Tendency for one's sensitivity to stimuli to be lessened overtime during continuous exposure.
Sensory Adaption

Give an example of an altered state of consciousness (ASC) and a non-altered state of consciousness.
1. A Buddhist monk who is meditating
- Sleep, dreams, hypnosis, hallucinations, meditations, and drug states (psychoactive and psychedelic drugs)
2. A person who had 8 hours of sleep (baseline state)

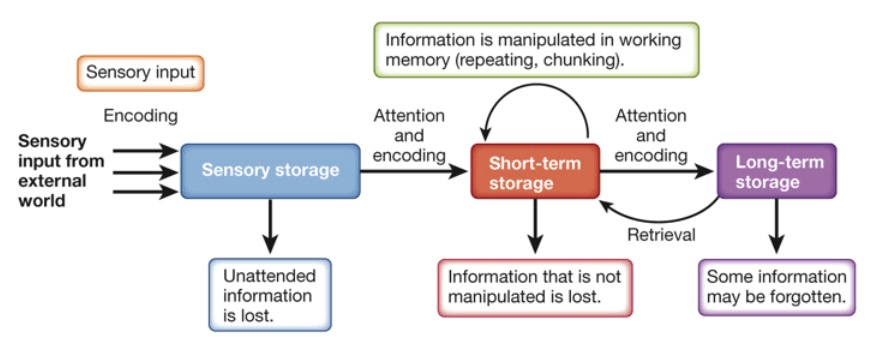
According to the information-processing perspective, memories are ...

Encoded, Stored, Retrieved
Encoding --> Storage --> Retrieval
What the two components of thought?
Mental Images: Representations of information in visual form
Concepts: Mental categories or groupings into which we put things that share certain characteristics and quality in common
EX: Food is edible substances

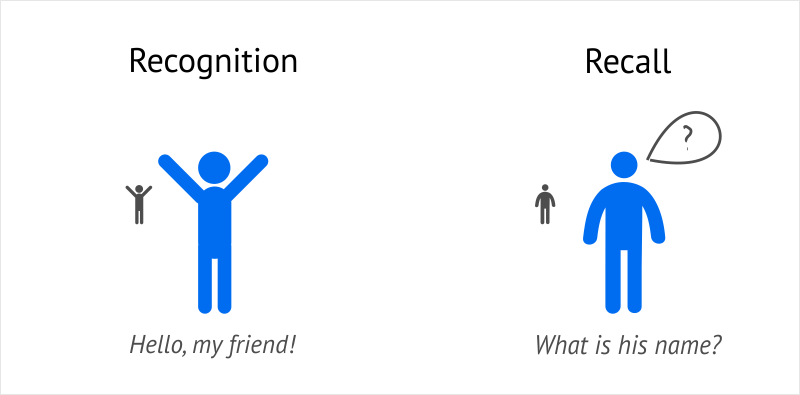
What is the difference between recall and recognition?
Recall: No context clues, essay, short answer
Recognition: Memory is prompted via retrieval cues, multiple-choice test
What is the just noticeable difference (JND)?
Smallest difference between two stimuli that the appropriate sense organ can detect, when you first are able to notice a difference in stimuli.
- Detecting the differences between two sensory stimuli
- Larger the stimulus the bigger the JND is
- Weber's law is the mathematical expression of the proportion of the standard (the original stimulus) to the JND
EX: Noticing the difference between the music lowering at a concert and noticing the difference between the music lowering on your laptop speakers
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-90079709-56a797d25f9b58b7d0ebf8f4.jpg)
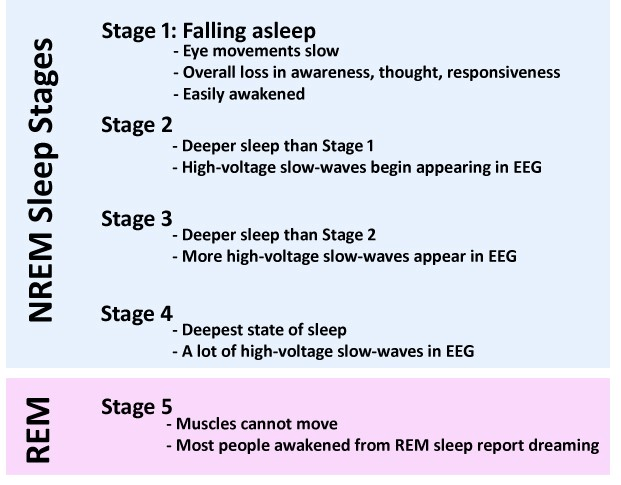
What stage of sleep does REM occur?
BONUS: What stage of sleep is the deepest?
The 5th stage.
- Muscle paralysis, intense dreaming, rapid eye movements
BONUS: Stage 4, NREM ("Delta wave sleep")

