Parents bring their child to the PCP after the child's teacher reports that the child seems to be constantly fidgeting with their hands, struggles to wait their turn, shouts out answers before questions are completed, and loses interest in school assignments. The nurse knows to recommend testing for this condition...
What is ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder)?
The clinic nurse instructs parents of a child with sickle cell anemia about the precipitating factors related to sickle cell crisis. Which, if identified by the parents as a precipitating factor, indicates the need for further instruction?
1. Stress
2. Trauma
3. Infection
4. Fluid overload
What is Answer 4?
"Rationale: Sickle cell crises are acute exacerbations of the disease, which vary considerably in severity and frequency; these include vaso-occlusive crisis, splenic sequestration, hyperhemolytic crisis, and aplastic crisis. Sickle cell crisis may be precipitated by infection, dehydration, hypoxia, trauma, or physical or emotional stress. The mother of a child with sickle cell disease should encourage fluid intake of 1.5 to 2 times the daily requirement to prevent dehydration."
Silvestri, L. A., & Silvestri, A. (2020). Saunders Q & A review for the NCLEX-RN examination. Elsevier Health Sciences.
The nurse is instructing the parents of a child with iron deficiency anemia regarding the administration of a liquid oral iron supplement. Which instruction should the nurse tell the parents?
1. Administer the iron at mealtimes.
2. Administer the iron through a straw.
3. Mix the iron with cereal to administer.
4. Add the iron to formula for easy administration.
What is Answer 2?
"Rationale: In iron deficiency anemia, iron stores are depleted, resulting in a decreased supply of iron for the manufacture of hemoglobin in red blood cells. An oral iron supplement should be administered through a straw or medicine dropper placed at the back of the mouth, because the iron stains the teeth. The parents should be instructed to brush or wipe the child’s teeth or have the child brush the teeth after administration. Iron is administered between meals because absorption is decreased if there is food in the stomach. Iron requires an acid environment to facilitate its absorption in the duodenum. Iron is not added to formula or mixed with cereal or other food items."
Silvestri, L. A., & Silvestri, A. (2020). Saunders Q & A review for the NCLEX-RN examination. Elsevier Health Sciences.
A child presents to the ED with a chemical burn. The priority care for this child is...
What is remove the chemical?
• Dilute or brush off
• DO NOT use another chemical
The nurse knows that a child of this age group might believe their parent died due to their bad behavior that is being punished...
What is a pre-school child?
A child with known sickle-cell disease comes to the ED with wheezing, a cough, and an oxygen saturation of 89% on room air. The nurse knows to suspect this complication of SCD...
What is acute chest syndrome?
An adolescent client with type 1 diabetes mellitus is admitted to the emergency department for treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. Which assessment findings should the nurse expect to note?
1. Sweating and tremors
2. Hunger and hypertension
3. Cold, clammy skin and irritability
4. Fruity breath odor and decreasing level of consciousness
What is Answer 4?
"Rationale: Diabetic ketoacidosis is a complication of diabetes mellitus that develops when a severe insulin deficiency occurs. Hyperglycemia occurs with diabetic ketoacidosis. Signs of hyperglycemia include fruity breath odor and a decreasing level of consciousness. Hunger can be a sign of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, but hypertension is not a sign of diabetic ketoacidosis. Hypotension occurs because of a decrease in blood volume related to the dehydrated state that occurs during diabetic ketoacidosis. Cold clammy skin, irritability, sweating, and tremors all are signs of hypoglycemia."
A child is diagnosed with tinea corporis. The nurse knows that the child will be treated with this type of medication for ____ weeks.
What are antifungals and 6 weeks?
The mother of a 4-year-old child tells the pediatric nurse that the child’s abdomen seems to be swollen. During further assessment, the mother tells the nurse that the child is eating well and that the activity level of the child is unchanged. The nurse, suspecting the possibility of Wilms’ tumor, should avoid which during the physical assessment?
1. Palpating the abdomen for a mass
2. Assessing the urine for the presence of hematuria
3. Monitoring the temperature for the presence of fever
4. Monitoring the blood pressure for the presence of hypertension
What is Answer: 1?
"Rationale: Wilms’ tumor is the most common intra-abdominal and kidney tumor of childhood. If Wilms’ tumor is suspected, the tumor mass should not be palpated by the nurse. Excessive manipulation can cause seeding of the tumor and spread of the cancerous cells. Hematuria, fever, and hypertension are clinical manifestations associated with Wilms’ tumor."
Silvestri, L. A., & Silvestri, A. (2020). Saunders Q & A review for the NCLEX-RN examination. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Three signs of impending death include...
