The basic problem within the study of economics where we have unlimited wants but limited resources
Scarcity
Elastic - large portion of income, has many substitutes, luxury
The dollar value of all final goods & services produce within a year in a country's borders
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The document that establishes the primary purpose of government is to protect the rights of the people and outlines ways in which the British violated these rights
Declaration of Independence
The process of how a person develops their individual political ideology
Political Socialization
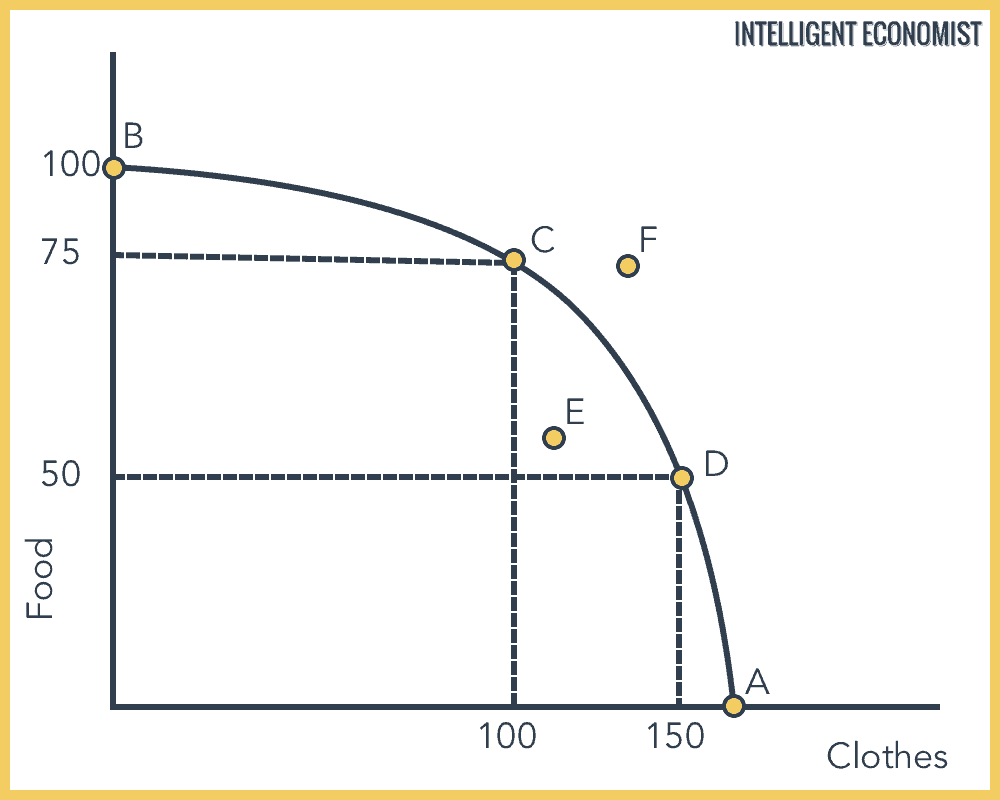
What is the opportunity cost of increasing food production from 75 units to 100 units?
100 units of clothes
What will change quantity demanded & quantity supplied?
Price
Adjusted for inflation
According to James Madison, the best way to control the effects of factions is with
Identify one element of a scientific poll
Appropriate sample size
Random selection
Representative sample
Margin of error is listed at around +/- 3%
Neutral Language
Tariff - tax on imported good
Quota - maximum # of goods a country can export to another country or that a country will import from another country
Embargo - stopping trade with another country
Liscenses - requiring liscenses to engage in trade
Define a price floor & identify the economic problem it causes.
Price floor - a minimum price that a product can be sold for
Causes surplus
Define the unemployment rate and identify one type of unemployment.
Unemployment rate is the percentage of the labor force that is out of work but actively seeking a job.
