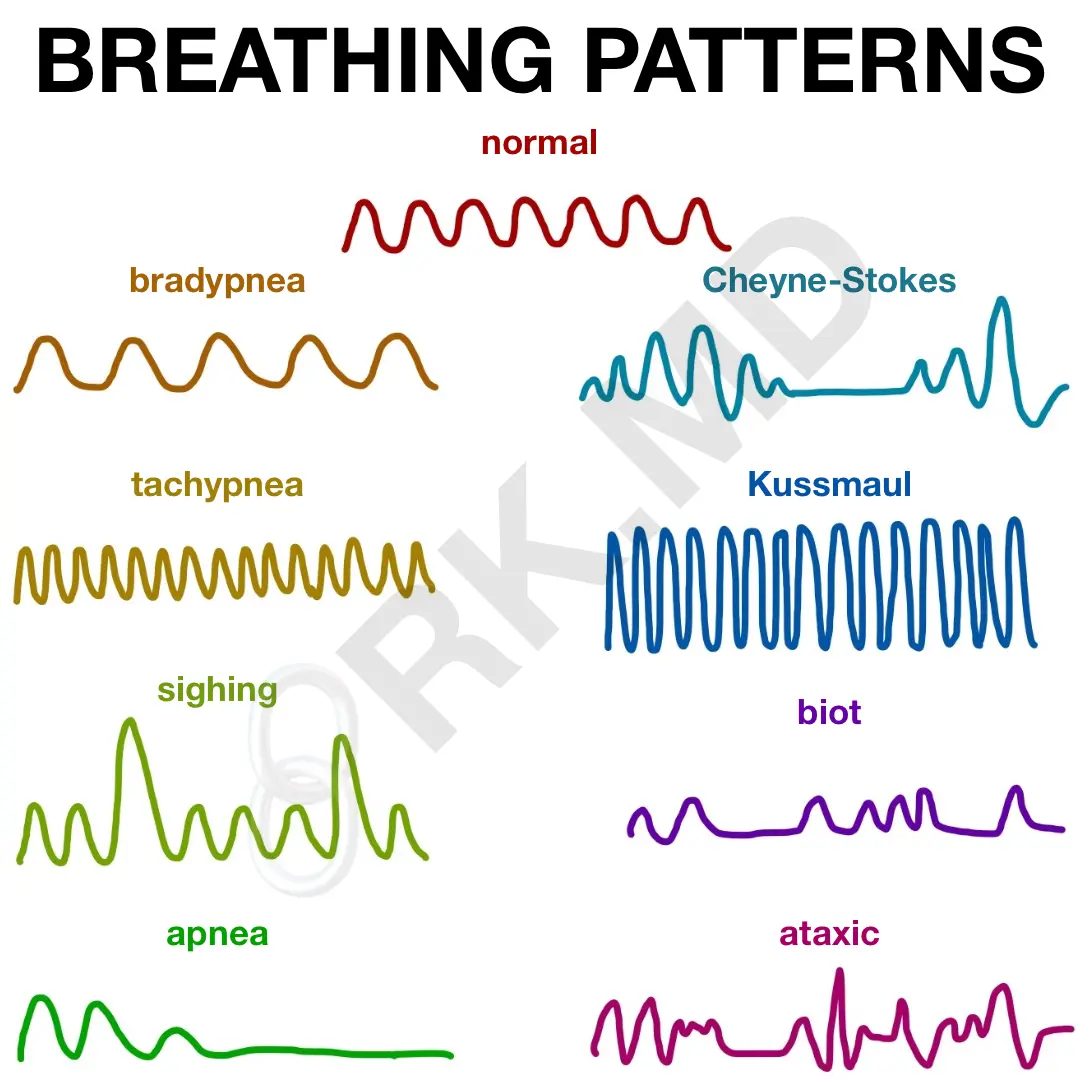
The breathing pattern of the RR and VT gradually increases and then gradually decreases to complete apnea, then gradually increases and repeats. CHF, brain damage
what is: Cheyne stokes
the following are side effects of ________ bronchodilators
-Palpitations, tachycardia, HTN, tremors, dizziness, weakness, restlessness, anxiety, fear, pallor(pale)
what is:
adrenergic bronchodilators
the normal heart range values for Tachycardia
what is:
>100
the scientist whose discovery helped create the function of a jet neb
what is:
Bernoulli
the oxygen delivery device that is used when:
-1/4 L to 6 LPM
-FiO2 22-44%
-Flows >4 LPM add humidifier
-Good for patients with low oxygen needs, stable breathing, or pts eating
what is the:
- Nasal Cannula

the Bourdon gauge measures what
Usually used for H Tanks, measures pressure and displays flow
the ____is the maximum amount of air that can be inhaled from end-expiration
Inspiratory Capacity-IC
minute ventilation formula VE
VE = RR x VT
the breathing pattern that is prolonged inspiratory gasps, interrupted by occasional expirations, due to damaged pons, associated with head trauma, severe brain hypoxia, or lack of flow to the brain
what is: Apneustic breathing

the brand name for Albuterol
what is:
Ventolin and Proventil
the normal heart range values for Bradycardia
what is:
<60
the compression to ventilation ratio for two-rescuer adult CPR according to AHA
what is:
30:2
The oxygen delivery device that is used when:
5-10 LPM
-FiO2 35-50%
-cause rebreathing of CO2
-variable flow & FiO2
-Use for mouth breathers
-easy to apply
-people requiring more oxygen than NC can provide which goes up to 6L/per min
what is the:
Simple Mask
The device takes humidity on exhalation and returns it on inspiration to help humidify the airway when it has been bypassed.
