Give an example of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation.
Intrinsic: Passion, growth, enjoyment, fun, purpose, curiosity, interested
Extrinsic: Money, promotion, prizes, fame, grades, praise, perks, winning, benefits, pay raise
Intrinsic = Comes from within, not for external reward
Extrinsic = Outside, external rewards or to avoid punishment
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795384-differences-between-extrinsic-and-intrinsic-motivation-5ae76997c5542e0039088559.png)
What are the three components of Personality?
BONUS: What is repression?

1. Organized: Personality forms a coherent picture that can be described in words
2. Integrated: Various aspects of personality are related to - and work with - one another. Aspects of personality form a whole.
3. Relatively Enduring: Personality is fairly consistent over time.
B: Taking an uncomfortable thought and moving it to the unconscious to keep it repressed; a Freud Ego Defense Mechanism.
According to the DSM-5 view, two primary conditions must exist in a psychological disorder. What are the two?
BONUS: What type of psychologist treats unconscious conflicts and what is the therapy called?

Dysfunction and Distress
Dysfunction = Not going to job, breakdown in the functioning
Distress = Negatively impacting you, upset
B: Psychoanalyst - Psychoanalysis and also Psychodynamic Therapy if a Neo-Freudian Psychoanalyst
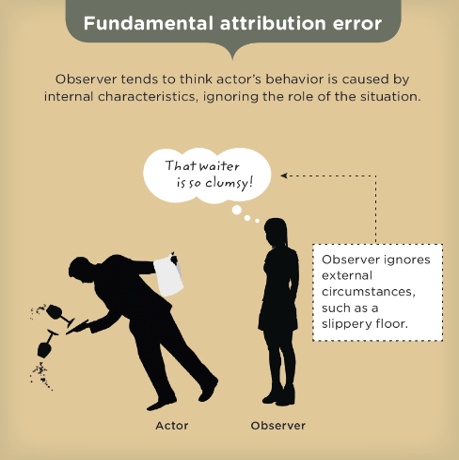
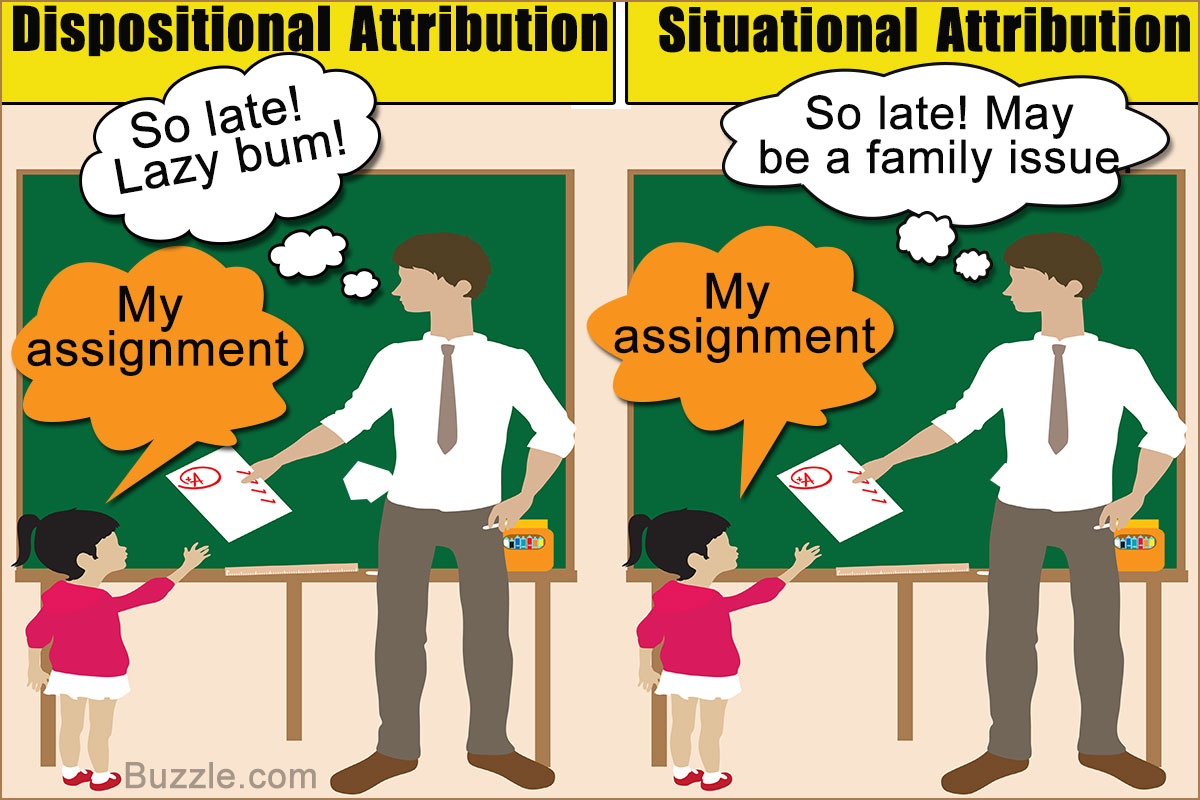
The tendency to attribute people's behavior to their (internal) dispositions while ignoring that the behavior may be influenced by situational (external) factors.
Fundamental Attribution Error (FAE)
- Blaming someone on something and ignoring what could be going on with them
Give an example of two traits and two states.

