What is red-shift vs. blueshift?
Blue-shift = shortened wavelengths tell you the object is moving TOWARDS you
What are the two main groups of planets?
Outer = Jovian
What is the most common group of minerals?
Silicates
What type of rock is prevalent in Starved Rock State Park?
Sandstone
What are the two conditions necessary for fossilization?
Rapid Burial
Possession of Hard Parts (shells, bones, etc)
What is the relationship between mass, distance, and gravitational force?
The greater the mass of two objects, the greater the force of gravity
The greater the distance of two objects, the lower the force of gravity
Why do we not have two eclipses per month?
Due to the moon's orbit being tilted.
Give the basic characteristics of calcite
Clear, cleavage = rhombus, medium hardness level, double refraction, reacts with acid
What rock types/names are typically associated with mountain regions?
Metamorphic rocks: Gneiss, Schist
Igneous rocks: granite
What is the difference between a mold and a cast fossil?
Mold fossils are the empty spaces where the organism used to be in the rock (shows an empty outline)
Cast fossils are when mineral matter fills in the mold and are a mineral replica of the organism
What is stellar parallax and how is it used in real life?
The apparent shift of an object against a distant background object. The smaller the shift in position, the further the object is from earth.
Used by looking at the shift of the object over a 6 month period (opposite sides of earth orbit)
What is a sunspot? What is its temperature and why do they occur?
A darker, cooler spot on the surface of the sun caused by magnetic field convection interference.
Name the detrital sedimentary rocks, their sediments, and their sizes
Shale = mud (xs/small)
Sandstone = sand (medium)
Breccia/Conglomerate = pebbles (large)
What are the two types of weathering? Give an example of each.
Chemical Weathering = hydrolysis, acid rain, etc
Mechanical Weathering = abrasion, frost wedging, etc
What is an index fossil and why are they useful?
Index fossils are fossils of organisms that existed during a short period of geologic time but were widespread geographically.
They are useful as they can help someone identify the general time period of a layer if they find an index fossil
What are Kepler's 3 laws of planetary motion?
1) All planets move in ellipses
2) Planets sweep equal areas in equal time
3) There is a relationship between distance from the sun and the orbit time of a planet
Starts in the core (product of nuclear fusion), then moves into the radiative zone (random walk), then the convection zone, reaches the photosphere and then takes about 8 minutes to reach the Earth
Explain how sand can become a metamorphic rock. Use all proper vocabulary and rock names.
Sand can become compacted and cemented into sandstone. The sandstone can then undergo contact metamorphism, which results in the non-foliated metamorphic rock quartzite.
What caused the formation of the Grand Canyon?
D = Deposition
U = Uplift
D = Downcutting
E = Erosion
How long will it take 600 grams of Plutonium-239 (half life = about 25,000 years) to decay to leave only 75 grams of Plutonium-239?
75,000 years
When a planet (such as Mars) moves "backwards" in its path in the night sky.
This is due to Earth passing Mars in orbit.
Explain the red giant phase
Nuclear fusion of hydrogen causes gravity to take over and collapse the core, which increases the temperature, and expands the outer layers, and the outer layers are cool and are "red".
A rock has large crystals. Tell me ALL possible vocabulary/descriptions associated with this rock.
Igneous: Coarse-Grained, Cooled Slowly, Intrusive
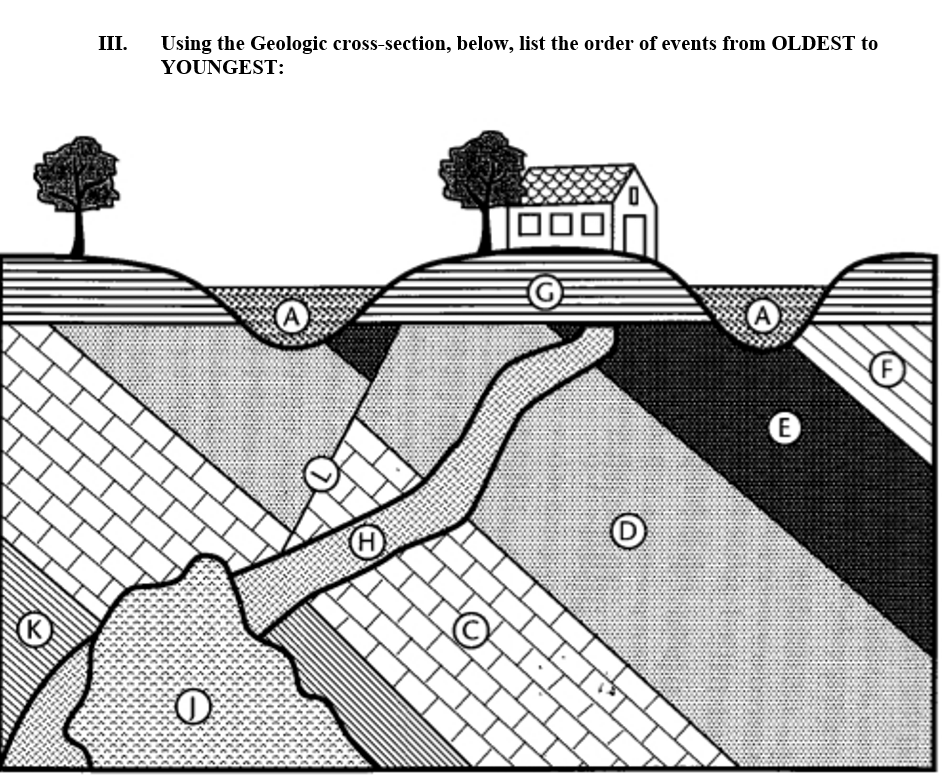
Put these layers in order from oldest to youngest:
A
G
I
H
L
F
E
D
C
K
Explain three examples of how a scientist could "recreate a prehistoric ecosystem"
-Look at paleomagnetism
-Do radiometric dating
-Specialist to uncover/detail the fossils
-Consider anatomy of organisms found
-Look at insects present
-Look at leaf structure (shape, size, etc)