what is:
HME: Heat and moisture exchanger
the___is the total amount of gas left in the lungs after a resting expiration
what is:
FRC- functional residual capacity
Alveolar minute ventilation
VA= RR x (VT - VD)
the breathing pattern that the tidal volumes are of identical depths, due to brain damage, and increased ICP’s
what is:
Biot-breathing

the brand name for Ipratropium Bromide
what is:
Atrovent
the term Tachypnea means
what is:
abnormally high RR
the difference between internal and external respiration
External respiration- gas exchange between lungs and blood (alveoli and capillaries)
Internal respiration- gas exchange between blood and tissues (capillaries and cells in tissues)
The oxygen delivery device that is used when:
-Various flows (LPM)
-FiO2 24-50%
-Good for COPD patients, gives higher flows with lower FiO2
-fixed entrainment, variable flow
-small jet= decreased FiO2 (increased room air entrainment), shear forces aid and energy taken from the wall, becomes a vacuum
-large jet= increased FiO2 (decreased room air entrainment)
what is a:
Air Entrainment mask (Venturi Mask)

the primary muscles of respiration
what is the:
Diaphragm and intercostals
the _____ is the maximum amount of air that can be inhaled after a normal quiet inspiration
what is:
IRV- Inspiratory reserve volume
Dead space to tidal volume ratio (VD/VT)
normal: .2-.4 or 20%-40%
VD/VT= PaCO2-PeCO2/ PaCO2
the breathing pattern where there is an increase in rate and depth is a deep gasping type of respiration caused by DKA(Diabetic ketoacidosis)
what is:
-Kussmaul

the brand name for salmeterol
what is:
Serevent
the term Bradypnea means