Traits: Stable, enduring personality attributed, long-term
EX: Extraverted, conscientious, cheerful, honest, compassionate, depressed
States: Emotions, moods, or other characteristics and attributes which are tempory.
EX: Mad, upset, happy, sad, frustrated
What is the difference between instrumental and hostile aggression?
Instrumental is planned, hostile is a reaction, impulsive (not planned).
Instrumental has an ultimate purpose other than causing harm to a victim, Hostile has the ultimate purpose of harming the victim.

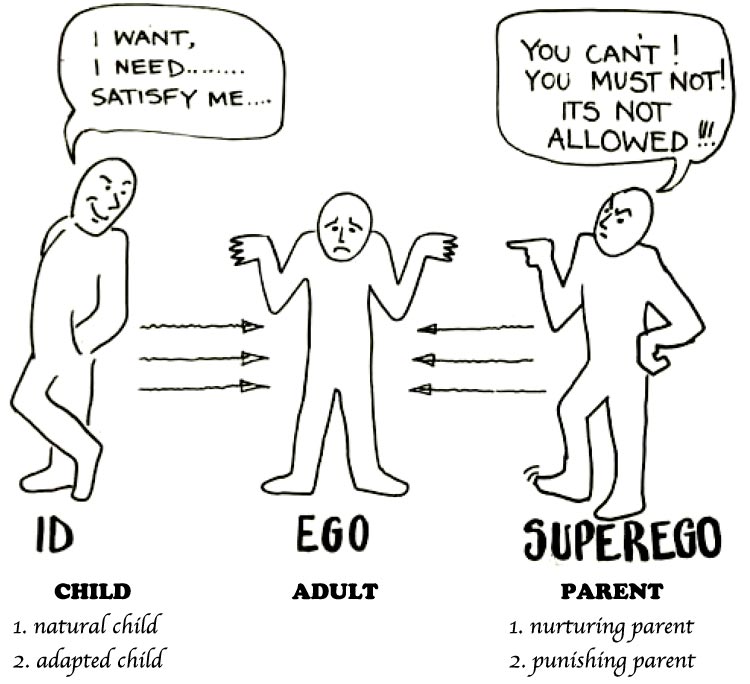
In Freud's Structural Model of The Mind, what principles do the ID and Ego operate by?
BONUS: What does the Superego do?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/2795946-the-conscious-and-unconscious-mind-5b180a1c303713003637fa48.png)
ID --> Pleasure Principle
Ego --> Reality Principle
B: The wellspring of conscience and morality. Passes judgment on actions guided by the ego.
What are the two predominant positive symptoms of schizophrenia?
BONUS: How would you treat schizophrenia?
Delusions and Hallucinations
Delusion: The CIA is trying to steal my brain
Hallucination: I see ghosts
- Postive = Addition
- Negative = Absence
BONUS: Pharmacotherapy with antipsychotics
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-symptoms-of-schizophrenia-2953120-cba74c5e1dd942ecafde1824217603f9.png)
In the Solomon Asch experiment, this tendency was observed.
BONUS: What is a confederate?
Conformity - Any change in behavior caused by another person or group.
B: An actor in an experiment

