This diagnosis usually results from RSV, with a telltale sign of diffuse crackles and wheezing.
Bronchiolitis
The amount of tidal volume found in an average adult
350-500mL
A 102kg pt has OD on Amitriptyline. This medication and dosage should be given to the pt.
Sodium bicarb / 102 mEq
a pt received hit a lightpole facefirst while skateboarding. he now has a "floating face". This is also called a:
La forte fracture
This term is defined as: cyanosis of the peripherals/extremities.
Acrocyanosis
During Anaphylaxis, Epi 0.3mg IM has been given along with Albuterol. After 3-5min with no improvement, this dose and route of Epi should be administered instead of redosing IM Epi if an IV is established.
0.01mg/kg Epinephrine 1:1,000 (Up to 0.1mg) IV
This is the most likely cause of Alveoli collapse and is commonly seen in COPD
Lack of surfactant
three p's that are indicative of hyperglycemia
polyuria, polyphagia, polydispisa
increased urine, thirst, appetite
What is cushings triad and what is it indicative of?
Increased ICP
- Bradycardia
- irregular respirations
- Hypertension
The Orange cranial bone is:
Temporal cranial bone
This term is defined as: characterized by progressive dilation of the ventricles with poor contraction of the myocardial muscle fibers resulting in low cardiac output and symptoms of heart failure.
Dilated cardiomyopathy
(most common cardiomyopathy of children)
If you see a "shark fin" on a capnography waveform, its safe to assume the pt has:
Bronchoconstriction/Bronchospasms

This stroke mimic is caused by inflammation of the 7th cranial nerve (facial nerve)
Bells palsey
Becks Triad: What its used to identify and the three triad signs
Identifies cardiac tamponade
- Hypotension
- muffled heart tones
- JVD
This diagnosis is usually seen by EKG and presents w/ ST segment depression and Inverted T waves
Ischemia
What is our MAXIMUM shock energy for defibrillation of pediatrics in cardiac arrest?
10 J/kg
Name what the acronym is and what it signifies:
FIO2
Fraction of inspired oxygen
The actual percentage of oxygen a person inhales
An major increase in thyroid stimulating hormones can cause this disease
Graves disease
What are you likely to hear with your stethoscope with a tracheal injury?
Subcutaneous emphysema
This spinal fracture is due to functional hemi section of the cord and complete damage to spinal tracts on the involved side.
usually has weakness or paralysis on effected side.
Brown-sequard syndrome
A pediatric pt presents w/ tachycardia at a rate of over 200bpm. The pt is altered and hypotensive. EKG shows possible Ventricular Tachycardia on the monitor. This treatment should be given to the pt according to the Tachycardia algorithm.
Syncronized cardioversion 0.5-1 J/kg
If not effective 2 J/kg
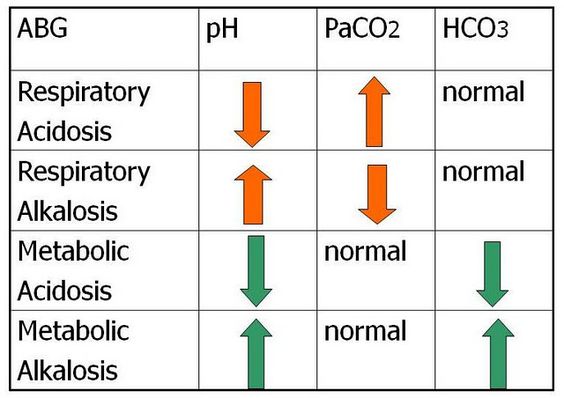
If a pt is experiencing respiratory acidosis they will have the following either increased or decreased:
PH, CO2, RR
Decreased PH and RR, increased CO2
HCO3 = bicarb
Name the doses for the following medications in our protocol:
- Diazepam, Lorazepam, Midazolam
Diazepam: (valium) 5-10mg
Lorazepam: (ativan) 2-4mg
Midazolam: (versed) 2.5-5mg
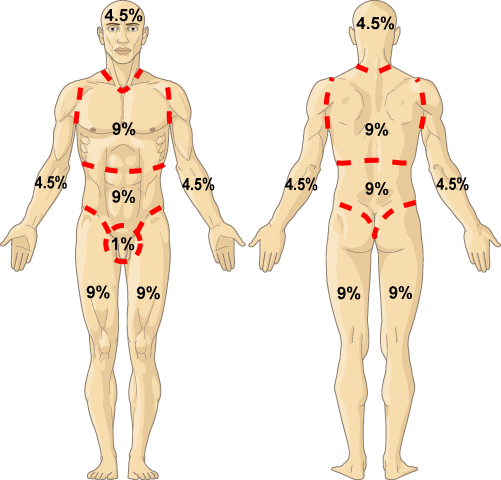
A pt would have this percentage of burns according to rule of 9's: Complete burn to right arm, head, front upper torso, and both legs.
54%
This medication and dosage is used for stable Afib with a rapid ventricular rate
Verapamil: 2.5-5mg IV over 2 min
Diltiazem: 0.25mg/kg IV over 2 min