The occipital lobe is crucial for which sense?
What is seeing or vision?
This psychologist focused on the psychosocial stages of development where each stage had a specific psychological-social challenge.
Who is Erik Erikson?
These sensory receptors are responsible for color in the retinas.
What are cones?
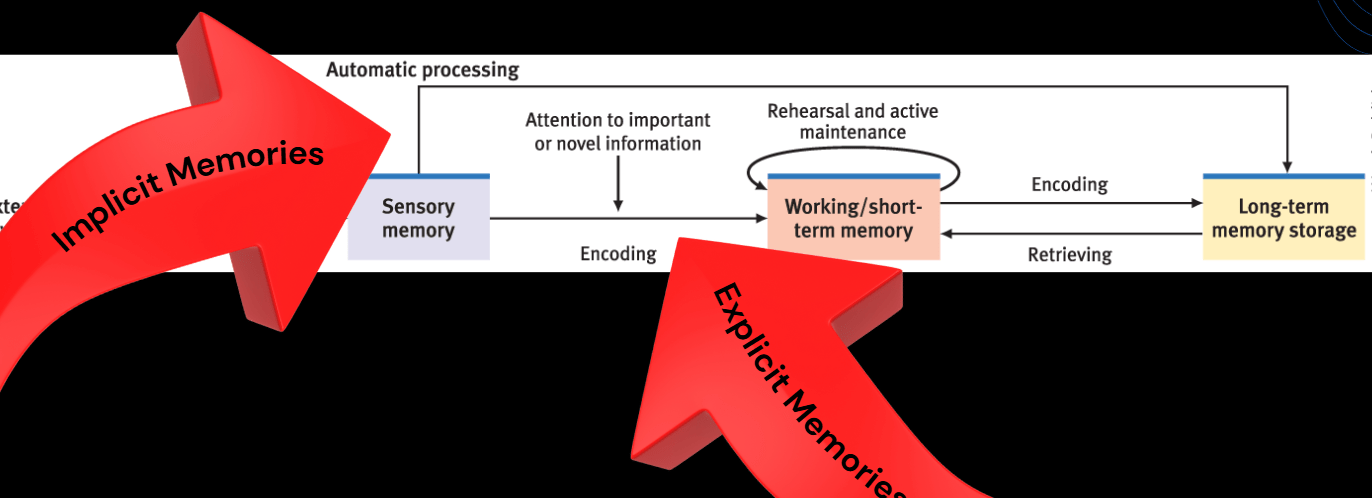
This memory is the first type of memory and it is held very briefly:
What is sensory?
This theory of emotion states that physical arousal (sensations) and thoughts/feelings happen simultaneously.
What is Cannon-Bard Theory?
When you know exactly where you stand on topic or opinion, this is considered an attitude.
This nervous system is made up of your brain and spinal cord. Injuries to the spinal cord could leave a person paralyzed.
What is the central nervous system?
This psychologist focused on the cognitive development of children.
Who is Jean Piaget?
This is the process of the brain when it takes the information it got from the senses and ORGANIZES and INTERPRETs it.
What is perception?
Implicit memories involve short-term/working memory. This is (true or false):
Emotions are said to have 3 primary things: 1) changes to the body, 2) behavior expressions, 3) .
What is peripheral?
A sub-nervous system of one of the primary nervous systems that helps you fight, fly, or freeze.

What is the sympathetic nervous system?
This style of attachment is marked by distress when the parent leaves and the child is NOT reassured when the parent comes back.
What is insecure attachment?
The process by which our sensory systems transform physical energy into neural impulses our brain can interpret is called
What is transduction?
Anthea is reading a text chapter for her psychology class and wants to make sure that the information gets into her brain, or is ________.
What is encode?
External rewards, such as praise, money, or grades, are said to be motivations.
The eating disorder that does NOT involve purging.
What is Binge Eating?
The process when neurotransmitters get reabsorbed into the neuron where they came from.
What is reuptake?
The type of attachment is marked by distress when a parent leaves but their distress lowers when the parent returns and they return to play time.
What is secure attachment?
This is the back layer of the eye that has cones and rods.
What is the retina?
If you're listening to a parent's instructions for how to make a dish (processing & storing), writing the steps down, and then immediately mixing the ingredients (recalling), this is using your memory.
What is short-term/working?
-determination theory focuses primarily on internal sources of motivation (intrinsic motivation).
What is Self?
What is comorbidity?
Phineas Gage's personality and social skills changed as a result of an injury to which part of his brain.
What is the frontal lobe?
What is sensorimotor stage?
People form schemas, or concepts, that they then use to interpret new stimuli. Those schemas are based on:
What are past experiences?
Riding a bicycle or starting your car is a type of implicit memory called memory. (Think basal ganglia)
What is procedural?
When a person is motivated by an activity that they find internally rewarding, they are said to be motivated by motivation.
What is intrinsic?
{Soft-hearted, helpful, trusting}
{Ruthless, uncooperative, suspicious}
Are spectrum traits of this Big Five trait:
What is agreeableness?
This part of your brain is highly related to emotional states.
What is the amygdala?
In Erik Erikson's theory of psychosocial development, what is the primary challenge faced during the "Identity vs. Role Confusion" stage (ages 12-18)?
What is developing a strong sense of self and personal identity?
In a class activity we used a marker to demonstrate our peripheral vision but we could not see the color of the marker. This is because are better at sensing movement and shades.
What are rods?
When you remember your parent teaching how to change your oil, that is called an memory.
What is semantic?
According to James-Lange Theory of emotions, people notice their first followed by thoughts/feelings:
What is bodily arousal/sensations?
Zorana spends most of her time home alone, usually reading a good book. Amara prefers going out with friends and enjoying a good party. The characteristics of Zorana and Amara indicate that each has a distinctive:
What is personality?