what is:
abnormally low RR
the device that adds molecular water to a gas. (>4L)
what is:
a humidifier
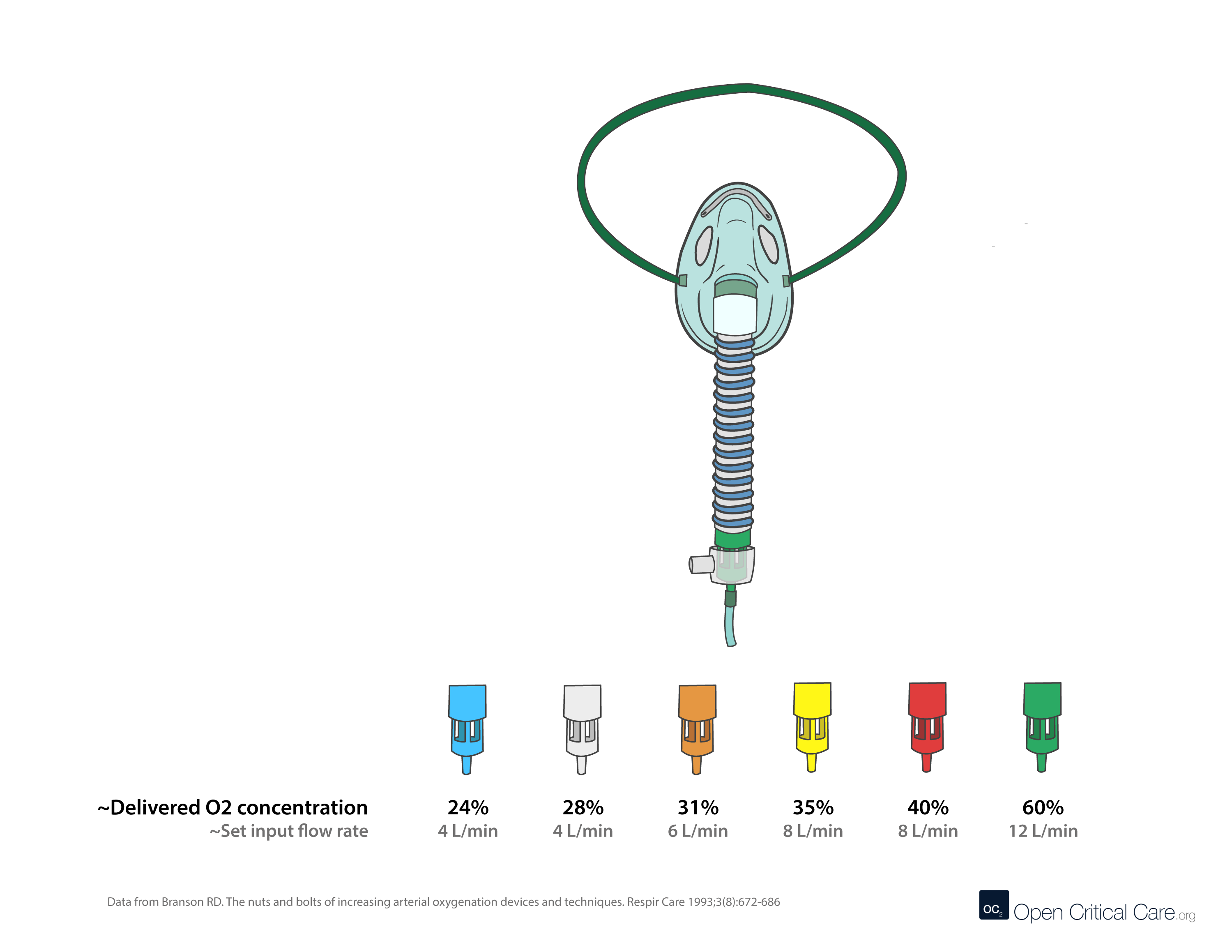
The oxygen delivery device that is used when:
-Minimum of 10 LPM (must be high enough to prevent the collapse of the bag)
-1L flexible reservoir bag increases reservoir volume, which provides higher FiO2
-40-70%
-No one-way valves, patient rebreathes about 1/3 of exhaled
-Used when nonrebreather not available
what is a:
Partial Rebreathing Mask
the accessory muscles of respiration
Inspiration-scalene and sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis major
Exhalation- abdominals, internal intercostals

the ___ is the volume of air that is inhaled or exhaled from the lungs during effortless breathing
what is:
Tidal Volume -VT
Total oxygen content of Blood(CaO2)
normal: 16-20ml/dl
CaO2= (PaO2 x .003)+ (Hb x 1.34 x SaO2)
the pattern of breathing where there is no breathing occurring
what is:
Apnea

the brand name for Acetylcysteine
what is:
Mucomyst
the range for Hypertension
what is:
> 140/90
the agency responsible for credentials RRT’s
what is:
NBRC- National Board for Respiratory Care
The oxygen delivery device that is used when:
Minimum of 10 LPM (must be enough to prevent the collapse of the bag)
-60-80%(highest FiO2 range available)
-One way valves; patient does not rebreathe CO2
-Trauma patients, smoke inhalation, critical patients
what is a:
Nonrebreathing mask

the components that must be included in a medication prescription and where would this order be located?
-Name, dosage, frequency, route of administration, and Dr.’s signature.
