What is a cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells?

Neuron
True or False:
Psychology is the scientific study of the human mind.
BONUS: Who founded Psychology, creating the first psychology lab?

False
Psychology is the scientific study of mental processes (mind) and behavior.
- We study animals!
B: Willhelm Wundt

Give two examples of a specific altered state of consciousness (ASC) and what is a non-altered state of consciousness?

1. A Buddhist monk who is meditating. A person under hypnosis by a psychologist.
- Sleep, dreams, hypnosis, hallucinations, meditations, and drug states (psychoactive and psychedelic drugs)
2. A person who had 8 hours of sleep (baseline state)

What is the name of this term:
Relatively enduring changes in knowledge and/or behavior resulting from specific experiences.

Learning
Explain what a teratogen is?
Anything that could harm a developing fetus.
EX: Cigarettes, alcohol, drugs, stress

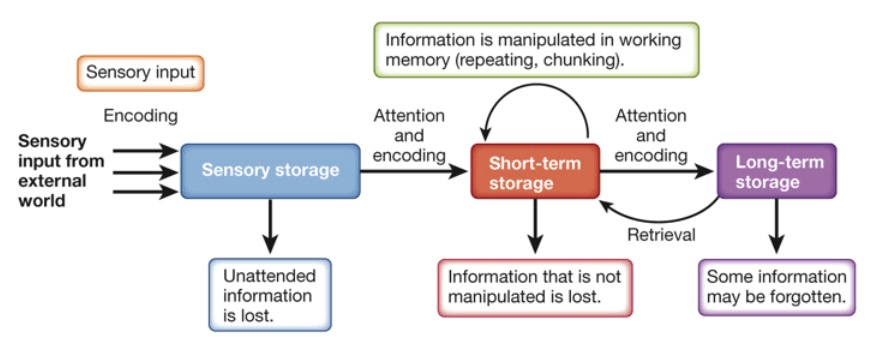
According to the information-processing perspective, memories are ...
BONUS: What is the difference between recall and recognition?

Encoded, Stored, Retrieved
Encoding --> Storage --> Retrieval
B: Recall: No context clues, essay, short answer
Recognition: Memory is prompted via retrieval cues, multiple-choice test

Identify three primary reinforcers and three secondary reinforcers.

Primary: Food, water, sex, air, shelter
Secondary: Money, status, praise, degree, trophy, grades

Fill in the blanks:
According to the modal model of memory, new information reaches __________ first, then the information is transferred into our __________, and then possibly encoded into our ____________.

1. Sensory Memory
2. Short-Term Memory (STM)
3. Long-Term Memory (LTM)
The tendency for one's sensitivity to stimuli to be lessened overtime during continuous exposure.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-selective-attention-2795022_final-5b6348f0c9e77c0050ba4710.png)
Sensory Adaption

What school/theory does this example demonstrate?
BONUS: What is the difference between recall and recognition?

Gestalt Schoool/Theory
- Humans create perceptions of "meaningful wholes" from fragmented and meaningless sensory signals.
B: Recall - No context clues, essay, short answer
Recognition - Memory is prompted via retrieval cues, multiple-choice test
Identify each lobe and explain what it does.
BONUS: What are the two non-colored structures at the bottom and what do they do?
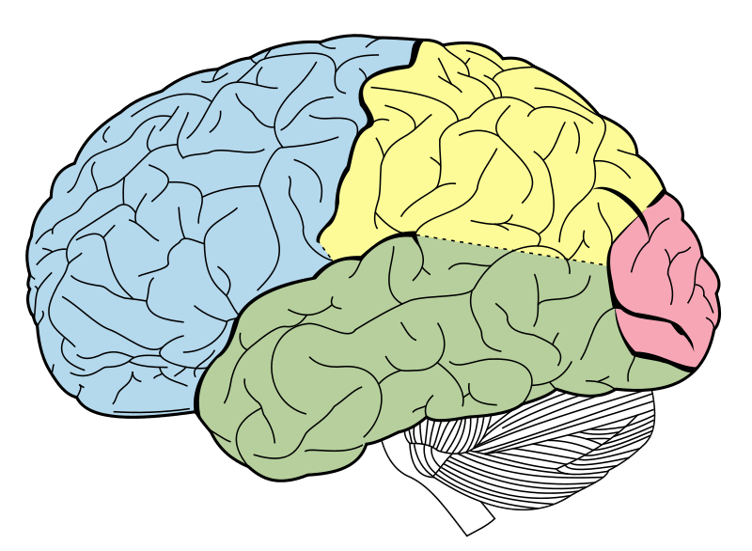
Frontal Lobe (Blue): "Executive functions," organization, planning, decision making
Temporal Lobe (Green): Sound
Parietal Lobe (Yellow): Touch
Occipital Lobe (Pink): Vision
B: Brain Stem - Relays information from the peripheral system, communication from body to brain
Cerebellum: Coordination, balance, movement, posture
Explain what the absolute threshold is.
BONUS: Explain what the just noticeable difference (JND) is.