• Loss of sensation to the body and thermoregulation
• Cool, pale skin, may become cyanotic
• Loss of bowel and bladder function
• Cheyne-Stokes respirations
• Changes in LOC
• Weakness, slurred speech
• Changes in vital signs and pain perception
• Decreased oral intake
**BONUS: What is the medical term for the whitish glow of the pupil?
What is retinoblastoma?
**Bonus: leukocoria (cat’s eye reflex)
The nurse knows that the tool that can be used along with visual inspection to diagnose Tinea Capitus, Tinea Corporis, Tinea Cruris and Tinea Pedis is called...
What is a Wood's Lamp?
The nurse is reviewing a health care provider’s prescriptions for a child with sickle cell anemia who was admitted to the hospital for the treatment of vaso-occlusive crisis. Which prescriptions documented in the child’s record should the nurse question? Select all that apply.
1. Restrict fluid intake.
2. Position for comfort.
3. Avoid strain on painful joints.
4. Apply nasal oxygen at 2 L/minute.
5. Provide a high-calorie, high-protein diet.
6. Give meperidine, 25 mg intravenously, every 4 hours for pain.
Answer: 1, 6
"Rationale: Sickle cell anemia is one of a group of diseases termed hemoglobinopathies, in which hemoglobin A is partly or completely replaced by abnormal sickle hemoglobin S. It is caused by the inheritance of a gene for a structurally abnormal portion of the hemoglobin chain. Hemoglobin S is sensitive to changes in the oxygen content of the red blood cell; insufficient oxygen causes the cells to assume a sickle shape, and the cells become rigid and clumped together, obstructing capillary blood flow. Oral and intravenous fluids are an important part of treatment. Meperidine is not recommended for a child with sickle cell disease because of the risk for normeperidine-induced seizures. Normeperidine, a metabolite of meperidine, is a central nervous system stimulant that produces anxiety, tremors, myoclonus, and generalized seizures when it accumulates with repetitive dosing. The nurse would question the prescription for restricted fluids and meperidine for pain control. Positioning for comfort, avoiding strain on painful joints, oxygen, and a high-calorie and high-protein diet are also important parts of the treatment plan."
Name three nursing actions pre-transfusion of blood product...
What are...
"• Do not call for the blood product until it is needed.
• Obtain a set of pretransfusion vital signs to ensure patient is clinically stable.
• Verify the health-care provider’s orders, including the appropriate product and volume to be infused. The transfusion must be started within 30 minutes after the blood has left the blood bank.
• The maximum time for the infusion is 4 hours. Transfusion needs to start immediately because of the risk of bacterial contamination and cell lysis. Most blood banks do not accept blood back after 30 minutes.
• Follow institutional policy for obtaining, verifying, and transporting blood products obtained from the blood bank.
• Complete appropriate forms and ensure accurate patient identification.
• Indicate product type and check for any special orders such as cytomegalovirus safe or irradiated.
• Always check to see if any premedications were ordered before administration.
• Use personal protective equipment. Be sure to wear goggles and gloves.
• All blood products must be checked at the patient’s bedside by two appropriate health-care providers and using two patient identifiers as per the institution’s policy.
Remember, the two patient identifiers must match the number on the blood product and the wrist band."
Scannell, M. J., & Ruggiero, K. (2021). Davis Advantage for Maternal-Child Nursing Care (3rd ed.). F. A. Davis Company.
The school nurse has provided an instructional session about impetigo to parents of the children attending the school. Which statement, if made by a parent, indicates a need for further instruction?
1. “It is extremely contagious.”
2. “It is most common in humid weather.”
3. “Lesions most often are located on the arms and chest.”
4. “It might show up in an area of broken skin, such as an insect bite.”
What is Answer 3?
"Rationale: Impetigo is a contagious bacterial infection of the skin caused by β-hemolytic streptococci or staphylococci, or both. Impetigo is most common during hot, humid summer months. Impetigo may begin in an area of broken skin, such as an insect bite or atopic dermatitis. Impetigo is extremely contagious. Lesions usually are located around the mouth and nose but may be present on the hands and extremities."
Reed-Sternberg cells are typically present with this type of cancer...
What is Hodgkin's Lymphoma?
HL is a cancer of the lymph system and clinical manifestations include:
• Swollen, firm lymph nodes
• Anterior mediastinal mass is present
• Unexplained fever
• Weight loss
• Night sweats
A neonate is found to have an intracranial hemorrhage. The nurse knows that the baby should be tested for which hematological disorder and will be diagnosed using these tests...
What is hemophilia and PT/PTT and/or a direct assay of plasma factor activity level for Hemophilia A and B?
