The (anterior/posterior) pituitary does not produce it's own hormones, it only stores ones made in the hypothalamus
BONUS 100: Name the 2 hormones it stores
The posterior pituitary only stores hormones (ADH and Oxytocin made in the hypothalamus)
Like the trunk of your car, you store things in the back
Arteries have a (higher/lower) pressure than veins and therefore a (thicker/thinner) tunica media
BONUS 200: Name 2 more differences between veins and arteries
Arteries have higher pressure and a thicker tunica media
Bonus Differences
- Arteries are away from the heart, veins are toward
- Arteries have more elastic connective tissue than veins
- Arteries do not have skeletal muscle pumps, while veins do
- Arteries have a smaller lumen than veins
- Arteries have a tortuous tunica intima while veins have a smooth tunica intima
This structure is present in veins and lymphatic vessels and helps to prevent ________
Valves are present in veins and lymphatic vessels and they help to prevent backflow
The smallest part of the respiratory system, where gas exchange occurs
Alveoli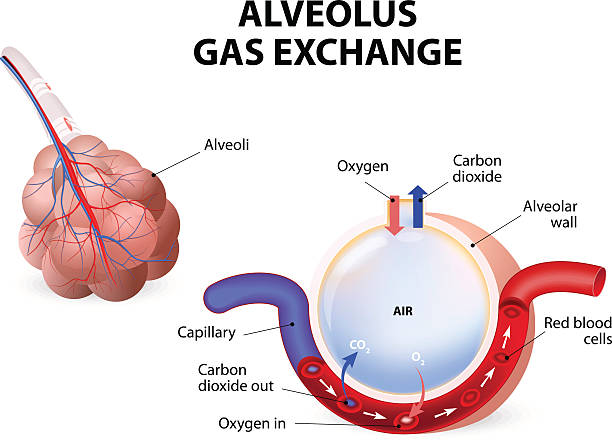
The mnemonic "Don't Jiggle It" represents what
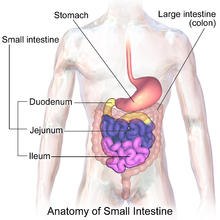
The sections of the small intestine from beginning to end
D - Duodenum: Food mixes w/ bile and digestive juices
J - Jejunum: Majority of digestion & absorption
I - Ileum: Absorbs final nutrients, leads to lsrge intestine
The functional unit of the kidney
The Nephron
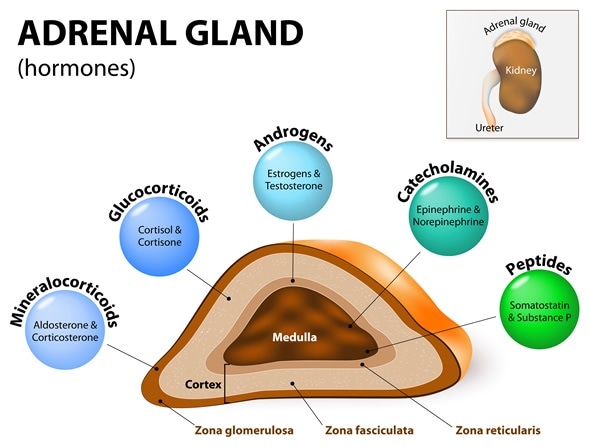
The adrenal cortex produces (corticosteroids/adrenalines) while the adrenal medulla produces (corticosteroids/adrenalines)
BONUS 100
Give 2 hormones for each region
Cortex = Corticosteroids (Cortisol, Aldosterone)
Medulla = Adrenaline (Epinephrine, Norepinephrine)
The outer layer of serous pericardium is called the (visceral/parietal) layer while the inner layer of serous pericardium is called the (visceral/parietal) layer.