Smallest intensity necessary for a stimulus to be detected, when you are first able to sense something.
B: Smallest difference between two stimuli that the appropriate sense organ can detect, when you first are able to notice a difference in stimuli.
- Detecting the differences between two sensory stimuli; larger the stimulus the bigger the JND
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/200258527-003-56a793363df78cf7729749df.jpg)
1. A parent characterized by high warmth and low control, little in the way of setting boundaries, limits, or rules (cool/best friend parent).
2. A parent with high warmth and high control, clear rules, fair enforcement, a warm environment, and the use of reason rather than force (best style).

1. Permissive
2. Authoritative
Authoritarian = Strict rules, the expectation of obedience, severe punishment (Dictator/Drill Sergeant Parent) - low warmth, high control
Uninvolved/Neglectful = No affection or presence in life (Absent/Doesn't Care Parent) - low warmth, low control
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/1095045-article-types-of-parenting-styles-5a7cb6aaa18d9e00362ef5eb.png)
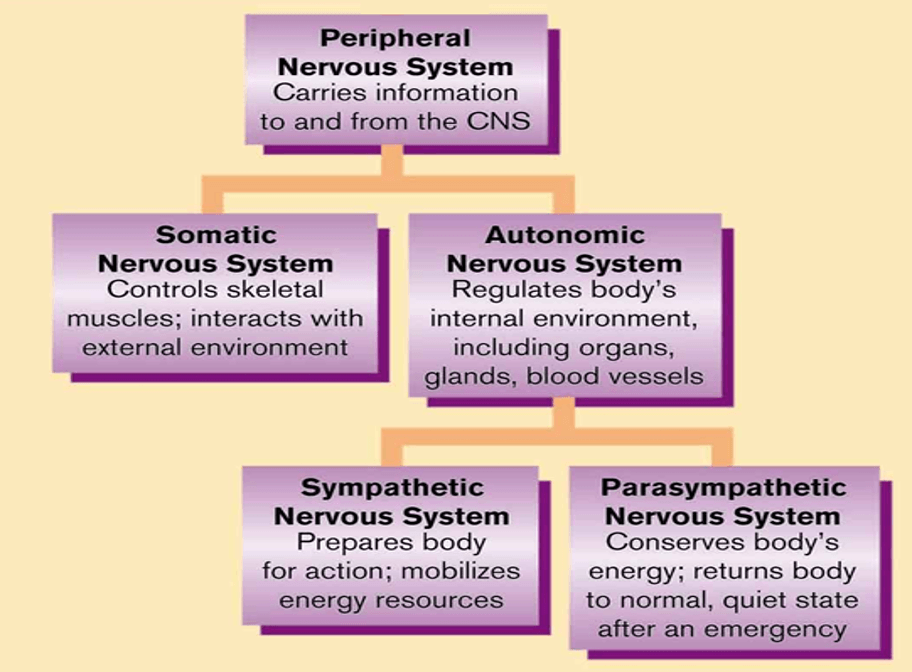
Inside the peripheral nervous system, what are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system and what does each one do?