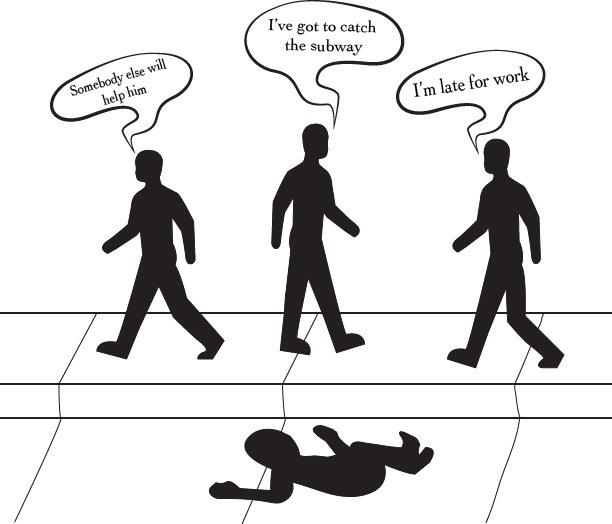
Tendency for a person to be less likely to intervene and help a stranger when other people are there who might help.
B: What is altruism?
Bystander Effect
- More present = less likely to aid
B: The offering of assistance to others without the expectation of immediate reward.
What are these terms?
The need to mingle with other people in the same space.
B: The need to experience frequent, positive interactions with people in stable, enduring relationships where there is concern for one another's welfare.
Need to affiliate
- Tempory, need to be with others, need to be accepted by a group
- Affiliation: Process of "flocking together" and does not necessarily imply that strong relationships will form.
B: Need to belong

In the Five-Factor Model (the "Big Five") what does OCEAN stand for?
BONUS: Explain what each means.
Openness - Creative, nonconforming, curious
Conscientiousness - Reliable, well-organized
Extraversion - Sociable, energetic
Agreeableness - Good-natured, kind, trusting
Neuroticism - Emotional, anxious (BAD)

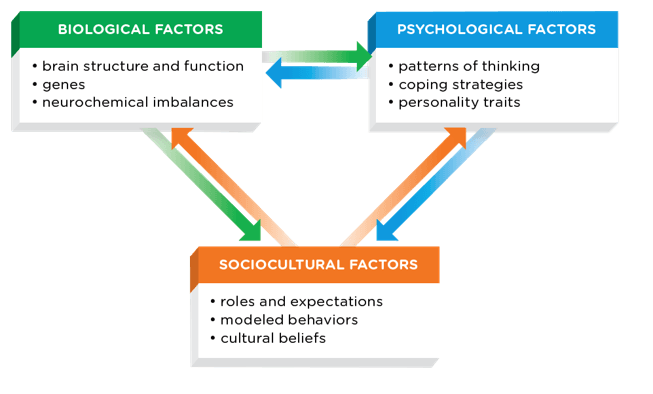
What are the 3 causes of psychological disorders?
BONUS: What type of psychologist would use client-centered therapy: promote personal growth in the client in a nondirective manner by treating the client with dignity, empathy, and unconditional positive regard
1. Biological factors
2. Psychological factors
3. Sociocultural factors
B: Humanistic
Give an example of Cognitive Dissonance.
Attitude (I like smoking) ----> Behavior (I smoke cigarettes) ----> Belief (Smoking is bad for my health)
- Anxiety or tension that arises when people behave contrary to their attitudes. 
Characterized by cycles of depression and mania that alternate over time, usually separated by serval months
Bipolar Disorder
Depression + Mania (Mood State)