Parietal = Outer layer, toward the body cavity
Visceral = Inner layer, against the organ

Lymph returns to its fluid to (venous/arterial) circulation to help maintain normal blood volume

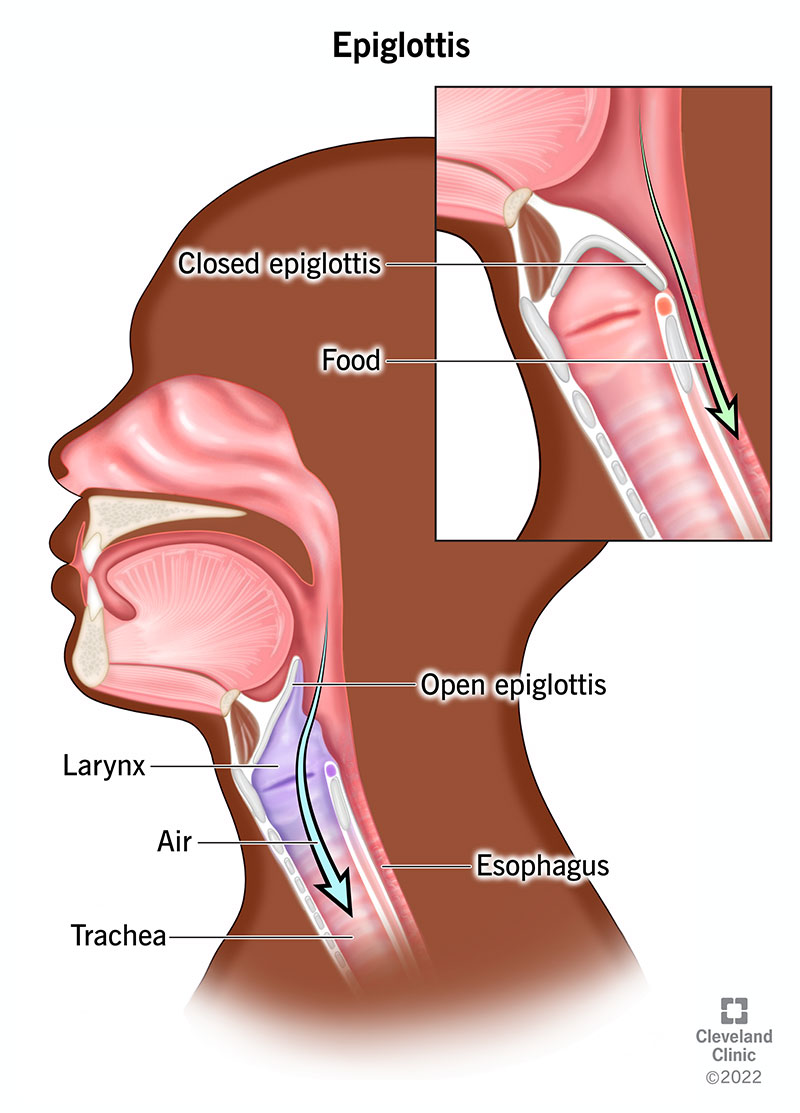
This structure covers the larynx during ________ to prevent _________
The epiglottis covers the larynx during swallowing to prevent aspirating food/choking
The muscular tube that transports food and liquid to the stomach
BONUS 200
Name the type(s) of muscle that can be found in the:
Superior Third
Middle Third
Inferior Third
The Esophagus
BONUS
Superior Third = Skeletal Muscle
Middle Third = Skeletal & Smooth
Inferior Third = Smooth Muscle

The Urinary System consists of these 4 structures
Kidneys
Ureters
Urinary Bladder
Urethra

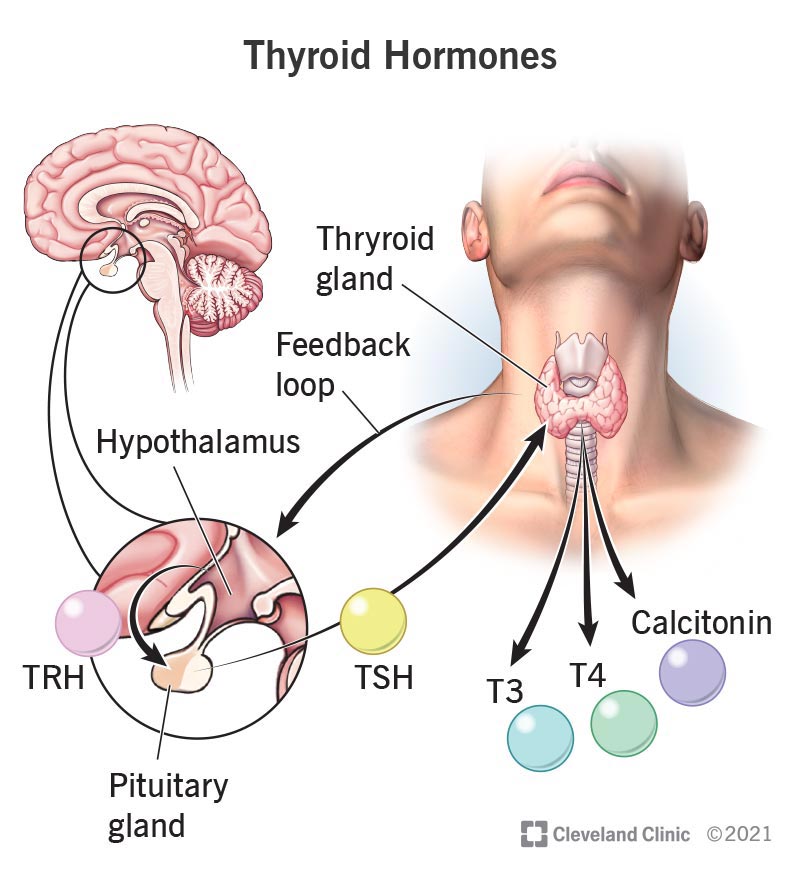
Calcitonin is produced here and is responsible for
BONUS 100
Name the other 2 hormones that can be found here