Sympathetic: Arouses body to prepare for action, 3 F's (Freeze, Flight, Fight), responds to threats, EX: Heart rate increases, lungs expand, digestion halts, causing your mouth to become dry
Parasympathetic: Returns body to resting-state after arousal (baseline), when we are not stressed
- Autonomic is non-conscious, regulates involuntary activities
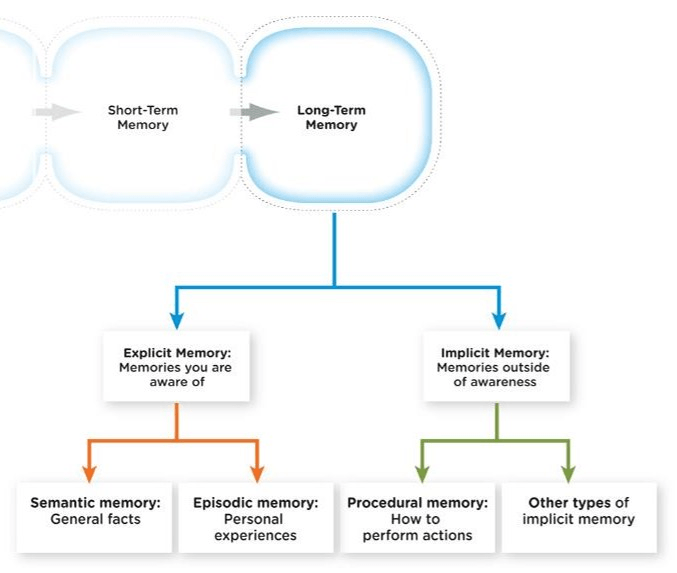
In long-term memory, what are the two subtypes of explicit memory and the one subtype of implicit memory?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Implicit-and-explicit-memory-2795346-5b84184146e0fb0050444414.png)
Explicit - Episodic Memory: Personal Experiences
Semantic Memory: Facts about the world
Implicit - Procedural Memory: How to do things
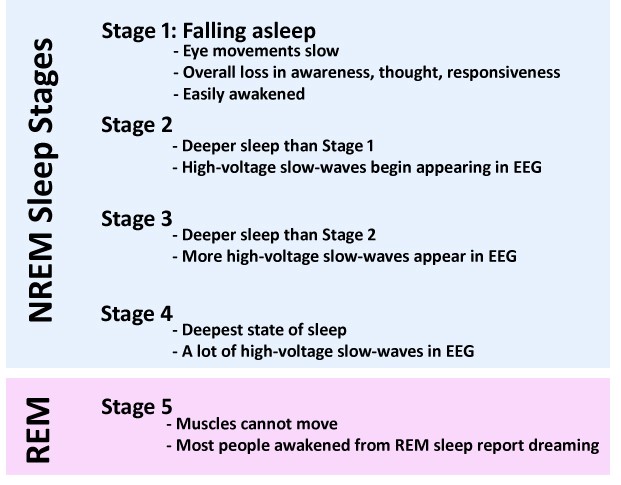
What stage of sleep does REM occur?
BONUS: What stage of sleep is the deepest, is it NREM or REM?

