What are the 5 steps of the scientific method?
Observing and asking questions
Inferring & forming a hypothesis
Designing a controlled experiment
Collecting & analyzing data
Interpreting data & drawing conclusions
What is the difference between an element and a compound?
Element- A substance made up of all the same atoms. Elements combine to make molecules.
Compound- When atoms of different elements react and combine in fixed proportions
Draw single, double, and triple covalent bonds
What is the electromagnetic spectrum and what does it represent?
Electric and magnetic fields travel through space as transverse waves at right angles- this is known as the electromagnetic field
The electromagnetic spectrum represents the entire range of light that exists
Shorter wavelength/higher frequency light waves have higher energy
State 2 properties and tendencies or gases.
Gas is a state of matter that forms homogenous mixtures with other gases regardless of the identities or relative proportions of the component gases
Gases always expand to fill the container they are in due to a lack of strong attractive forces
Gas pressure is the force exerted by a gas per unit surface area of an object
The SI Unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa)
1 Pa = N/m2
What are the differences between scientific theory and a scientific law?
Scientific Theory- A reliable scientific explanation of events in the natural world that unifies many repeated observations and incorporates well-supported hypotheses.
Scientific Law- A description of an observed phenomenon. It doesn't explain why the phenomenon exists or what causes it. True and universal
Where are Protons, Neutrons, and electrons found in an atom? What are their charges
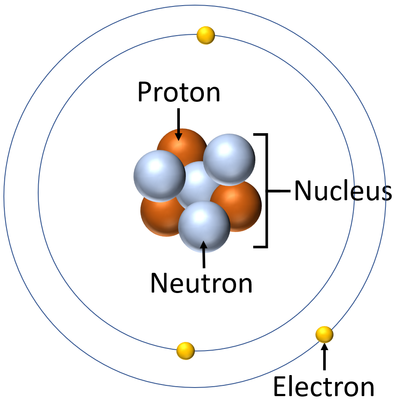
Proton- Positive
Neutron- Neutral/ no charge
Electron- Negative charge
What is molarity and its equation?
Molarity (M) is expressed as moles of solute per liter of solution
Molarity= Moles of solute/ moles of solution
How does a catalyst affect the speed of a reaction?
The presence of a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a reaction. This in turn speeds up the reaction.
What is the kinetic theory of gas?
Based upon the idea that all matter is made of particles that are in constant motion.
Assumptions of Kinetic Theory
The particles of a gas are considered to be small with insignificant volume.
No attractive or repulsive forces exist between the particles.
The motion of the particles in a gas is rapid, constant, and random.
All collisions between particles in a gas are elastic.
The average kinetic energy of a gas is proportional to the absolute temperature.
What is pseudoscience?
Pseudoscience - Statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are not supported by research using the scientific method
What is an ion and how do you find it's charge?
Ion- Atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
How to find an Ion's charge-
1) Find the sign of the charge by determining whether protons outnumber electrons or electrons outnumber
2) Find the magnitude of the charge by determining the difference between the number of protons and electrons in the ion.
Moles-
What is the particle equivalent of a mole?
What are molar-mass relationships?
List the mole-volume relationship?
A mole (mol) of a substance is 6.02 x 1023 representative particles of that substance
The atomic mass of an element is equal to the mass of 1 mole of that element
What are the differences between exothermic and endothermic reactions?
Endothermic reactions require energy to be present as a reactant.
- Energy is absorbed by the change taking place.
- You will see energy added to the reactants side (left) of an equation
Exothermic reactions require energy to be present as a product.
- Energy is released by the change taking place.
- You will see the energy added to the products side (right) of an equation
What is Avogadro’s law?
Avogadro’s law states that equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules.
1 mole of any gas at 0 C and 1 atm will contain 6.02 x 1023 particles and will occupy a volume of 22.4L
Avogadro’s hypothesis states that the volume of a gas maintained at constant temperature and pressure (STP) is directly proportional to the number of moles of the gas.
V1/n1= V2/n2
What is 2050000 in scientific notation?
2.05x10^6
What are ionic and covalent bonds, which one is stronger?
Ionic bond- Involves the complete transfer of electrons between atoms
- Always metal and non-metal
- High melting points
- good conductors of electricity
Covalent bond- Formed between atoms held together by sharing electrons.