-This is found in the MD orders.
the ___ is the total amount of gas that can be exhaled from the lung after a quiet exhalation
what is:
ERV- Expiratory Reserve volume
Alveolar air equation PAO2
norm 100mmHg if pt on room air
PAO2=FiO2(PB-PH2O(47))-PCO2/.8
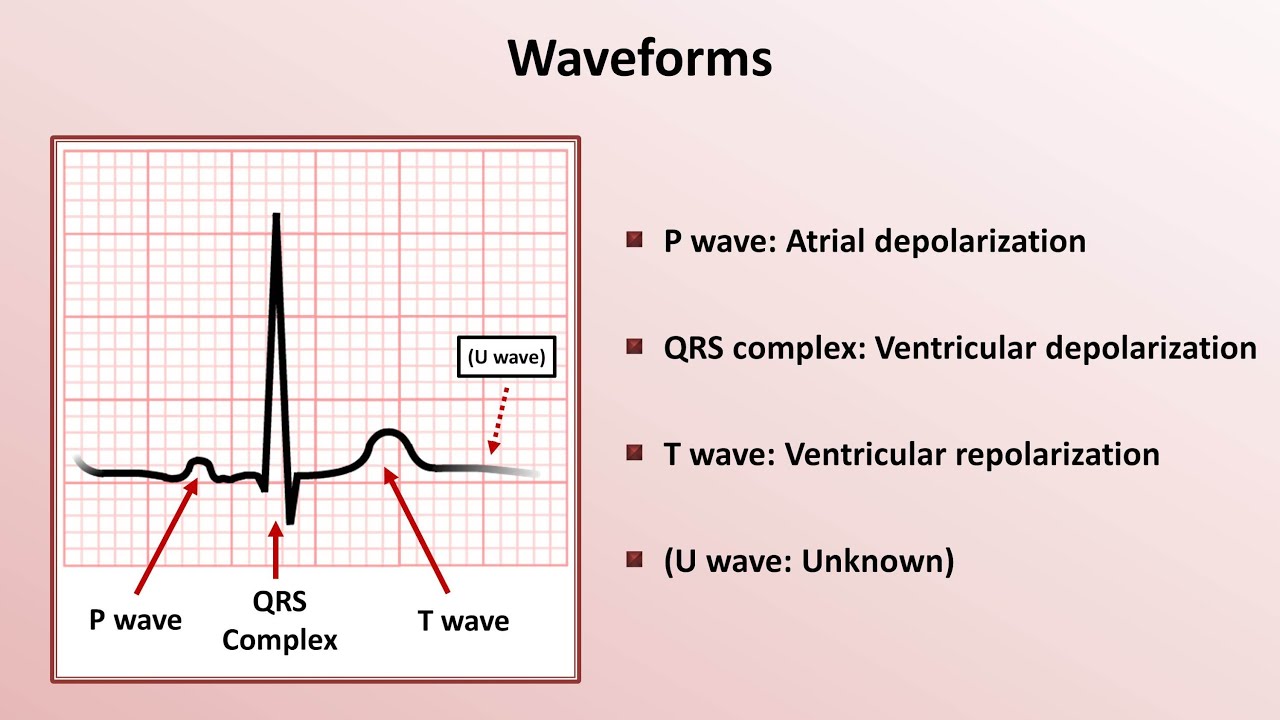
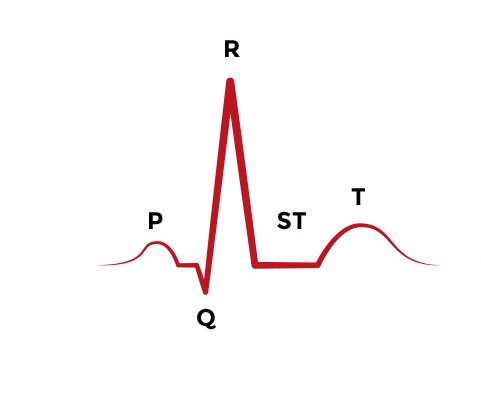
the P wave in an ECG means
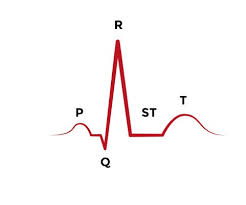
what is:
P wave- depolarization of atria
the brand name for Dornase Alfa
what is:
Pulmozyme
the range for Hypotension
what is:
<90/60
the rate of L of O2 increases in delivery
starting at 1L= FiO2 approximately 24%
what is :
increase by 4% per Liter
1lp= 24%
2lpm= 28%
3lpm= 32%
4lpm= 36%
5lpm= 40%
the mask that is variable FiO2 range 24-98% and can be used to deliver medication
Air Entrainment Nebulizer

The first 15 generations of the respiratory tract are known as
The conducting zone.