The 5th stage, only REM stage
- Muscle paralysis, intense dreaming, rapid eye movements
B: Stage 4, NREM ("Delta wave sleep")
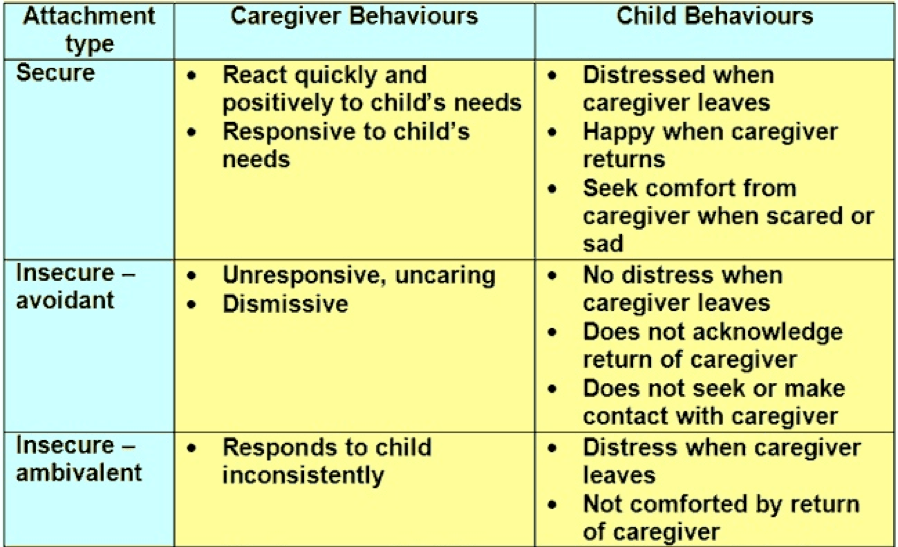
In Mary Ainsworth's "Strange Situation," what were the three types of attachment styles exhibited by the children?

1. Secure: Upset when mom leaves, happy when she comes back (best)
2. Avoidant: Doesn't care when mom leaves, ignores mom when returns
3. Insecure-Ambivalent: Upset when mom leaves, when mom returns is angry, seeks and reject
A homeless man runs into a store and steals food because he is hungry.
What would an adolescent in Kohlberg's preconventional level say about this situation if they believe its morally wrong?

"I could get into trouble with the police"
"My parents told me that it is wrong"
"I might get taken to jail"
1. Preconventional - Based on the prospect of reward or punishment, blind obedience to authority (Parent told me that it was wrong and could get me in trouble)
2. Conventional - Based on respect for the law, social norms, rules set by authorities (It's wrong because it's illegal)
3. Postconventional - Based on abstract principles and personal beliefs (It's wrong because it goes against my own personal ethical code)

Where are the primary motor, somatosensory, visual, and auditory cortexes? What does each one do?
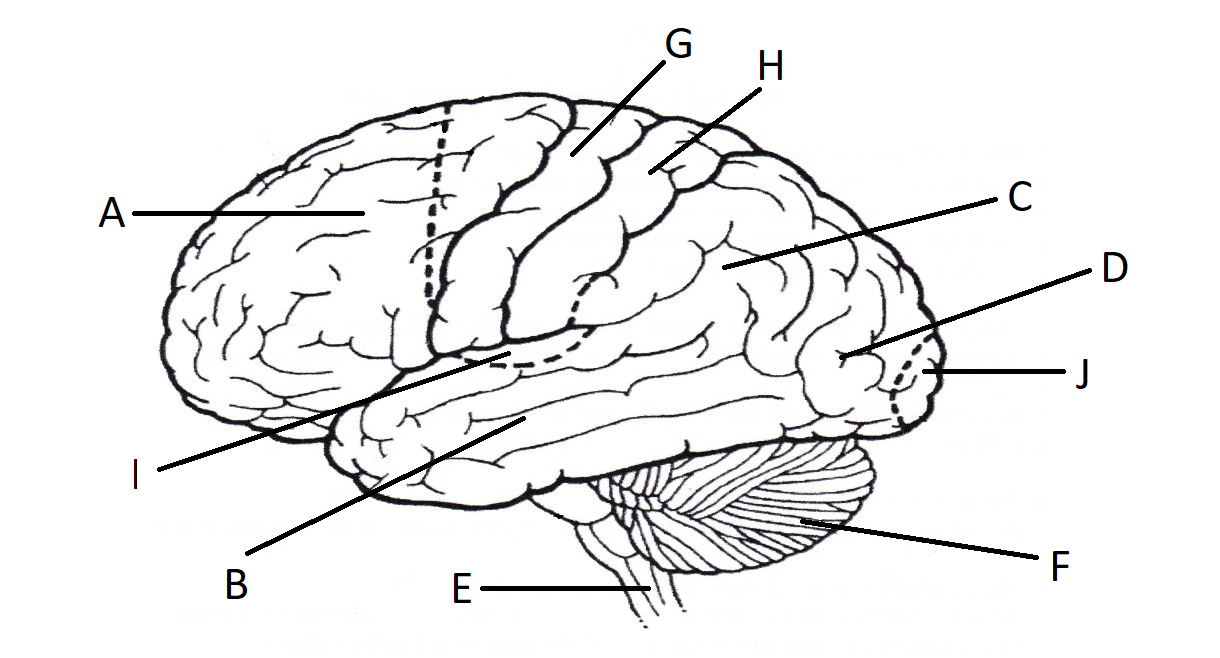
Primary Motor Cortex (G): Body movements (housed in the frontal lobe)
Primary Somatosensory Cortex (H): Differentiate one object from another by touch, determine the position of objects; pain, temperature, complex senses (housed in the parietal lobe)
Primary Visual Cortex (J): Where we actually see
Primary Auditory Cortex (I): Where we actually hear