A child with ____% TBSA burns requires IV fluids during treatment and the urinary output goal for these patients are _______.
***DAILY DOUBLE***
What are 10% and 0.5ml – 1 ml/kg/hr?
The nurse analyzes the laboratory values of a child with leukemia who is receiving chemotherapy. The nurse notes that the platelet count is 19,500 mm3 (19.5 × 109/L). On the basis of this laboratory result, which intervention should the nurse include in the plan of care?
1. Initiate bleeding precautions.
2. Monitor closely for signs of infection.
3. Monitor the temperature every 4 hours.
4. Initiate protective isolation precautions.
What is Answer 1?
"Rationale: Leukemia is a malignant increase in the number of leukocytes, usually at an immature stage, in the bone marrow. It affects the bone marrow, causing anemia from decreased erythrocytes, infection from neutropenia, and bleeding from decreased platelet production (thrombocytopenia). If a child is has a low platelet count usually less than 50,000 mm3 (50.0 × 109/L), bleeding precautions need to be initiated because of the increased risk of bleeding or hemorrhage. Precautions include limiting activity that could result in head injury, using soft toothbrushes, checking urine and stools for blood, and administering stool softeners to prevent straining with constipation. In addition, suppositories, enemas, and rectal temperatures are avoided. Options 2, 3, and 4 are related to the prevention of infection rather than bleeding."
Silvestri, L. A., & Silvestri, A. (2020). Saunders Q & A review for the NCLEX-RN examination. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Name 3 of the 6 "C's" of minor burns...
6 “C’s”
• Clothing – remove any clothing that is hot or has
chemicals on it
• Cooling – use cool saline soaked gauze. DO NOT
use ice
• Cleaning – Wash with mild soap and water and
rinse well
• Chemoprophylaxis – Bacitracin, tetanus booster
• Covering – Cover with nonadherent gauze
• Comfort – Give acetaminophen or ibuprofen to
decrease pain.
The following "sunburst" pattern is typically seen with this diagnosis...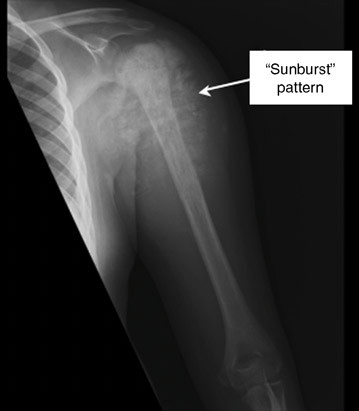
What is osteosarcoma?
A newborn screening is performed on a 1-day-old infant. The results indicate an abnormally low T4 and high TSH levels. The newborn would most likely be diagnosed with...
What is hypothyroidism?
Name and describe the three phases of leukemia treated with chemotherapy...
What are...
1: Remission-induction: reduce tumor to undetectable size
• Multiple Chemo drugs for 4 weeks
• CNS prophylaxis
• Outpatient once stable
2: Consolidation: destroy any residual leukemic cells
• Chemotherapy administered in high doses
• Not hospitalized
• Radiation may be required
3: Maintenance: control leukemia
• Can last for 2–3 years after diagnosis
• Usually carried out in outpatient setting
Which specific nursing interventions are implemented in the care of a child with leukemia who is at risk for infection? Select all that apply.
1. Maintain the child in a semiprivate room.
2. Reduce exposure to environmental organisms.
3. Use strict aseptic technique for all procedures.
4. Ensure that anyone entering the child’s room wears a mask.
5. Apply firm pressure to a needle-stick area for at least 10 minutes.
What are Answers 2, 3, 4?
"Rationale: Leukemia is a malignant increase in the number of leukocytes, usually at an immature stage, in the bone marrow. It affects the bone marrow, causing anemia from decreased erythrocytes, infection from neutropenia, and bleeding from decreased platelet production (thrombocytopenia). A common complication of treatment for leukemia is overwhelming infection secondary to neutropenia. Measures to prevent infection include the use of a private room, strict aseptic technique, restriction of visitors and health care personnel with active infection, strict hand washing, ensuring that anyone entering the child’s room wears a mask, and reducing exposure to environmental organisms by eliminating raw fruits and vegetables from the diet and fresh flowers from the child’s room and by not leaving standing water in the child’s room. Applying firm pressure to a needle-stick area for at least 10 minutes is a measure to prevent bleeding."
The CDC uses the ALARM acronym for which condition and the acronym stands for...
What is autism?
• A-autism is prevalent
• L-listen to patients/parents
• A-act early
• R-refer
• M-monitor