the ___ is the volume of gas remaining in the lungs after a complete exhalation
what is:
RV- Residual Volume
Alveolar to arterial gradient(A-a)
norm:5-10 for anatomic shunt < is another shunt
-after finding PAO2 w/ alveolar air equation
PAO2-PaO2
the meaning of a T wave on an ECG
what is:
repolarization of the ventricles

the brand name for Ipratropium & Albuterol combined
what is:
Duoneb-SVN
Combivent-MDI
the abbreviation QID means
4 x a day
the rate at which C02 diffuses how many times faster across the AC membrane than 02
what is:
20 x faster
the part of the chart that is a continuing account of the patient’s progress for the physician, is the most up-to-date information.
what is:
Progress sheet
the gas exchange starts to occur in the respiratory tract where?
-Respiratory zone (specifically the respiratory bronchioles), generations 16 and beyond.

the __ is the total amount of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inspiration
what is:
Vital Capacity
cardiac output formula
CO=HRxSV
the meaning of a ST segment on an ECG

what is:
the resting phase
the brand name for Fluticasone
what is:
Flovent
the abbreviation TID means
what is:
3 x a day
the term that matches the following statement
-is a condition where 02 availability is less than cellular 02 needed
what is:
Hypoxia
the part of the chart that Describes the nursing care given to the patient, SOAP note/data
what is:
Nurse's notes
the flow that is straight and streamlined
what is:
Laminar
the ___ is the total amount of gas in the lungs after a maximum inspiration
what is:
TLC- Total Lung Capacity
celsius to Fahrenheit
c=(F-32)/1.8
the QRS complex mean on an ECG
what is:
Depolarization of the ventricles