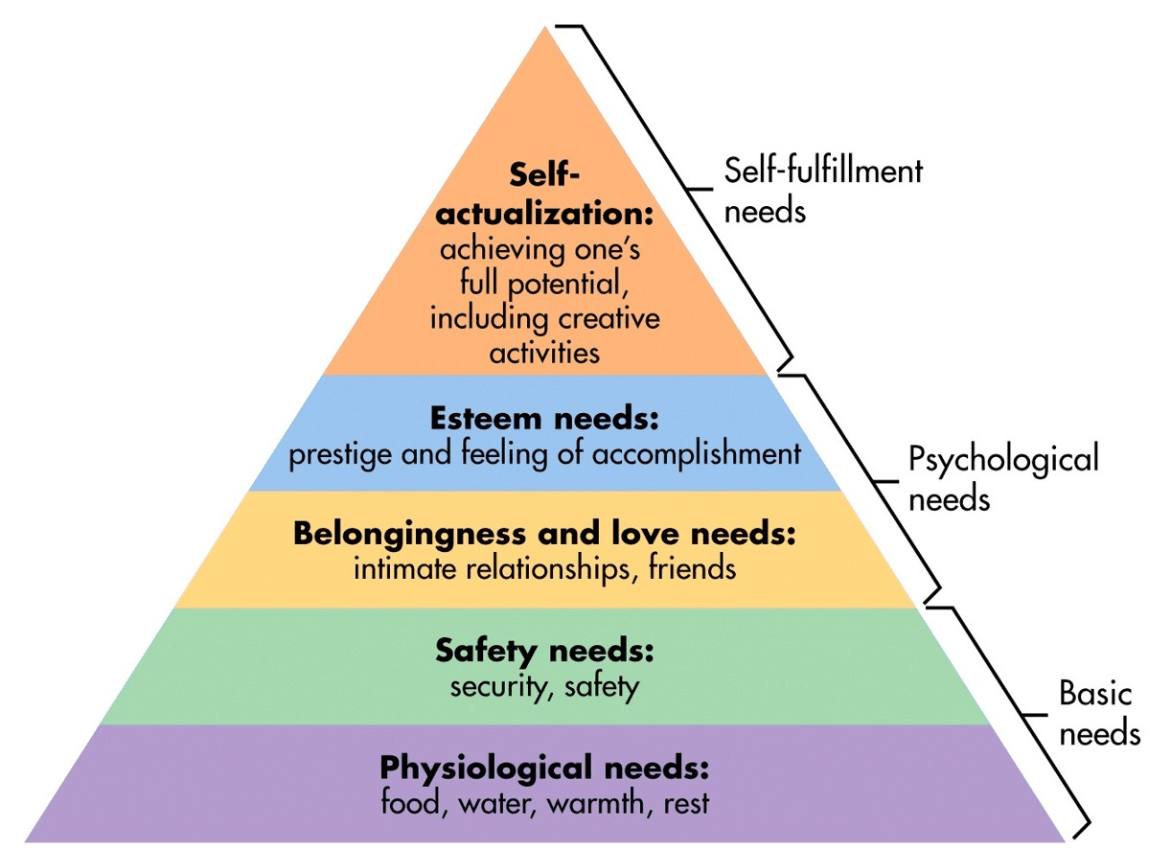
Draw Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs and explain what each stage is.
BONUS: What is a need?
B: Need - An internal state of tension that motivates a person to perform some action.
A humanistic term developed by Carl Rodgers: States that relationships where the love and approval a person receives from important others is given freely and is not dependent on conditions.
BONUS: How do Behaviorists view personality?
Unconditional Positive Regard
B: That it comes from learning in behaviors created by conditioning and reinforcement. 
Involves controlled, incremental, exposure to phobic stimuli while simultaneously practicing relaxation techniques that are incompatible with anxiety.
BONUS: What type of psychologist would practice this?
BONUS: What is the opposite of this therapy?
Systematic Desensitization
B: Behaviorist
B: Flooding - Non-incremental, total immersion to anxiety-producing phobic stimuli for a prolonged period.

The process of explaining behavior in terms in terms of causes that refer to characteristics of the person (dispositional cause), the situation (situational cause), or an interaction between the two; or in terms of behavior is intentional or unintentional.
Attribution
What are validity and reliability?
BONUS: What is an objective and projective test?
Validity = Accuracy
Reliability = Consistent
BONUS: Objective - Computer analysis to empirically measure personality characteristics (TAT and MMPI)
Projective - Reflect personality as it is "projected" on to test materials by the test-taker (Rorshach)

What is the activation, persistence, and intensity of a fireman?

Activation: I use my hoose to start putting water on a flaming house
Persistence: I continue to stop the fire until its finished and go to the next places that are on fire
Intensity: I work day and night to make sure there are no fires, I constantly work out to stay in shape, I read books on how to be a better firefighter, I go to firefighter conventions to learn new things
________________________________________
A: The first behavior to initiate the first thing you do in your job
P: Continuing and finishing your job/what you're doing
I: Working hard and improving at what your doing, putting more time and effort into your job to become better, adding concentration and vigor
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-motivation-2795378_color4-5b61dbeec9e77c0050889e49.png)
What are the five stages of Freud's Psychosexual Development (in order)?

