast?
NADH goes back o NAD+ and 2 ATP is made.
Humans: Lactic Acid
Yeast: Ethanol
Explain Meiosis!
1. Prophase I - Nuclear membrane breaks down. DNA condenses to chromosomes. Synapsis occurs then Crossing over occurs
2. Metaphase I -Homologous chromosomes line up in series at equatorial plate
3. Anaphase I -Homologous chromosomes are separated
4. Telophase I - 2 non identical cells that are haploid are formed
Briefly describe transcription intiation and elongation.
RNA polymerase binds to promoter, unwinds the DNA strands & begins making a strand of pre-mRNA at the start point.
RNA polymerase keeps making a strand of pre-mRNA & the DNA rewinds behind it
RNA polymerase falls off the template strand