This bone is found in the proximal row of carpal bones.

What is the scaphoid?
suture connects the parietal bones to the frontal bone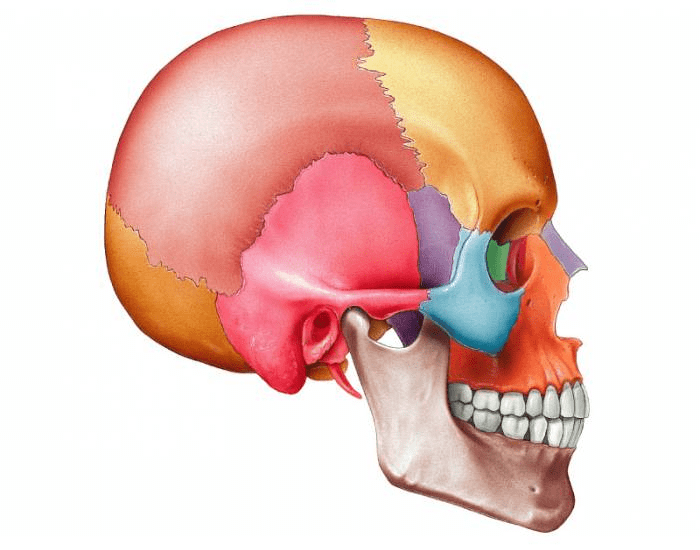
What is the coronal suture?
In anatomical position, the tibia is positioned relative to the fibula
What is medial?
The carpals are classified as this type of bone.
What are short bones?
This movement occurs when turning the palm upward.
What is supination?
What type of joints allow for no movement and are found in the sutures of the skull?
What is to act as a shock absorber?
What connective tissue is found in the medullary cavity and makes up yellow bone marrow?
What is adipose tissue?
Movement toward the midline of the body at the shoulder joint.
What is adduction?
The fibula is classified as this type of bone.
What is a long bone?
Moving the phalanges toward the tibia
What is dorsiflexion?
The head of the femur articulates with this part of the pelvis.
What is the acetabulum?
What type of connective tissue connects bone to muscle?
What is dense regular connective tissue? What is a tendon?
During plantar flexion at the ankle, the phalanges move in this direction.
Answer: What is inferiorly?
Sternum, ribs, cranial bones, ilium
What are flat bones?
Movement allowed by saddle joint of thumb
What is opposition?
The pubic symphysis is classified as this type of joint.
What is a cartilaginous joint?
The intervertebral discs are primarily made of this type of cartilage.
What is fibrocartilage?
The nasal bone is positioned relative to the zygomatic bone.
What is medial?
Zygomatic, maxilla, sacrum, vertebrae
What are irregular bones?
Hormone that raises blood calcium
What is PTH
joint between trochlear notch and trochlea of the humerus
What is a hinge joint
The ends of long bones are composed of this type of cartilage.
What is hyaline cartilage?
The sacrum is positioned relative to the coccyx.
What is superior?
a passage or tunnel leading to the interior of the body.
What is a meatus?
Three organ systems that regulate calcium