the brand name for the DPI that Fluticasone & Salmeterol are combined
what is:
Advair
the abbreviation Q4H means
what is:
every 4 hours
the term that matches the following
-abnormally low Pa02, can cause hypoxia
what is:
Hypoxemia
the part of the chart that is a record of the MD orders and prescriptions
what is:
Physician’s orders
the flow that is irregular eddy currents of flow (chaotic pattern)
what is:
Turbulent
What phospholipid does the body naturally secrete to decrease surface tension?
Surfactant
Fahrenheit to Celsius
F=(C x 1.8) + 32
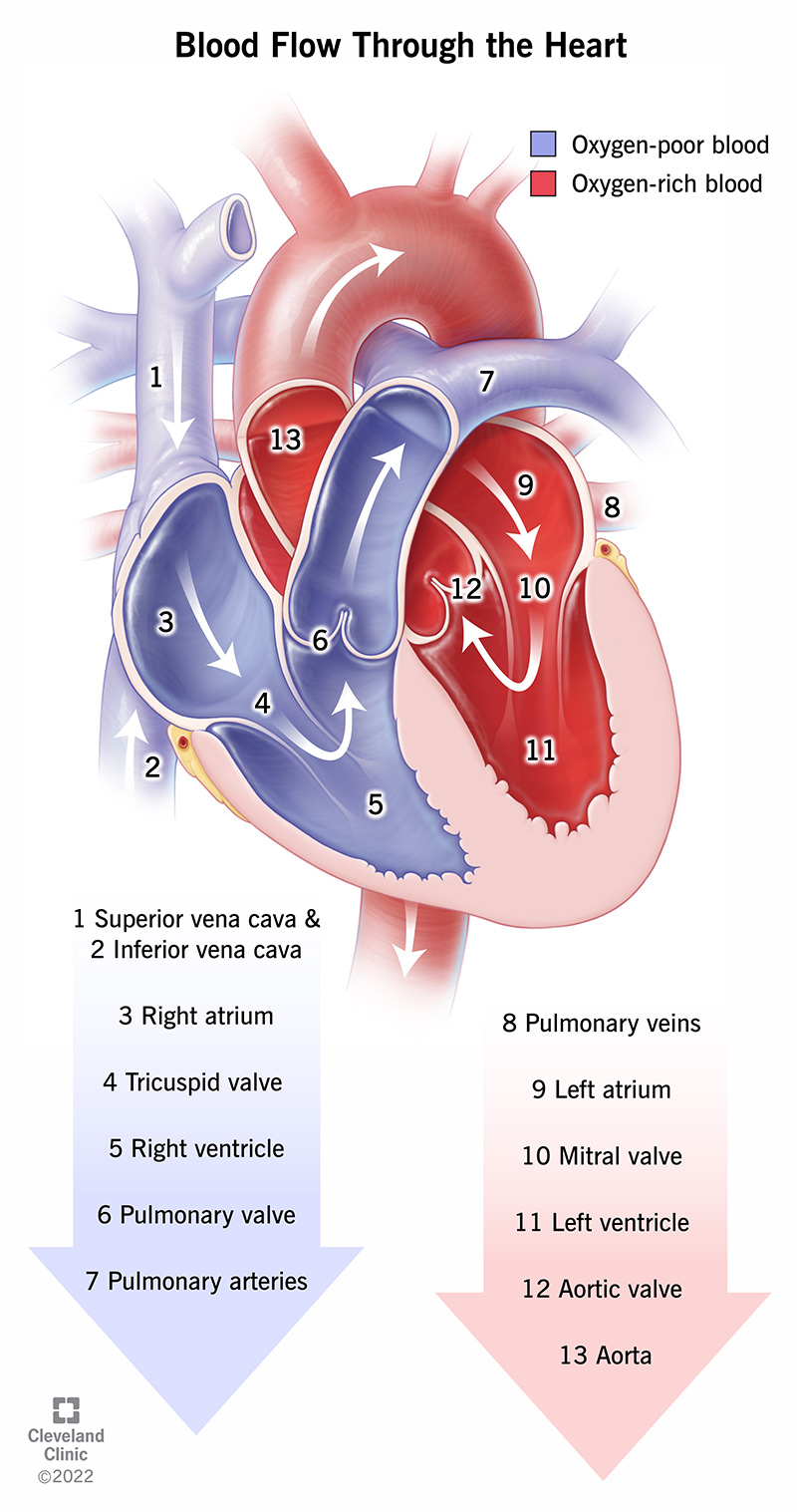
the blood flow route through the heart
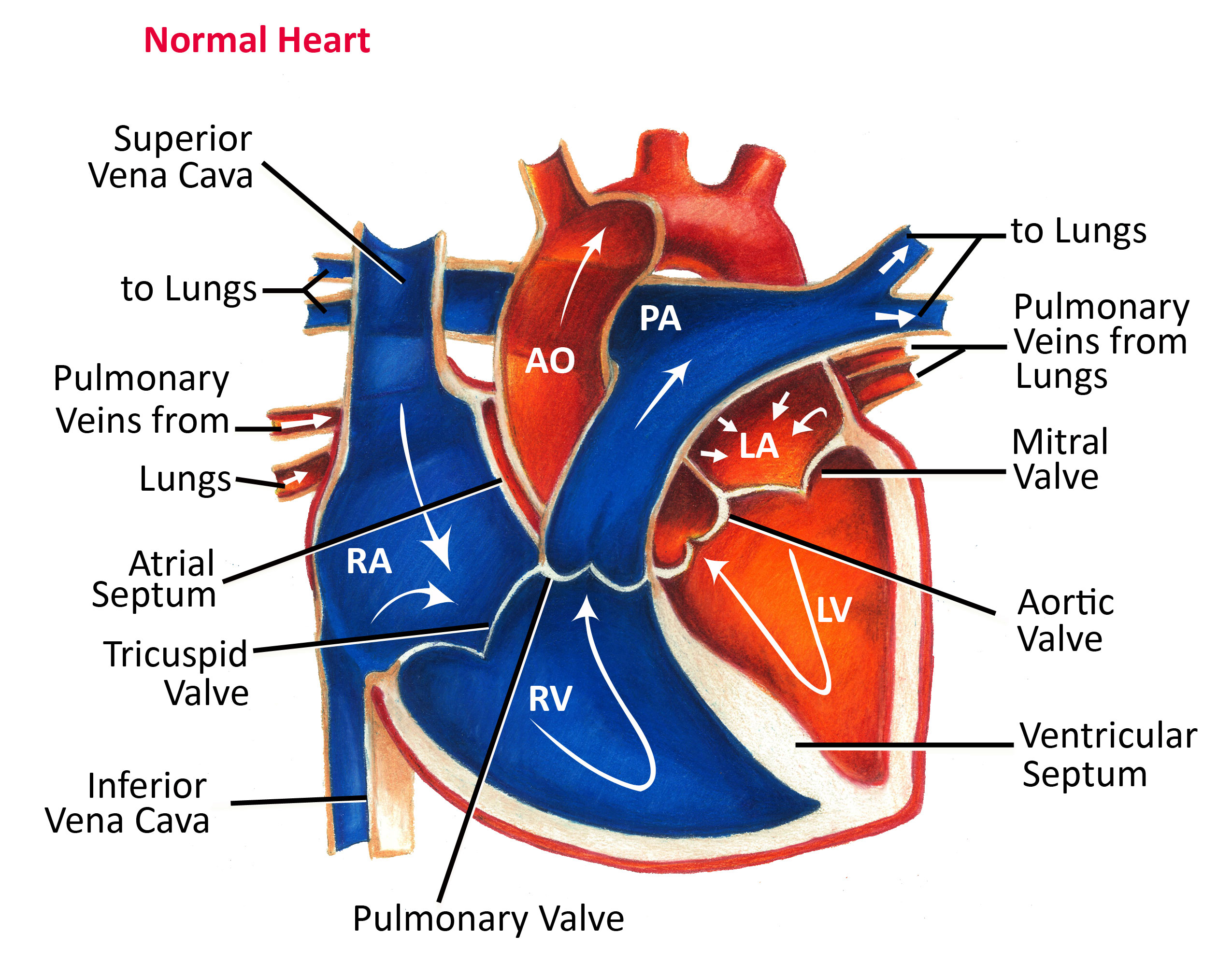
SVC ---->RA--->Tricuspid valve--->RV---------------->Pulmonary Valve -->Pulmonary artery--->LUNGS --->Pulmonary veins ---> LA ---> Mitral valve(bicuspid valve)--------->LV--->Aortic Valve----->Aorta---->BODY
Deoxygenated blood flows from the vena cava into the right atrium, which then passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle, from which it then passes through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery, by which it travels to the lungs to be reoxygenated. One oxygenated, the blood travels from the lungs through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, then the mitral valve, then the left ventricle, then the aortic valve, and finally the aorta, by which oxygenated blood is sent out to the rest of the body.
the main difference in mode of action for albuterol versus ipratropium bromide?
-Albuterol stops bronchospasm by inducing an adrenergic response by releasing Norepinephrine and epinephrine to stimulate bronchodilators.
- Ipratropium blocks the release of ACH on the PSNS nerve site to prevent bronchoconstriction.
