Membrane Transport & Feedback
Membrane Transport & Feedback
Cellular Energetics
Genetics, Heredity, & Evolution
During this process, small nonpolar molecules move through the phospholipids of the cell membrane.
(Simple) Diffusion
During which part of photosynthesis is a water molecule split?
Light dependent reactions
A heterozygote (has the recessive allele for the trait, but does not express it)
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration require the uptake and release of gasses. What type of membrane transport will be used?
passive transport
Differentiate between RNA polymerase and DNA polymerase.
RNA polymerase is used to create mRNA in transcription (protein synthesis), DNA polymerase is used to synthesize a new DNA strand during DNA synthesis (S phase of cell cycle)
Bulk transport
Cell Respiration has the citric acid/krebs cycle
A roan cow is the result of a red hair cow crossing with a white hair cow. What is this an example of?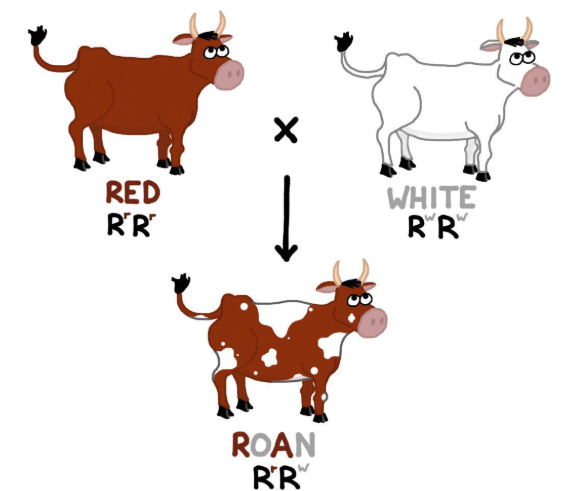
Codominance
In what organelle will the genetics be more heavily related to energy levels?
Mitochondria have their own DNA, so at this organelle the genetics will relate more strongly to creating energy in the form of ATP
What phase occurs before both mitosis and meiosis?
Interphase
During this type of process signals are used to move a process to completion
Positive feedback loop
Where is ATP created in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Electron Transport Chain- more specifically ATP Synthase
On an X-linked gene, how many alleles will be required for a son to express the trait?
One (they only have one X to carry an allele)
ATP synthase is an example of what type of membrane transport? Why?
Facilitated diffusion
Moves charged protons (H+) down the concentration gradient.
How are fossils used for genetic engineering and evidence of evolution?
Genetic Engineering: DNA from fossils can be integrated into modern DNA as part of genetic engineering.
Evidence of evolution: The fossils can be used to compare homologous structure, change over time, or to extract DNA to compare the sequence.
Which type of feedback will help maintain homeostasis?
Negative feedback
Sometimes photosynthesis and cellular respiration are considered one big cycle. Why?
The products of one are the reactants for the other.
A mutation is a change to the nucleotide sequence (genetics) of an organism.
It is not genetic engineering as it is not intentional.
Pyruvates, large molecules, move across the mitochondrial membrane using this type of transport.
Active transport via carrier protein
During what phase of the cell cycle are the homologous chromosomes separated?
Anaphase I
Explain how neurons represent cell communication, feedback, and membrane transport.
Neurons use active transport for the Na+/K+ pump to send signals, communicating what the organs and tissues they come in contact with should do. This may increase the stimuli (positive feedback) or cause a decrease in the stimuli (negative feedback).
Differentiate between the sources of energy and the energy molecules created in photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
Photosynthesis
Main Source: Light
Creates: NADPH & ATP
End product: Chemical Energy in form of glucose
Cell Resp
Main source: Chemical Energy in form of glucose
Creates: NADH & FADH2
End Product: ATP (Chemical Energy)
Is it more likely for a swap in one nucleotide or the deletion of one nucleotide to cause a bigger change in the protein?
It is more likely that the deletion of one nucleotide has a bigger impact because it shifts the reading of the codons over one.
A swap to one nucleotide may cause a change in the amino acid, but there are many codons for each amino acid, so it also may not.
How is protein synthesis related to feedback loops?
If a process requires more of a protein to go to completion or bring us to homeostasis, then protein synthesis will occur & vice versa.
Give an example of how proteins are used in all 3 units.
Answers may vary- up to teacher discretion (example below)
Proteins are used for facilitated diffusion, carrier proteins for passive & active transport.
Proteins are used for transport of molecules as stated above in photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Enzymes (a type of protein) are used when cutting and combining DNA.