Whenever you go to the eye doctor, you get a little puff of air in your eye and it causes you to blink. Right before this puff of air, you hear a beeping noise. Now, every time you hear that beeping noise, you blink your eye.
In classical conditioning, identify the UCS, NS, UCR, CS, and CR.
UCS: Puff of air
NS: Beeping noise
UCR: Blinking
CS: Beeping noise
CR: Blinking
________________________________________
UCS = Unlearned stimulus - Naturally, and automatically triggers a response (Food)
NS = A stimulus that triggers no innate response; the subject has no relationship with this stimulus at the beginning of conditioning (Bell)
UCR = Unlearned response that occurs naturally in response to the unconditioned stimulus (Salivation)
CS = A neutral stimulus that, after being repeatedly presented (paired) prior to the unconditioned stimulus, evokes a similar response as the unconditioned stimulus (Bell)
CR = Acquired/conditioned response triggered by the CS, which used to be the NS (Salivation)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2794859-article-classical-conditioning-5ac50cc9c5542e0037d54692.png)
What are the four stages of Jean Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development (in order) and what develops in each stage?

1. Sensorimotor: Develops object permanence [Birth-2]
2. Preoperational: Becomes egocentric, also develops symbolic thought (language) [2-7]
3. Concrete Operational: Develops conservation [7-11]
4. Formal: Develops hypothetical thinking, abstract reasoning (Feather breaks glass) [11+]
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795457-article-piagets-stages-of-cognitive-development-5a95c43aa9d4f900370bf112.png)
1. Every time I sell 5 pieces of chicken I get 2 dollars.
2. To make sure athletes aren't using steroids, the NFL randomly checks in on its athletes during the season.
What partial reinforcement schedule are these?
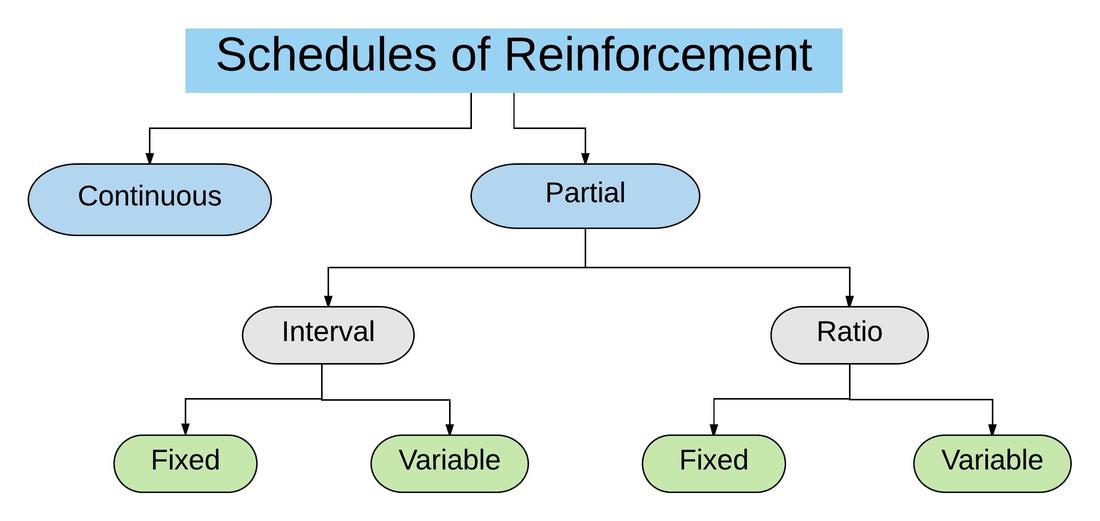
1. Fixed Ratio
2. Variable Interval
________________________________________
Fixed = Specific
Variable = Random, unpredictable
Ratio = Number of responses
Interval = Time
Describe the Freudian perspective of why we dream.

