Which type of fracture is most concerning in pediatric patients?
What is....
A spiral fracture in a non-ambulating patient.
Negative toddler behaviors are best managed by doing what?
Ignoring (unless safety is concern)
Reward positive behaviors
Time-out ( age-appropriate )
Keep routines to help cut down on negative behaviors (tired kids = cranky kids)
What are interventions to review with parents of a child receiving Digoxin?
Must assess the pulse for 1 minute
Needs to be the apical pulse ( even with home care)
Do not give the medication if their heart rate is less than 90
Should be given on an empty stomach
Identify at least 3 differences between adult and pediatric respiratory systems?
What is…
Decreased number of alveoli
Shorter, narrower airways
Small oral cavities and large tongues
Higher bifurcation of larynx and glottis
Obligatory nose breathers until 3-4 months of age
Breathe with diaphragm
Neck cartilage is weaker increased rick of airway compression
what is urticaria ?
Hives
Normal bowel sounds occur at what rate?
5-30 per minute
Which findings would indicate to use that a child might have a neuromuscular disorder?
What is...
Gross and fine motor delays and prolonged primitive reflexes
Explain 3 ways we can increase levels of vitamin D
What is…
Dietary options
Vitamin D supplementation
Increase sunlight exposure
Explain the steps that should be completed when a patient has a reaction to a blood transfusion?
What is…
Stop the infusion and begin to infuse normal saline
Contact the provider and the blood bank
Frequent assessments and vitals
Save all remaining product and tubing for blood bank analysis
Name a way we can decrease separation anxiety for younger children?
What is...
Consistent routine such as dropping off and picking up at the same time
Goodbye ritual
Arranging time for child to be separated from parents if doesn't go to school or daycare
Security object
Explaining when you'll be back at an age appropriate level
Identify the main difference between the pediatric and adult heart?
What is...
The heart muscle is under developed in pediatric patients. Therefore, the cardiac output is influenced more by the heart rate than the stroke volume
The nurse is caring for a child who is experiencing stridor, tachypnea, and anxiety. The nurse would expect for the provider to order which medication?
What is...
Racemic Epinephrine
What are the differences in the skin between infants and adults?
List at least 2/3
Lack of subcutaneous tissue (impacts thermoregulation)
Demis and epidermis are loosely connected
Great body surface area
Changes to more adult like in late-school age/adolescents
How could we determine that treatment for Nephrotic syndrome was not effective?
What is...
Edema
Decreased urine output
Dark, frothy urine
Bilateral crackles or diminished breath sounds
Serum cholesterol/triglycerides increased
Decreased albumin levels in serum
Increased albumin levels in the urine
Elevated BUN and creatinine
What assessment finding in a child with AVM would be concerning?
Any changes neurologically-- high risk for hemorrhagic stroke
Symptoms can vary based on the location of the hemorrhage in the brain, but may include headache, numbness or weakness in part of the face, difficulty speaking, or difficulty walking.
What must be considered when determining if scoliosis can be treated with a brace?
What is…
The degree of the curvature
If the patient is still growing
Compliance
What is the reason for multiple dose changes with medications in younger children?
What is…
Rapid growth patterns and dosing being weight based
Identify strategies we can use to help a school aged child achieve Erikson's physchosocial stage.
What is...
Help to master tasks
Make sure that the activity matches child's ability
Set realistic and achievable goals
Offer support and encouragement when set backs occur
Coronary aneurysm
How can we include a school aged child in the management of their asthma?
What is...
Demonstrate how the medication works by allowing the to breathe thru a coffee straw versus a regular sized straw
Complications of hand-foot-and-mouth include?
Vesicular or pustular lesions on hands, feet, mouth
Fever
Pain
Dehydration
Daily fluid requirements for pediatric patients are?
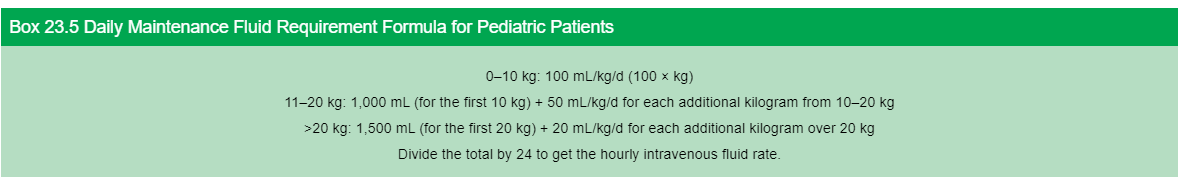
What are important teaching strategies for parents related to Reye Syndrome?
Avoid Aspirin containing products (especially when sick with a viral infection)
Monitor for any neurological changes
What assessment findings are associated with Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip? Name at least 4-5
What is…
Positive Ortolanis and Barlows sign
Leg length disparity
Trendelenberg gait
Gazelizzi Sign
What is the expected urine output for an adolescent patient?