- Low melting points
- Always two non-metals
-Poor conductors of electricity
Where are each chemical families found and what are their properties?


Metals- Lustrous, good conductors, malleable and ductile
Non-metals- Often gases or brittle solids at room temperature, poor conductors
Metalloids- Solids at room temperature, less brittle than nonmetals, less malleable than metals
Noble gases- Nonreactive, gases at room temperature, each emits different color light when excited electrons return to a ground state
Halogens- Highly reactive nonmetals, gain one electron to complete octet and have –1 charge as ions
Alkali Metals- Highly reactive metals, lose one valence electron to form ions with +1 charge
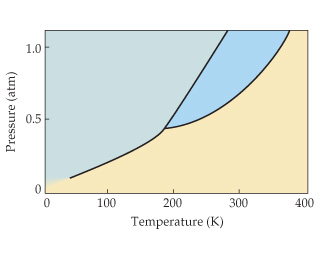
What is a phases change diagram and what happens at-
AB
AC
Point A
Point B
Phase diagrams display the state of a substance at various pressures and temperatures and the places where equilibria exist between phases.
AB line is the liquid-vapor interface. Each point along the AB line is the boiling point of the substance at that pressure.
AC line the solid and gas phases are in equilibrium; the sublimation point at each pressure is along this line.
Point A represents where all three states are in equilibrium.
Above point B represents critical temperature, where liquid and vapor are indistinguishable from each other.
What is the ideal gas law and equation? In what situation would this be used?
An ideal gas follows rules that scientists have created and remains in gas at any temperature and pressure (These do not actually exist)
A real gas changes into liquid or solid at low temperatures and high pressures
In real gases, the particles have volume and experience intermolecular forces.
The ideal gas law allows us to calculate volume, pressure, number of moles, or temperature
PV = nRT
P = pressure (kPa) OR (atm)
V = volume (L)
n = number of moles (mol)
R = ideal gas constant (8.31 L.kPa/mol.K) OR (0.0821 L.atm/mol.K)
T = temperature (Kelvin)
What are precision and accuracy?
Precision – How closely repeated measurements approach one another (consistency)
Accuracy – Closeness of measurement to the true or accepted value
Scientific data aim to have both precision and accuracy, to provide quality data.
Describe each reaction
(drawings can be used)
Synthesis reaction
Decomposition reaction
Single-replacement reaction
Double-replacement reaction
Combustion reaction
Synthesis reaction- Two or more reactants combine to form one product
Decomposition reaction- One reactant breaks down into two or more products
Single-replacement reaction- A reactive element replaces another element in a compound
Double-replacement reaction- Two compounds break up into ions and change the cation or anion they are bonded to, forming two new compounds
Combustion reaction- A compound reacts with oxygen gas and releases energy in the form of light and/or heat
reactant + O2 → product(s) + energy
What are the differences between and chemical and nuclear reactions?
Chemical reactions occur because of instability in electron configurations and involve the interactions of electrons between different substances. In order to become more stable (have 8 valence electrons).
Nuclear reactions occur because of instability in the nuclear geometry of an atom and involve nuclear fission or nuclear fusion such that the nucleus becomes more stable.
Nuclear fission- Splitting nuclei
Nuclear fusion- nuclei coming together
Nuclear reactions are more energetic than a chemical reaction
How does the quantization of energy happen at the atomic level? and how does this affect wavelength?
Electrons absorb enough energy to move them from their ‘ground state’ to their ‘excited state’ in a stair-step pattern, requiring more and more energy to be bumped up to a higher energy state.
Electrons then emit energy in the form of light (electromagnetic radiation) as they transition from their excited state back to their ground state.
What are Charles law, Boyle's law, and Gay-Lussac’s Law?
Charles law- If the temperature goes up then the volume goes up.
V1/T1 = V2/ T2
Boyle's law- If the volume goes down the pressure goes up.
P1V1 = P2V2
Gay-Lussac’s Law- If the temperature goes up then the pressure goes up.
P1/T1=P2/T2
**Remember to change the temperature to Kelvin for Boyle and Gay-Lussac's law
273 + C = K