Freud's Wish-fulfillment Model of Dreams: Dreams expressed, in disguised and sometimes symbolic form, wishes and desires experienced by the dreamer on an unconscious level -- wishes and desires would be unaccepted or threatening if they were made conscious.
Simple answer: Wishes and desires
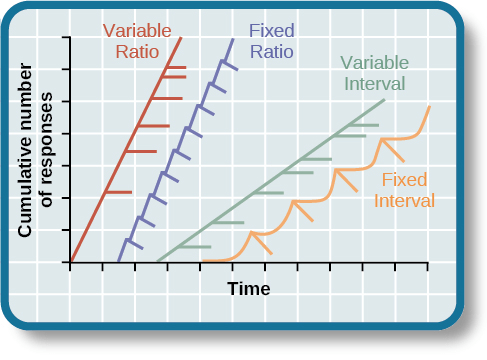
Mr. Smith wanted to see if the color of light shined on a plant had an effect on the number of leaves it had. He gathered 2 groups of the same species of plants, gave them the same amount of water, and did the test for the same amount of time. On one group of plants, he used white light. In the second group, he changed the light color to red.
In the experimental method, identify the IV, DV, EG, and CG.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/female-college-student-conducting-scientific-experiment-in-science-laboratory-classroom-683734687-58a0d65c5f9b58819c12cfca.jpg)
Independent Variable: the red light
Dependent Variable: the effect on the number of leaves
Experimental Group: Group with red light
Control Group: Group with white light
________________________________________
IV = What is being manipulated, what I change
DV = What is being measured, what I observe
EG = Group that receives IV, group the experimenter is messing with
CG = Group that doesn't receive the IV, comparison/baseline group
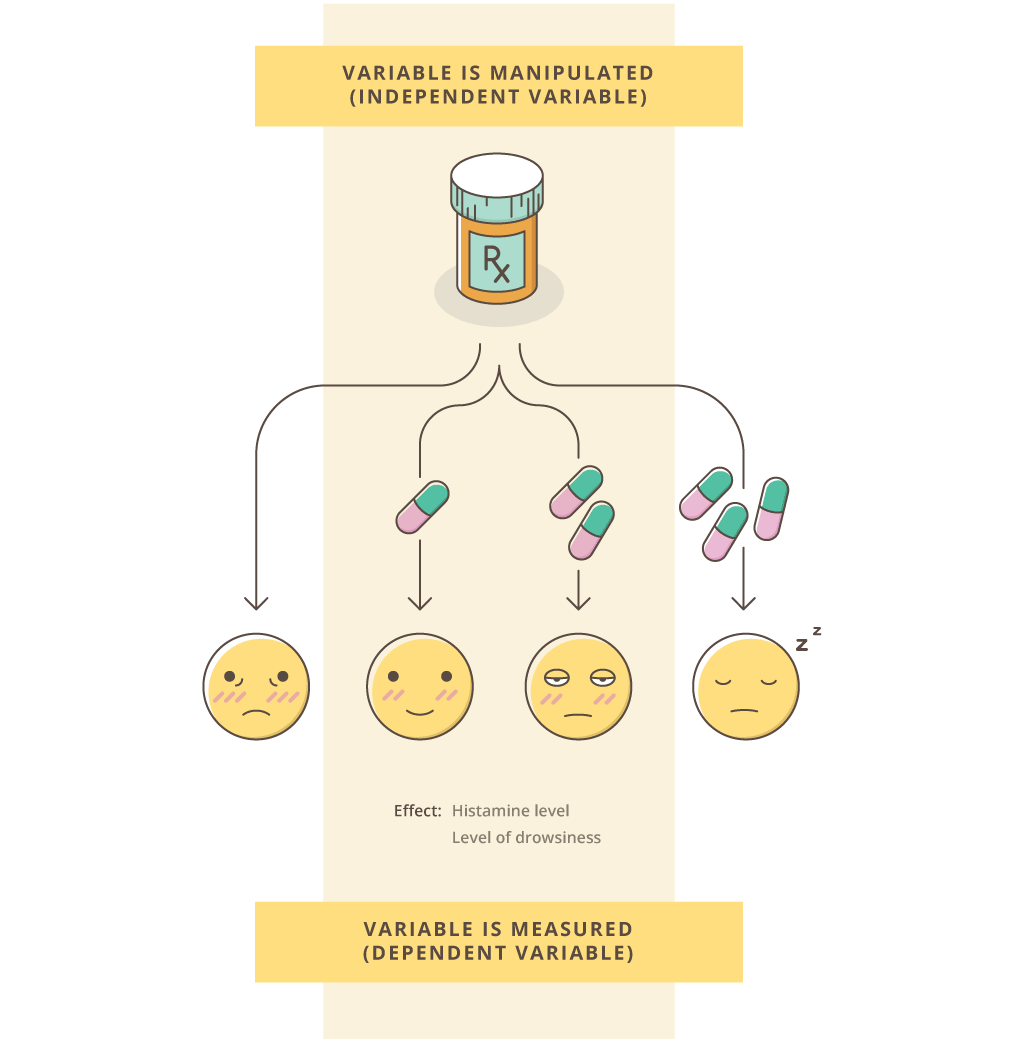
Draw Ebbinghaus's Forgetting Curve and explain what it means.