Types of unemployment: frictional, structural, cyclical
Federalists supported the ratification of the Constitution because they wanted a stronger central government
Anti-Federalists did not support the ratification of the Constitution because they wanted the states to maintain most of the power & felt the Constitution didn't do enough to protect the rights of the people
Identify the two tools used in fiscal policy & who has the power to use these tools
Tools: taxing & spending
Who: Congress passes budget & Pres signs or vetoes
Identify & describe the three major economic systems
Command - the government makes all economic decisions
Traditional - tradition & customs determine how the society will answer basic economic questions
Market - the laws of supply and demand determine what's produced, how it's produced, and for whom to produce it for
List the events that will change supply
Disaster
New Technology
Change in the # of producers
Producer price expectations
Change in the P of factors of production
Government regulations, taxes, subsidies
Define inflation & explain the two causes of inflation
Inflation - value of the dollar decreases as prices of goods & services increases
Causes:
demand pull - where too much money in circulation causes an increase in demand which will result in higher prices
cost push - where prices for factors of production increase causeing supply to decrease and price to increase
Explain why the Articles of Confederation failed and identify the event that forced delegates to reconvene at a Constitutional Convention to amend the Articles of Confederation
Central government didn't have enough power. Biggest problem was they didn't have the power to tax, coin money, or fund a standing army. Shay's rebellion highlighted the economic problems that resulted from the states printing money & refusing to pay taxes. The federal government had no standing army to suppress such rebellions. This event forced the need to ratify the Articles of Confederation, but since this required a unanimous vote, it couldn't be changed & an entirely new Constitution was written instead.
Identify and describe the two major political ideologies in the U.S.
Liberalism: more gov involvement in the economy but less in social issues
Conservative: more gov involvement in social issues but less in the economy
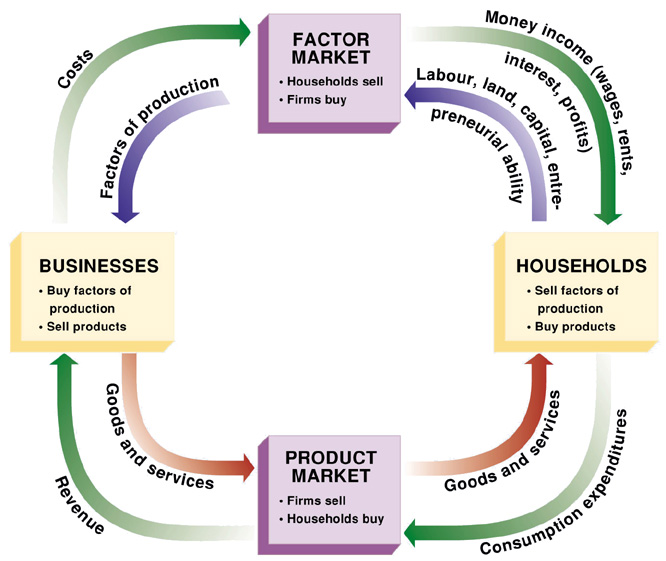
Explain the circular flow of economic activity.
Holiday season is here! Many people want a Christmas tree to decorate their homes. Please explain how this event will change demand, what is the demand shifter, and how equilibrium price & quantity change as a result.
Demand increases & shifts to the right
Change in consumer taste
P & Q increase
List & describe the 5 parts of the business cycle
Trough - the lowest point of a contraction before economy recovers
Expansion - GDP increase & prices go up (inflation)
Peak - the highest point of an expansion before the economy slows down
Contraction - GDP slows or decreases as unemployment rises (recession if this lasts longer than 6 months & is a depression if it becomes severe)
Trend line - ideal slow, steady growth
Define federalism & explain how McCulloch v Maryland and U.S. v Lopez helped to define federalism over time.
Federalism - power is shared between federal government & smaller regional government
McCulloch v Maryland expanded powers of the federal government by solidifying the power of the federal government to create a national bank through the necessary & proper clause & protected the supremacy of the federal government prohibiting states from taxing the federal government
U.S. v Lopez limited the powers of the federal government by placing restrictions on Congress' use of the commerce clause & upholding the power of the states to regulate public schools within their state
The U.S. is experience a rise in unemployment. Identify where we are in the business cycle & explain how the Federal Reserve can use monetary policy to stabilize the economy.
Contraction/Recession
Reserve Requirement: decrease
Discount Rate: decrease
Fed Funds Rate: decrease
Open Market Operations: buy