Thyroid Gland
Responsible for lowering blood calcium
Calcitonin = Calcium-In(-to the bones and out of the blood)
BONUS - T3 & T4 (triiodothyronine & thyroxine)
Responsible for metabolism regulation
The mnemonic "Never Let Monsters Eat Babies" represents what
The WBCs from most abundant to least abundant
N - Neutrophils: Non-Specific Immunity
L - Lymphocytes: Specific Immunity
M - Monocytes: Pathogen Phagocytosis
E - Eosinophils: Parasites and allergic response
B - Basophils: Major allergic response cell, mast cells, inflammation, seasonal allergies

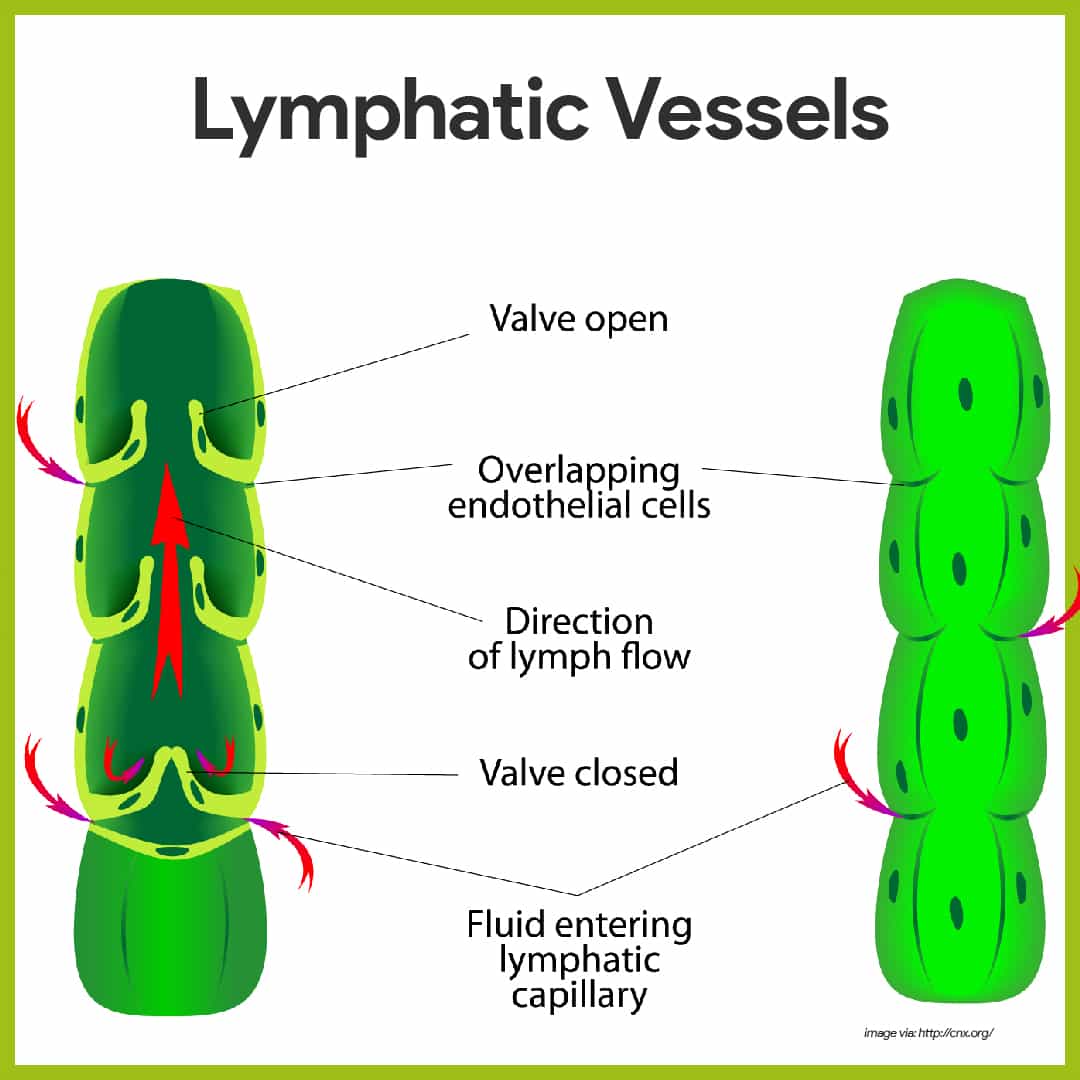
Lymphatic Vessels have (single cell/multi cell) walls
Single cell walls
T2 Alveolar Cells secrete __________, which helps decrease the _________ __________ in the alveoli
Surfactant
Surface Tension

The movement of food through the digestive tract is called (peristalsis/segmentation) whereas the mixing and breakdown of food is called (peristalsis/segmentation)
