What is spontaneous generation?
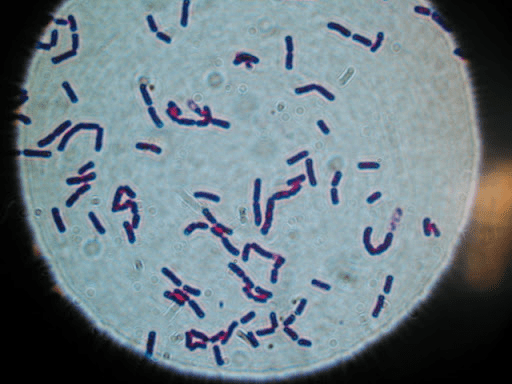
Name the cell shape seen above.
What is bacillus?
Bacteria divide through the process known as ___________.
What is binary fission?
The process of removing and destroying all microbial life.
What is sterilization?
Antimicrobial drugs that can affect only a certain group of microbes are referred to as being ___________.
What is Narrow Spectrum?
This type of host supports the non-reproductive parasite. Usually acts as a vector.
What is an Intermediate Host?
This group of microorganisms does not contain any human pathogens.
What are Archaea?
Prokaryotic cell structure involved in conjugation.
What is Pili?
Organisms that require moderate temperatures to survive. Contain human pathogens.
What are Mesophiles?
Provide an action of microbial control methods.
What is Damage the cell membrane, denature proteins, or damage nucleic acids?
Transduction is a form of _______ gene transfer.
What is Horizontal?
Fungi that exhibit mold-like and yeast-like forms are called _____________.
What are Dimorphic Fungi?
An organism's scientific name is composed of these two components.
What is the genus and specific epithet?
Name the cell wall seen below.
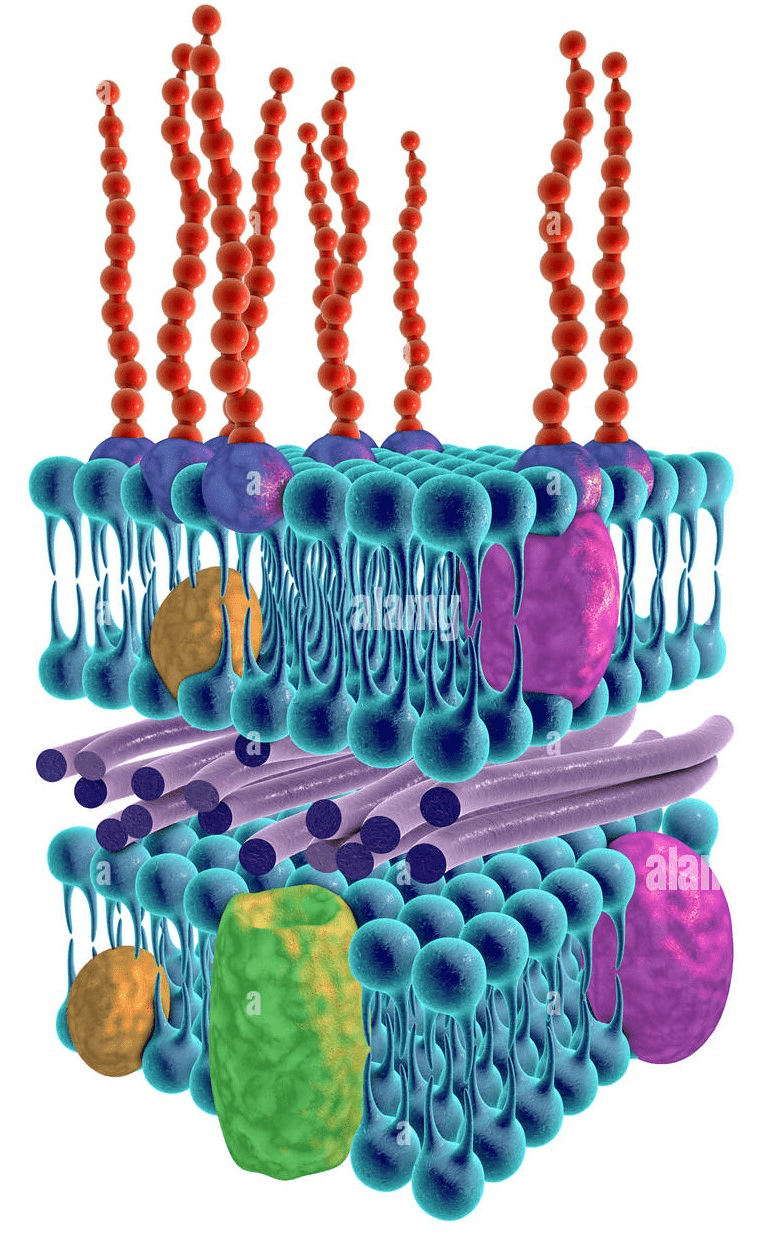
What is a gram-negative cell wall?
Organisms that can switch metabolic processes depending on whether oxygen is present or not.
What are Facultative Anaerobes?
Chemical control method that is an effective antimicrobial in very small amounts.
What are Heavy Metals?
An antimicrobial drug targeting this cell structure would be very effective in stopping LPS contact.
What is the Plasma Membrane?
The feeding and growing form of protozoa.
What are Trophozoites?
This type of enzyme inhibitor fills the active site of an enzyme instead of a substrate.
What is a competitive inhibitor?
If a bacterium encounters a repellent in the environment, its flagella will rotate to cause a ______.
What is a tumble?
This enzyme is important for breaking down the toxic radical hydrogen peroxide.
What is Catalase?
This oxidizing agent will be ineffective if a microbe produces catalase.
What is Peroxygen?
If you are trying to inhibit the synthesis of peptidoglycan, you better make sure that the bacterium does not have this enzyme present.
What is Penicillinase?
Parasitic worms need to adapt to live in a host. Provide one of these adaptations.
May lack a digestive system, reduced nervous system, reduced or lacking locomotion, and a complex reproductive system.
What is an inorganic final electron acceptor?
Provide two differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Prokaryotes: 70S ribosomes, nuceloid, and no membrane-bound organelles
Eukaryotes: 80S ribosomes, nucleus, and membrane-bound organelles
This phase of the growth curve is where organisms are more susceptible to antimicrobials or disinfectants.
What is the Log Phase?
Describe the difference between ionizing and nonionizing radiation.
Ionizing -> causing single- or double-strand breaks in DNA
Nonionizing -> introducing the risk of developing thymine dimers in a DNA strand
Antifungals must be specific in targeting structures not found in humans. What is one of these structures?
What are Chitin or Ergosterols?
Parasitic worms that are defined by having flat-shaped bodies and suckers for attaching to hosts.
What are Platyhelminths?