Forgetting follows a pattern according to the passage of time, with most memory loss occurring rapidly, and the pace then slowing.
- Participants learned a series of nonsense syllables and were repeatedly tested. Demonstrated that forgetting occurs quickly after the event.
Identify the type of operant conditioning:
1. After making a D on your final exam for not studying, your parents yell at you.
2. Your father keeps nagging at you to clean your room, so you clean your room to stop him from nagging.

1. Positive Punishment
Aversive Stimulus = Parents yelling
Behavior = Not studying
2. Negative Reinforcement
Aversive stimulus = Father nagging
Behavior = Cleaning your room
- Negative reinforcement is not the same as punishment
- You are removing a stimulus (negative) to increase a behavior (reinforcement)
- EX: Putting your seatbelt on (behavior) to get rid of the annoying seatbelt alarm (aversive stimulus), taking an Advil to get rid of a headache, using sunscreen to stop getting sunburnt, doing good in school to stop your Dad from criticizing you

What is the sensation and perception of this image?

Sensation: Light waves bounce off the image into my rods and cones, which are transducted into neurochemical impulses and sent to my primary visual cortex.
Perception: I see a leaping tiger and also see a monkey climbing a tree.
________________________________________
A + B + transducted + neurochemical impulses + C
A = light waves, sound waves
B = retina or rods and cones (inside retina), cochlea
C = primary visual cortex, primary auditory cortex

Identify the type of operant conditioning:
1. After staying out past his curfew, Bob's parents take his TV away and don't allow him to hang out with his friends.
2. Every time my dog listens to me and stops barking I give it a treat.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/2794863-operant-conditioning-a21-5b242abe8e1b6e0036fafff6.png)
1. Negative Punishment
Positive Stimulus = TV and hanging out with friends
Behavior = Staying out past curfew
2. Positive Reinforcement
Positive Stimulus = Treat
Behavior = Stops barking
________________________________________
Positive = Addition of stimulus
Negative = Removal of stimulus
Reinforcement = Goal to increase a behavior
Punishment = Goal to decrease a behavior

