Unit 1
Unit 2
Unit 3
Unit 4
Unit 5
100
This type of hepatitis is the most common. It is transmitted via oral-fecal route.
What is Hepatitis A?
100
The nurse prepares a discharge teaching plan for a 44-year-old male patient who has recently been diagnosed with coronary artery disease. Which modifiable risk factor should the nurse plan to focus on during the teaching session? (Select all that apply) 1. Serum total cholesterol 250mg/dL 2. Mother has a history of myocardial infarction 3. Client smokes 1 pack of cigarettes daily 4. Hemoglobin A1C 7.1%
What is 1,3,& 4?
100
Patients with this level of SCI will have complete control of upper extremities, making it possible to have independence in wheelchair and ADLs.
What is T1-T6?
100
This is the primary symptom associated with Sickle Cell Crisis.
What is pain?
100
Clinical features of delirium and dementia.
What is see Table 22-2 on page 340?
200
Two factors that are commonly associated with pancreatitis.
What is alcoholism and biliary tract disease?
200
A commonly ordered test to determine if a stroke has occurred and what kind of stroke.
What is CT scan without contrast?
200
The client with an C6 spinal cord injury complains of suddenly being too warm, with nasal congestion and a very red face. What is your next assessment? A. temperature B. blood pressure C. input and output for previous 8 hours D. bowel for impaction
What is B? This is autonomic dysreflexia and is usually associated with hypertension. Sit them up quickly.
200
Labs to be monitored for the client with Leukemia.
What is Leukocytes (WBCs), Hemoglobin, Hematocrit, & Platelets?
200
How to establish a therapeutic relationship.
What is being available, listening, clarifying, sharing observations, & accepting silence?
300
Stages of acute renal failure and labs associated with renal function.
Stages: initial, oliguric, diuretic, & recovery phase. Labs: creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine clearance, & monitoring hourly urine output.
300
Answer the following patient question: "What do I need to know about taking sublingual nitroglycerin?"
What is take one tablet or spray for symptoms of angina, If symptoms are unchanged/worse after 5 minutes, may repeat up to total of 3 doses every 5 minutes. Call EMS if no relief after first dose. Have available at all times. Store away from heat/light sources. Replace every 6 months. May have a tingling sensation when administered. May have headache, dizziness, or flushing. Change positions slowly to prevent orthostatic hypotension. Important to tell patient exactly how to administer medication. Patient should sit or lie down at onset of chest pain.
300
This type of glaucoma is considered a medical emergency.
What is angle-closure or acute glaucoma? IOP may be > 50 mmHg. It causes sudden, acute pain.
300
Using the Rule of Nines, calculate the TBSA affected in a client admitted to the Emergency Department with burns in the posterior and anterior surface of both arms and the anterior right leg. Also name phases of burns.
What is 27%? Each arm is 9% & the leg is 9%.
Phases: Emergent, Acute, & Rehabilitation.
300
Side effects of antipsychotic medications.
What is orthostatic hypotension, extrapyramidal side effects, acute dystonic reactions, parkinsonian syndrome, tardive dyskinesia, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome?
400
A. This type of dialysis occurs more slowly, causes weight gain, and is usually performed more often. B. This type of dialysis takes less time, may cause dysrhythmias, and occurs through vascular access.
A. What is peritoneal dialysis? B. What is hemodialysis?
400
Causes and treatment for hypovolemic shock
Causes: loss of blood, plasma volume loss of > 20%, extreme dehydration, severe diarrhea & vomiting, & excess shift of plasma (burns, pancreatitis, & intestinal obstruction)
Treatment: controlling fluid loss (correct reason losing fluid or blood), administer IVF and/or blood products, administer colloids, frequent vital signs, apply oxygen, frequent assessments, & provide psychosocial support?
400
Isolation precautions used for Tuberculosis.
What is Airborne Isolation Precautions? Wear HEPA respirators or N95 masks; private room; keep door closed; negative pressure ventilation system; & client wears surgical mask when leaving room
400
Care of the client experiencing epistaxis.
What is instruct patient to sit down, lean head forward, pinch nostrils shut for at least 10 minutes, & advise not to pick or blow nose for several hours?
400
Clinical manifestations of anorexia.
What is severe weight loss, dry skin, amenorrhea, lanugo hair over back and extremities, cold intolerance, low blood pressure, abdominal pain, constipation, complaints of feeling bloated after eating small amount of food?
500
Clinical manifestations of Cushing Syndrome and Addison Disease.
Cushing Syndrome: truncal obesity, protein wasting, moon face, purple striae, osteoporosis, hypokalemia, & hirsutism (excess hair)
Addison Disease: progressive weakness, lethargy, abdominal pain, malaise, hypoglycemia, hyperkalemia, skin hyperpigmentation, & loss of body hair
500
Identify the following cardiac rhythm and discuss causes.
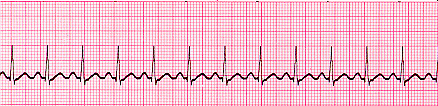

What is sinus tachycardia?
Causes: exercise, fear, shock, pain, dehydration, anxiety, HF, medications, excessive caffeine, recreational drugs, tobacco use, fever, hypovolemia, increased SNS stimulation, stress, MI, & alcohol (etoh)
500
Signs of increased intracranial pressure.
What is change in LOC, pupillary changes, altered motor function, posturing, inability to regulate body temperature, & changes in vital signs (Cushings Triad- widening pulse pressure, bradycardia, changes in respiratory pattern- considered a late sign)?
500
Suicide precautions in the hospital environment.
What is see Handout- Box 34-1 on page 1130 in Cooper & Gosnell?
500
Difference in delusion and hallucination.
Delusion: fixed belief that cannot be changed even when there is conflicting evidence
Hallucination: sensory experience that occurs without an external stimulus