Fill in the blanks:
According to the modal model of memory, new information reaches __________ first, then the information is transferred into our __________, and then possibly encoded into ____________.
1. Sensory Memory
2. Short-Term Memory (STM)
3. Long-Term Memory (LTM)
What is a prototype?
An example of a concept or category that is thought to be particularly typical or representative.
- What we think is the best example representative for a concept
Concept (Dog) ---> Prototype (Golden Retriever)
Concept (Food) ---> Prototype (Pizza)
Concept (Vehicle) ---> Prototype (Bicycle)

Mental problem-solving short-cuts or "rules of thumb," helps us make judgments when not all facts are known.
Heuristics

Smallest intensity necessary for a stimulus to be detected, when you are first able to sense something.
Absolute Threshold
- By the appropriate sense organ 50% of the time
EX: In order for you to hear the couple in the apartment next door to you arguing, they have to be going at it loudly enough for your ears to hear
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/200258527-003-56a793363df78cf7729749df.jpg)
Light sleep, unaware of the environment but relatively easily awakened. Preparation to enter deeper levels of sleep.
What stage of sleep is this and is it NREM or REM?
Stage 2, NREM
What is the length and capacity of STM and LTM?

STM - Length: 20s, Capacity: 7 ± 2
LTM - Length: 2-3 minutes to a lifetime, Capacity: Unlimited
A step-by-step set of systematic "instructions" that can be used to solve any problem of some given type.
BONUS: The most basic problem-solving strategy, where solutions are eliminated one at a time.
Algorithms
BONUS: Trial and Error

What are the functions of sleeping?

Rest and restoration (Restorative function), consolidate and retain memories, Evolutionary Function
What school/theory does this example demonstrate?
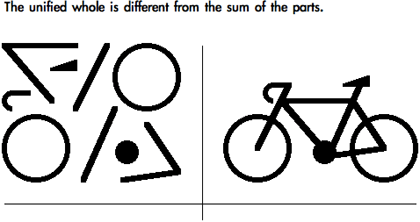
Gestalt Schoool/Theory
- Humans create perceptions of meaningful "wholes" from fragmented and meaningless sensory signals.
Name the three components of consciousness.

1. Qualitativeness - Our conscious experiences have quality.
EX: Eating a good breakfast feels different from learning you that you scored a 100 on your test.
2. Subjectivity - Consciousness can only be experienced by 1 person, its unique to you.
EX: If we are both eating the same ice cream, it's still two different experiences.
3. Unity - Consciousness is a single unified experience, all integrated into one experience.
EX: I sit here typing, I do not just feel the keyboard keys under my fingertips, see the words form on the computer screen, hear the sounds of the computer speakers, and think that it's been raining too long -- I experience all these cognitive and sensory experiences together as one consciousness.
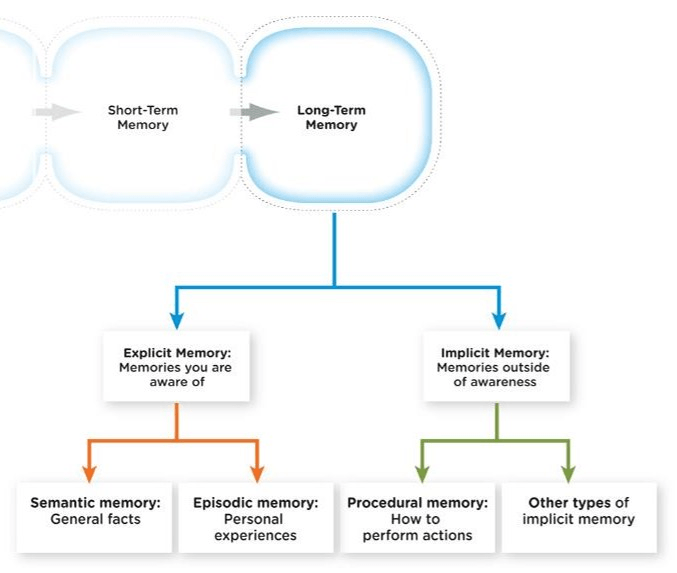
What are the two divisions of the LTM, what do they mean?
BONUS: What are the divisions of those two divisions and what does each mean?
1. Explicit Memory - Memories you are aware of
2. Implicit Memory - Memories outside of awareness
B: Semantic Memory - General facts (Explicit)
Episodic Memory - Personal Experiences (Explicit)
Procedural Memory - How to perform actions (Implicit)
Used when coming to a judgment about how often something occurs or how likely it is to occur in the future. Biases us towards information that is more easy to recall.
BONUS: What does the term "base rate" mean?
Availability Heuristic
- Helps us make quick decisions about the likelihood of something occurring
B: Indicates the probability of how prevalent something is in a population or how frequently it occurs, expressed in a percentage, and is usually failed to take into account.
EX: "If it looks like a duck and walks like a duck – and the base rate of ducks is low – it is probably a goose or a gallinule!"
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/availability-heuristic-2794824_color1-5b76d4b046e0fb00509bbb7a.png)
Explain what general intelligence (g) and practical intelligence is?
General - Book smarts
Practical - Street smarts
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-general-intelligence-2795210_final2-5b3f90eb46e0fb005bb17b85.png)
What is the sensation and perception of this image?