Food Propulsion = Peristalsis
Food Smashing/Mixing = Segmentation
Male and female gonads both produce these 2 things
Gametes (sperm and egg) and Hormones (Estrogen, Progesterone, Testosterone)
The beta islet cells of this organ produce __________
Pancreatic beta islet cells produce insulin
Name the 3 branches off the aorta from right to left
Brachiocephalic Trunk --> Left Common Carotid --> Left Subclavian
The 3 components of lymph are...
1. Interstitial Fluid
2. Lymphocytes (T Cells, B Cells, and NK Cells)
3. Macrophages
The Upper Respiratory System consists of...(3 Things)
And the Lower Respiratory System consists of... (5 Things)
Upper Respiratory System
Nose, Nasal Cavity & Sinuses, Pharynx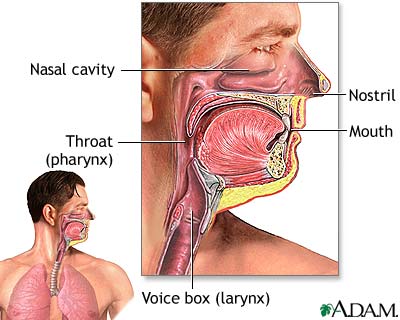
Lower Respiratory System
Larynx, Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli
The 4 regions of the stomach are...