the abbreviations BID mean
what is:
Twice a day
Avogadro’s Law states 1 mole of any gas at STP=
what is:
22.4 L
the part of the chart that is a history of the present illness
what is:
History and Physical(H&P)
the flow that is a combination of laminar and turbulent
what is:
Transitional
Answer the following
IRV+VT+ERV+RV=
IRV+VT=
TLC-FRC=
IC+FRC=
FRC-ERV=
Answer the following
IRV+VT+ERV+RV= TLC
IRV+VT= IC
TLC-FRC= IC
IC+FRC= TLC
FRC-ERV= RV
relative humidity percentage formula
RH%= AH/Sat cap
the most common cause of the obstructed airway in the adult
what is:
the Tongue
the mucolytic treatment should be given with what other drug to prevent bronchospasm
what is:
Albuterol (a beta-adrenergic/parasympathomimetic)
the abbreviations for QD means
what is:
Once a day
the largest artery in the body
what is the:
Aorta
the white blood cell for allergic reactions/parasites
what is:
Eosinophils
the indications for a low flow 02 system(3 parts)
what is:
Vt 300-700 ml’s,
regular and consistent Vt,
and RR < 30 br/min
What is the difference between a bubble and a Passover humidifier?
-bubble humidifier breaks or diffuses an underwater gas stream into small bubbles, they are unheated and can provide 15-20mg/L of AH, at high flow rates aerosols are produced.
-Passover humidifier directs gas over a surface containing water - Simple reservoir, Wick, and membrane type.
body humidity percentage formula
BH%= AH/43.8
The ratio of actual water vapor content to its saturate capacity at any given temperature.
what is:
Relative humidity
the stimulation of alpha receptors for the SNS causes
what is:
Vasoconstriction occurs within the arteries and veins.
the electrical conduction of the heart starting with the SA node.