Orphan Annie was a Pretty Little Girl.
Oral - (Birth-18months) Oral Incorporative and Oral Sadistic
Anal - (18m-3yrs) Anal Expulsive and Anal Retentive
Phallic - (3-5/6) Oedipus Complex
Latency - (6-Puberty) None
Genital - (Puberty) None
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-a-fixation-2795188_color-6b6fccdd74a64ad1bb660e352a0a21d9.gif)
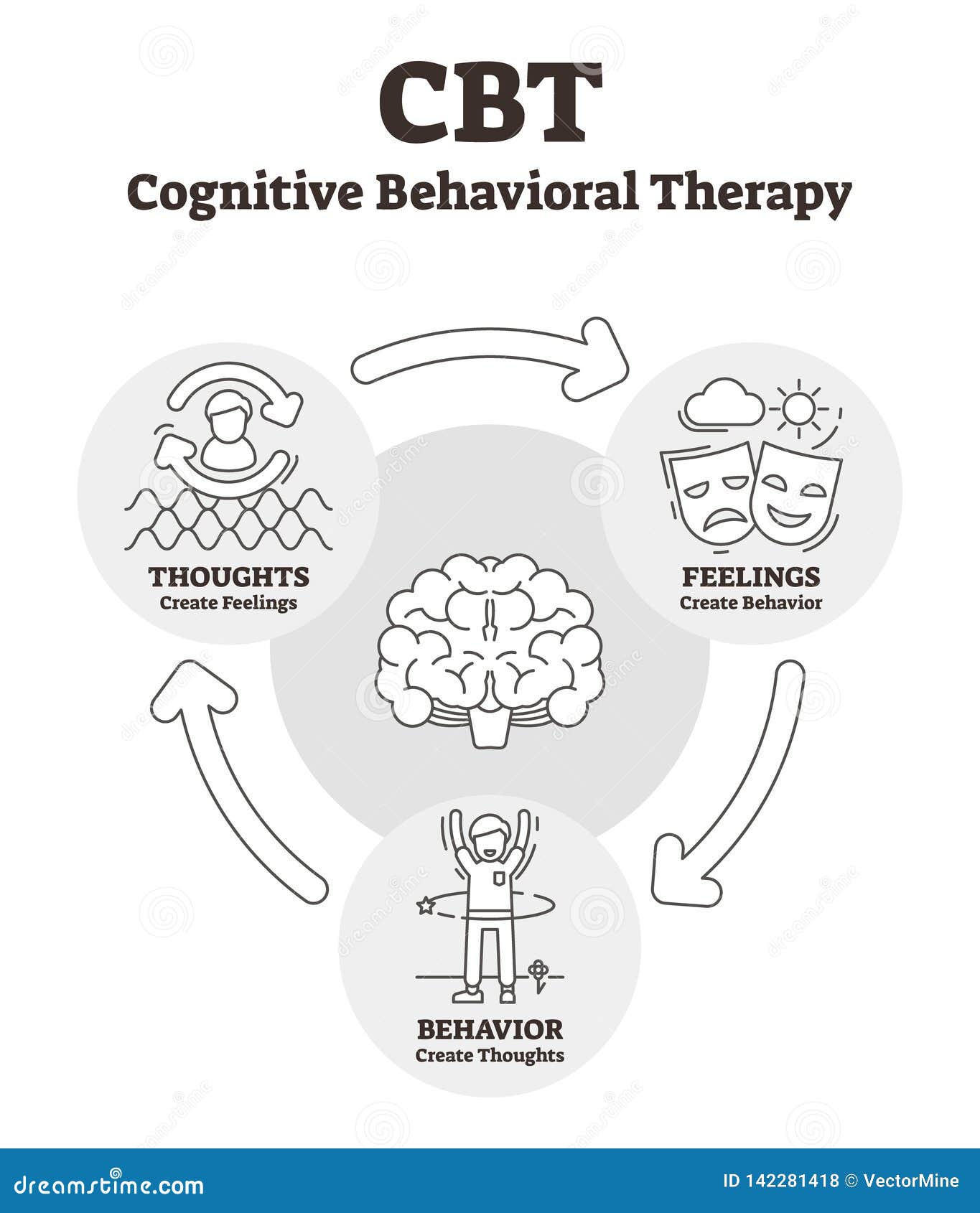
Based on the idea that cognition, emotion, and behavior are linked in a circle of mutual influence and reinforcement. Attempts to make biased distorted thoughts and maladaptive behavior adaptive.
Cognitive-Behavior Therapy (CBT)