Cardia
Fundus
Body
Pylorus
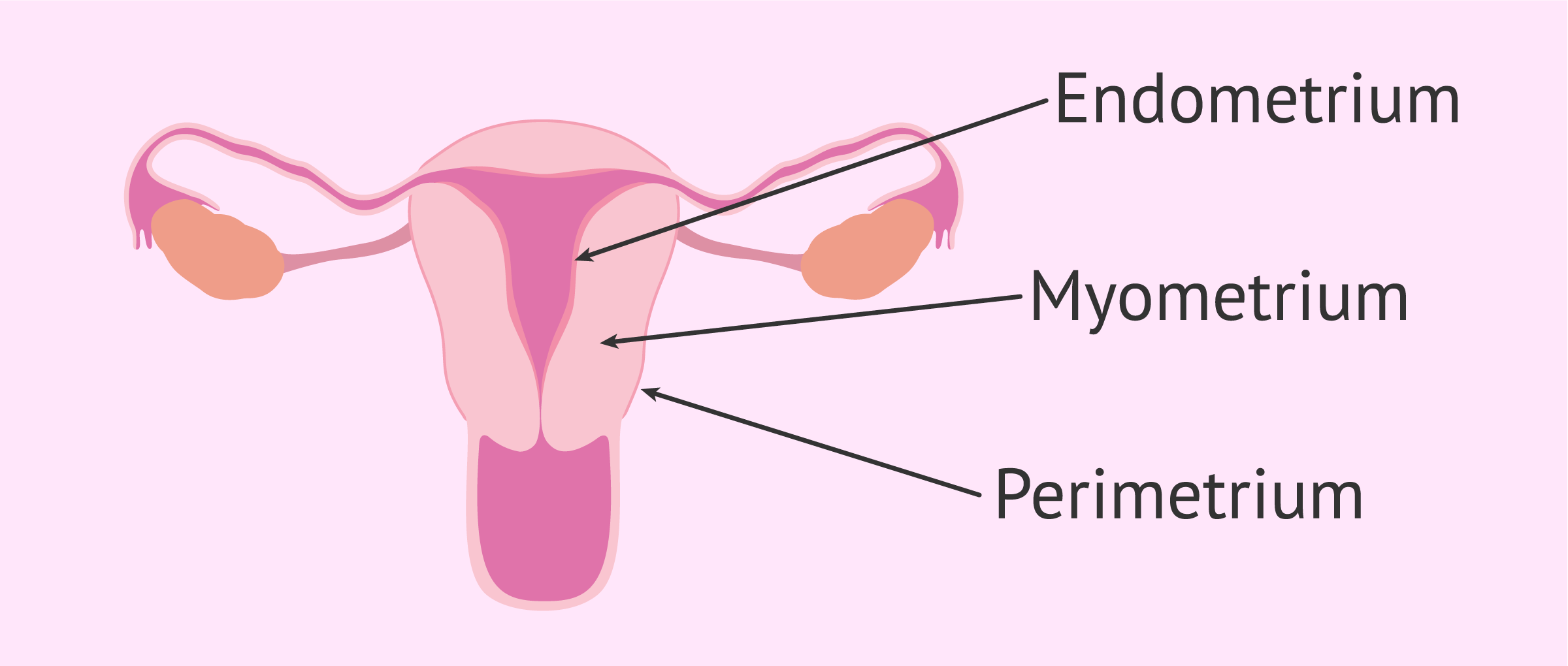
Name the layers of the uterus from superficial to deep
Perimetrium
Myometrium
Endometrium
ACTH, FSH, and PRL, among others, can be found in this endocrine gland. Name the gland, the other 3 hormones that are missing, and all hormone functions
Anterior Pituitary

Also makes/stores LH, TSH, and GH
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone): Acts on adrenal cortex and tells it to produce corticosteroids (cortisol, aldosterone)
FSH (Follicular Stimulating Hormone): Acts on gonads and tells them to produce sperm and egg
LH (Luteinizing Hormone): Acts on gonads and tells them to produce androgens (Estrogen, Testosterone, Progesterone)
PRL (Prolactin): Acts on mammary glands and tells them to produce milk
TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone): Acts on thyroid and tells it to release it's hormones (T3/T4 & Calcitonin)
GH (Growth Hormone): Acts on tissues, tells them to grow
List the bloodflow through the heart starting from the venous system
1. Superior/Inferior Vena Cava and Coronary Sinus
2. Right Atrium
3. Tricuspid or Right A/V Valve
4. Right Ventricle
5. Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