SA node--->Bachman’s bundles--->AV node---->bundle of HIS-(R and L bundle branches)--->purkinje fibers--->ventricles
the method of heat transfer is used to keep infants warm in the delivery room
what is:
Radiation
the white blood cell for allergic reactions secrete heparin (less than eosinophils)
what is:
Basophils
Using a reservoir oxygen mask, you notice that the bag keeps collapsing on inspiration what should you do to ensure the patient is getting adequate 02?
Increase the flow
The ______ _____ device directs gas over a surface of water or fluid and the surface for gas-fluid interface is limited.
simple reservoir
tank duration for cylinder
PSi x tank factor(O2 .28)/ liter flow
-may need to divide by 60 for hours and multiple decimal by 60 for mins
The actual amount or weight of water vapor in a gas must be measured.
what is:
Absolute humidity
the normal values for Respiratory rate
what is:
12-18
the term that matches the following:
-Air is warmed in one location and circulated to carry the heat elsewhere, mixing fluid molecules at different temps. Heats and moves it—most common!
what is:
Convection
the most common use of racemic epinephrine
what is:
Upper airway/ Large airway obstructions- tracheal edemas
the white blood cell that is the most abundant response, bacterial infections, reduced w/bone marrow dz., low-immunodeficiency
what is:
Neutrophils
Why is it necessary to keep a Simple Mask’s liter flow @ 5lpm?
To avoid the accumulation and rebreathing of C02
The _____ ______ uses capillary action to draw water from a reservoir with an absorbent material and increases the surface area for dry air to interface with heated water, only water vapor molecules can pass and not liquid, no bubbling occurs and no aerosol is produced.
wick humidifier
liquid tank duration formula
lbs x 344/ liter flow
-may need to divide by 60 for hours and multiple decimal by 60 for mins
the actual amount of water vapor in a gas at any temp given. (how much water is in the cup)
what is:
Content
the normal value for Blood pressure
what is:
90-140mmHg systolic
60-90mmHg diastolic
-ideal: 120/80
the term that matches the following:
- heat without direct contact usually infrared in the health care setting, radian warmers, heat loss is related to surrounding temp and surface area
what is:
radiation
the difference between a red blood cell and white blood cell
-Red blood cell carries 02
-White blood cells are for immune response
the white blood cell that is the second most abundant WBC, viral infections, reduced w/ immunodeficiency syndromes
what is:
Lymphocytes
the following would cause the O2 dissociation curve to go toward the ____(*increased affinity)
-Decreased C02, decrease temp, decrease 2,3 DPG,
-increase pH CoHB, MetHb, Fetal Hb
towards the Left
The ______ ______ separates the water from the gas stream by hydrophobic membrane. Only water vapor molecules can pass the membrane (liquid and pathogens cannot cross membrane).
membrane humidifier
conversion factor & formula
-HeO2 80:20
&
-HeO2 70:30
-1.8, liter flow x 1.8 =actual flow
-1.6, liter flow x 1.6= actual flow
The total amount of water vapor a gas can hold at any given temp. (size of the cup)
what is:
Capacity
the normal heart rate range & SpO2
what is:
60-100bpm
92-100%
the terms that match the following:
transfers heat by transfer in solids through direct contact
&
-change in the state of a substance from liquid form to gaseous form occurring below its boiling point.
what is:
Conduction
& Evaporation
the difference between platelets and plasma
-Platelets are also called thrombocytes, the smallest formed element in blood, responsible for clot formation (coagulation), Norm- 150,000-400,000mm3
-Plasma is the liquid portion of blood, 90% water, and the rest are proteins and coagulants
the white blood cell is for phagocytes, foreign material
what is:
Monocytes
the following would cause the O2 dissociation curve to go toward the ____(decreased affinity)
Increased C02, increased temp, increased 2,3 DPG and Sickle Cell Anemia- HbS,
-decreased pH
to the right
the formulas in order needed to compare TF & PIF
1. 100-FiO2/FiO2-21=air to oxygen ratio
2. (air ratio + oxygen(1)) x LPM= total flow
3. VE= RR x VT
4.PIF= VE x 3 then compare to TF
TF>PIF to be adequate PIF>TF not enough
Dose & volume formula
& concentration conversions for 1:100 or 1%
dose: vol(ml) x conc(ml/mg)= dose mg
volume: dose(mg)/conc(mg/ml)= volume ml
1:100= 1/100 x 1000 then divide by the 100 getting 10
1%= Move the decimal to the right once make 10%