What is...
40-80mL/h (800-1,400 mL/d)
Identify 3 gross motor and 3 fine motor delays and when we would expect to see them?
What is
Primitive Reflexes - Rooting until 4 months, sucking until about 4 months, moro until 2 months, stepping until 2 months, tonic neck until 5-7 months, palmar grasp until 5-6 months, plantar grasp until 9-12 months, and babinski until 2 year (pg 177-179)
Gross Motor - Moves arms and legs together and holds chin up when lying on the stomach (1 month); lifts head and chest when lying on the stomach and keeps head steady when in a sitting position (2 months); supports self on elbows and wrist when on belly, rolls from stomach to back (4 months); rolls from the back to the stomach, sits in tripod position, sits briefly without support (6 months); sits well without support, pulls to stand, able to go from a lying position to a sitting position and crawl (9months); stands independently and may take first steps (12 months) pg 188-189
Fine motor - 1 month open fingers slightly at rest; brings hands together and opens and closes hands (2 months); keeps hands relaxed, grasps objects, and brings hands to the mouth (4 months); transfers objects from 1 hand to the other, raking grasp, bangs objects on a surface (6 months); feeds self, 3 finger and thumb grasp, lets go of objects on purpose, and bangs objects together (9months); pincer grasp, can eat with cup and spoon, holds crayon with whole hand (12 months) pg 189-191
Heart rate
Respiratory rate
Perfusion
Weight
Skin turgor
Neurological ( not moving enough air/oxygen can cause neurological deficits)
What are the 4 cardinal signs of respiratory distress?
What is...
Restlessness
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Diaphoresis
Interventions for headlice include?
Nix is the appropriate OTC treatment for lice.
Combing nits should occur every 2-3 days until they are eliminated (hair should be wet)
Discouraging sharing personal hygiene items
Soaking/washing items in hot water is recommended.
Items that are unable to be washed should be sealed in a bag for at 72 hours.
Identify 5 UTI prevention strategies to prevent recurrent infections.
What is…
* Adequate hydration
* Loose fitting cotton underwear
* Avoid tight fitting pants
* Girls wipe front to back
* Avoid holding urine
* Watch for cues that children have to pee
* Discourage frequent bubble baths
Priority interventions for meningitis include?
List at least 3
Private room
Antibiotics/antivirals as ordered
Reduce environmental stimulation
Frequent neurological checks
Seizure precautions
Antipyretics
What importance does the level that a myelomeningocele have in improving patient outcomes?
What is...
The level of the defect and everything below it is typically non functional. If the defect is higher up in the spine it could affect the respiratory status of patient.
Identify infection prevention strategies to be reviewed with patients who are at an increased risk of infection?
What is...
Wear a face mask in public
Avoid sick contacts
avoid raw veggies, fruits, and meats
Remove live plants from the home
Observe heals for delayed healing and s/s of infection
Seek medical attention for s/s of infection
What are Erickson's stages of development and how might we assess these?
Trust vs Mistrust
Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt
Initiative vs Guilt
Industry vs Inferiority
Identity vs Role Confusion
Identify at least 4 medications used to manage heart defects and how the work?
Prostaglandin E helps to keep the ductus arteries open
Digoxin to increase contractility of the heart
Duiretics to decrease fluid in circulatory system
Ace inhibitors decrease blood pressure, peripheral resistance, after load, preload, and heart size
Beta 1 adrenergic beta blockers decrease excitability of the heart and cardiac output, decreases blood pressure
Identify the appropriate order to give CF breathing treatments, and chest physiotherapy
What is…
1. Albuterol
2. Hypertonic Saline
3. Pulmozyme
4. Chest physiotherapy
5. Long acting bronchodilator
Identify 3 types of fungal skin infections, where they occur at on the body, and appropriate pharmacological treatment
What are...
1. Tinea Corporis (ringworm, causes elevated red rash with central clearing on the body) Treat with topical anti fungal creams for 2 to 4 weeks
2. Tinea pedis (excoriation and peeling skin in between toes and on the soles of the feet). Treat with topical antifungals
3. Tinea capitis (resembles seborrheic dermatitis or psoriasis - can lead to kerions. Treated with griseofulvin
Why are we not able to repair a cleft lip/cleft palate at the same time?
The cleft lip is the priority because the repair allows the infant to have a better ability to latch/suck = better nutritional status.
The palate needs to wait in order to allow more time for natural growth and development. If the repair happens too early it may cause longer term damage
What are nursing interventions for seizures?
ABC's
Protect head
Administer rescue medications if indicated ( status epilepticus
Keep anything away from head/neck/airway
Do not put anything in their mouth
Loosen tight/restrictive clothing
Care for Cerebral Palsy can includes multidisciplinary team approach. Who should be included on this team?
Who is...
developmental physician, occupational therapist, physical therapist, speech therapist, case manager, teachers.