6. Pulmonary Artery
7. Lungs
8. Pulmonary Vein
9. Left Atrium
10. Bicuspid/Mitral or Left A/V Valve
11. Left Ventricle
12. Aortic Semilunar Valve
13. Aorta
14. Body
Repeat

Name the 2 primary lymphoid tissues and explain what occurs there
Bone Marrow (Red): Immature B and T cell production and B Cell maturation
Thymus: T Cell maturation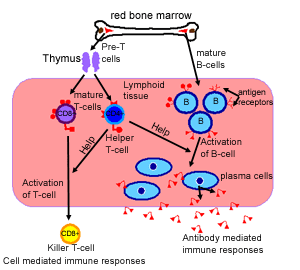

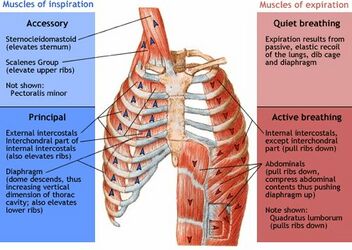
All muscles used for quiet breathing inspiration/expiration
AND
One example of an accessory inspiratory muscle and one example of an accessory expiratory muscle
Quit Breathing
Inspiration: Diaphragm and External Intercostals
Expiration: Relaxation of inspiratory muscles
Accessory Muscle Breathing
Inspiration: Sternocleidomastoid, scalenes, pec minor, serratus anterior
Expiration: Internal Intercostals, abdominal muscles
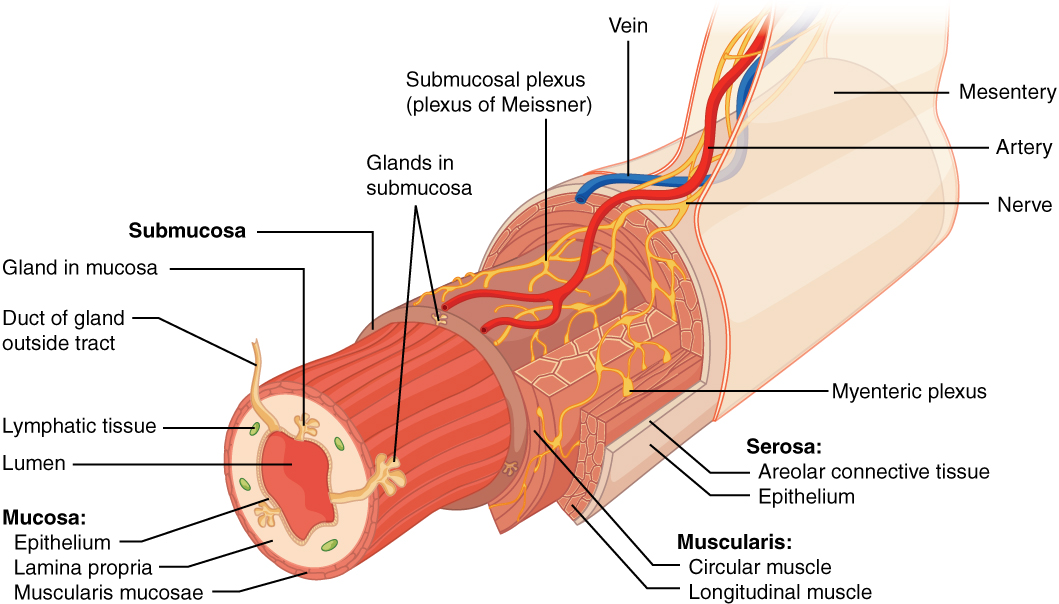
Name the 4 layers of the digestive tract from the lumen to the most superficial layer
1. Mucosa (most deep)
* Epithelium
* Lamina Propria
* Muscularis Mucosa
2. Submucosa
3. Muscularis Externa
4. Serosa (most superficial)
Where filtrate collects before leaving the kidney
Collecting Ducts