S: Light waves bounce off the image into my rods and cones, which are transducted into neurochemical impulses and sent to my primary visual cortex.
P: I see a woman with long hair and lipstick on
A + B + transducted + neurochemical impulses + C
A = light waves, sound waves, odors, food molecules, tactile sensations
B = rods and cones (inside retina), cochlea, olfactory, taste buds, mechanoreceptors
C = primary visual cortex, primary auditory cortex, thalamus/frontal lobe, primary somatosensory cortex
- But really just focus on visual and sound.
Describe the Freudian perspective of why we dream.

"Royal road to the unconscious"
Freud's Wish-fulfillment Model of Dreams: Dreams expressed, in disguised and sometimes symbolic form, wishes and desires experienced by the dreamer on an unconscious level -- wishes and desires would be unaccepted or threating if they were made conscious.
Draw and explain the Serial Position Curve. Also, show where the primacy and recency effects are at and what they mean.
When people asked to memorize list of words, their recall is most reliable for words presented first (primacy effect) and words presented last (recency effect).

Give an example of the representativeness heuristic.
Sarah tells Jasmine that she works at an elementary school, Jasmine assumes that Sarah is a teacher, but Sarah is actually the secretary.
Making a judgment by comparing a new person or thing to our ideas and beliefs of a "typical" member of the group to which it belongs.
- Used to quickly determine the category or group to which a new object or person belongs
- Failure to take base rates into account, prejudice, stereotyping, gambler's fallacy
/representativeness-heuristic-2795805-5b841fdc46e0fb0025f76b56.png)
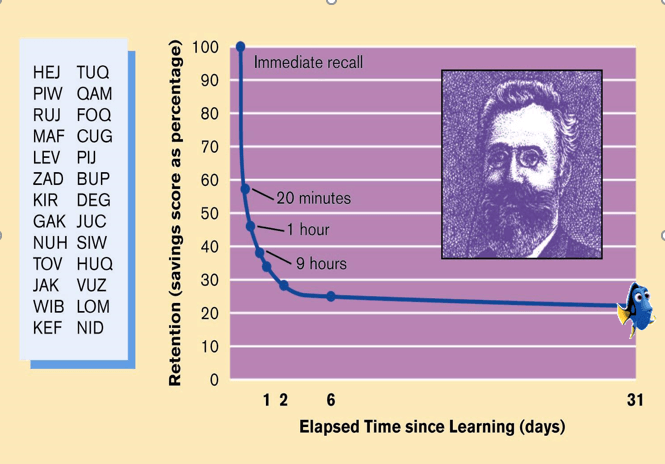
Draw Ebbinghaus's Forgetting Curve and explain what it means.
Forgetting follows a pattern according to the passage of time, with most memory loss occurring rapidly, and the pace then slowing.