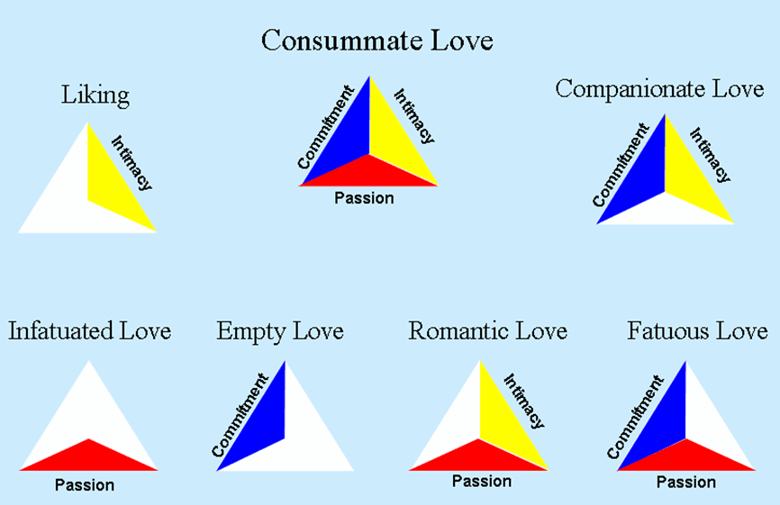
Name the 3 components of Sternberg's Triangular Theory of Love and name 3 types of love.
Intimacy - feelings of closeness, connectedness, and bondedness
Passion - feelings and desires that lead to physical attraction, romance, and sexual consummation
Commitment - feelings that lead a person to remain with someone and move toward shared goals
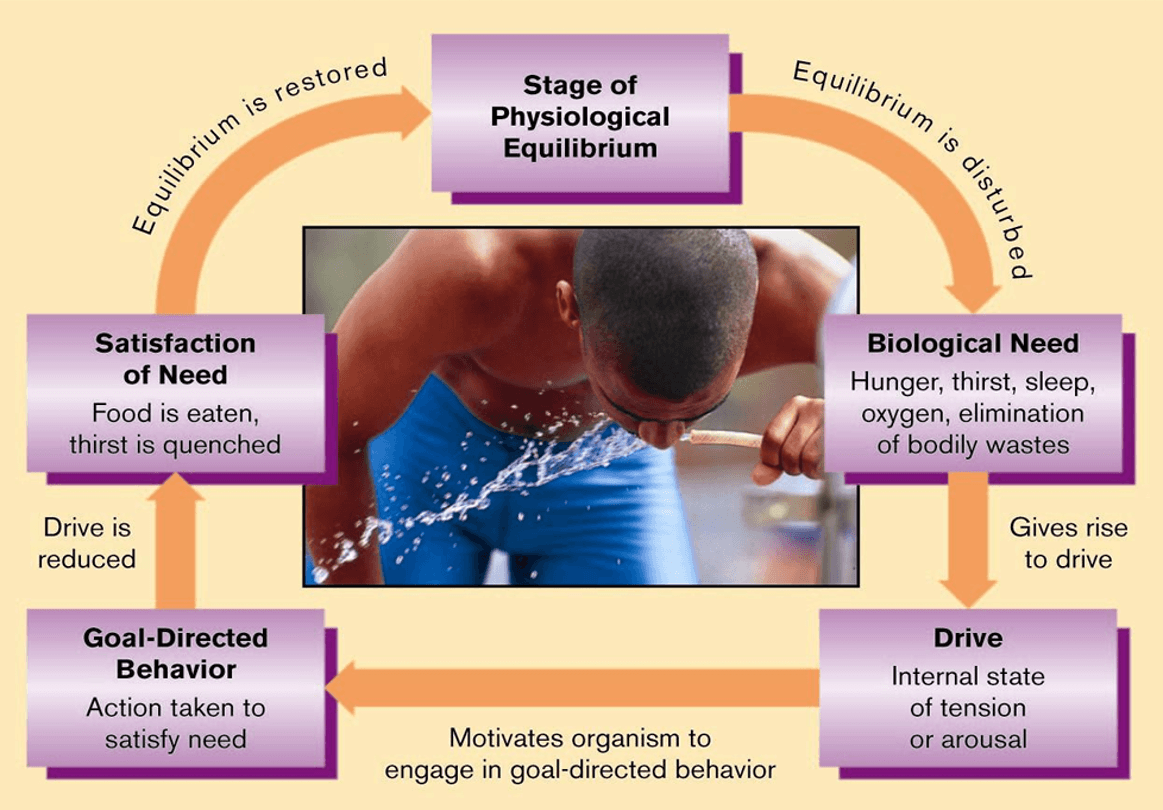
Draw Drive Theory/Drive-Reduction Theory and explain it.
Behavior is motivated primarily by the desire to reduce unpleasant conditions of arousal (drive) which have resulted from basic physiological needs.