What is Gout?
Deposits of uric acid that form a tophus (crystals) on the affected joint
cloudy urine
systemic or local infection?
UTI!
local, does not become systemic until fever
What is the diabetes insipidus
no production of the antidiuretic hormone from the hypothalamus
leading causes of kidney failure
diabetes
hypertension
Heart disease
Long term NSAID use
What is the name of the firefighter Jackson dates in Grey Anatomy?
bonus if you know the station number
VIC (Victoria)
Station 19
List some acute disorders
Broke bones
gastroenteritis
flu
Pink eye
Think very limited time frame
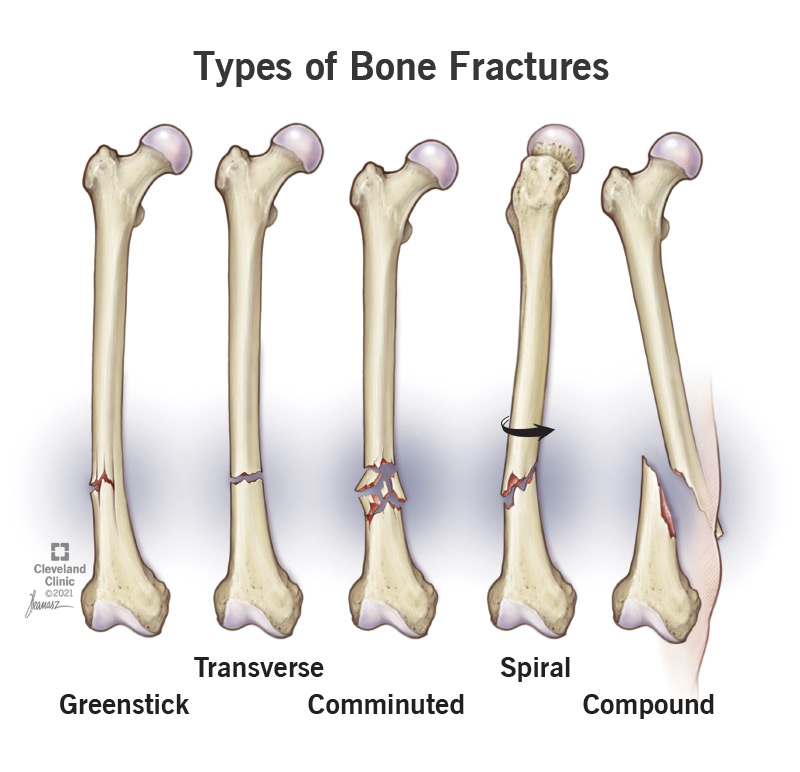
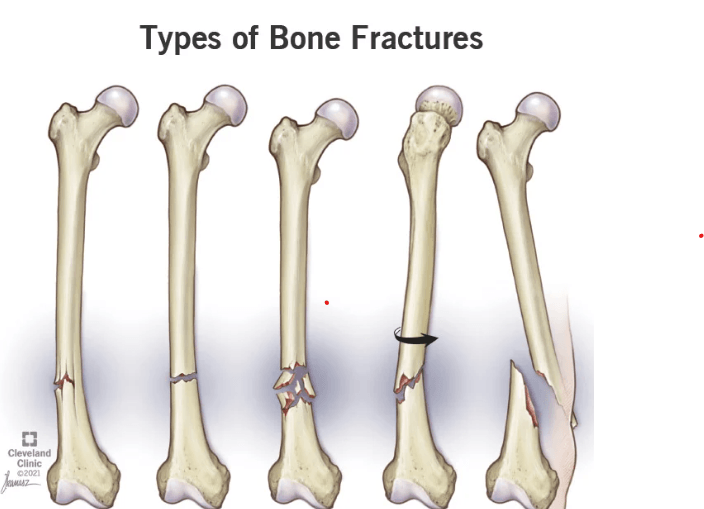
Name the types of fractures
If my patient comes to the clinic with
Rapid heart rate
weight loss
enlarged thyroid
heat intolerance
budging eyes
I am concerned for...
Hyperthyroidism
Graves disease
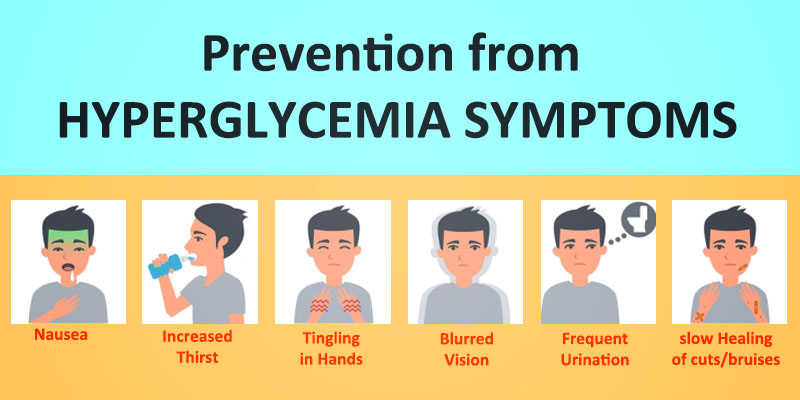
Signs and Symptoms of HYPERglycemia
Left sided heart failure S/S
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/congestive-heart-failure-vs-heart-failure-5212245-Final-3bde2a6f988c4065aff177a075b5256b.jpg)
Describe the roll of histamine
increases capillary permeability
vasodilates
increases heart rate
bronchoconstriction
anything allergy related (itchy eyes/runny nose)
What other conditions does hypertension cause?
Link to diabetes (obesity/hyperlipidemia etc)
Stroke
Aneurysm
Heart attack
Esophageal varices
Kidney damage
What is compartment syndrome
Its always a medical emergency!
A painful and dangerous condition caused by pressure buildup from internal bleeding or swelling of tissues.
poor skin turgor
tachy
low urine output
confusion
low blood pressure
dehydrated!
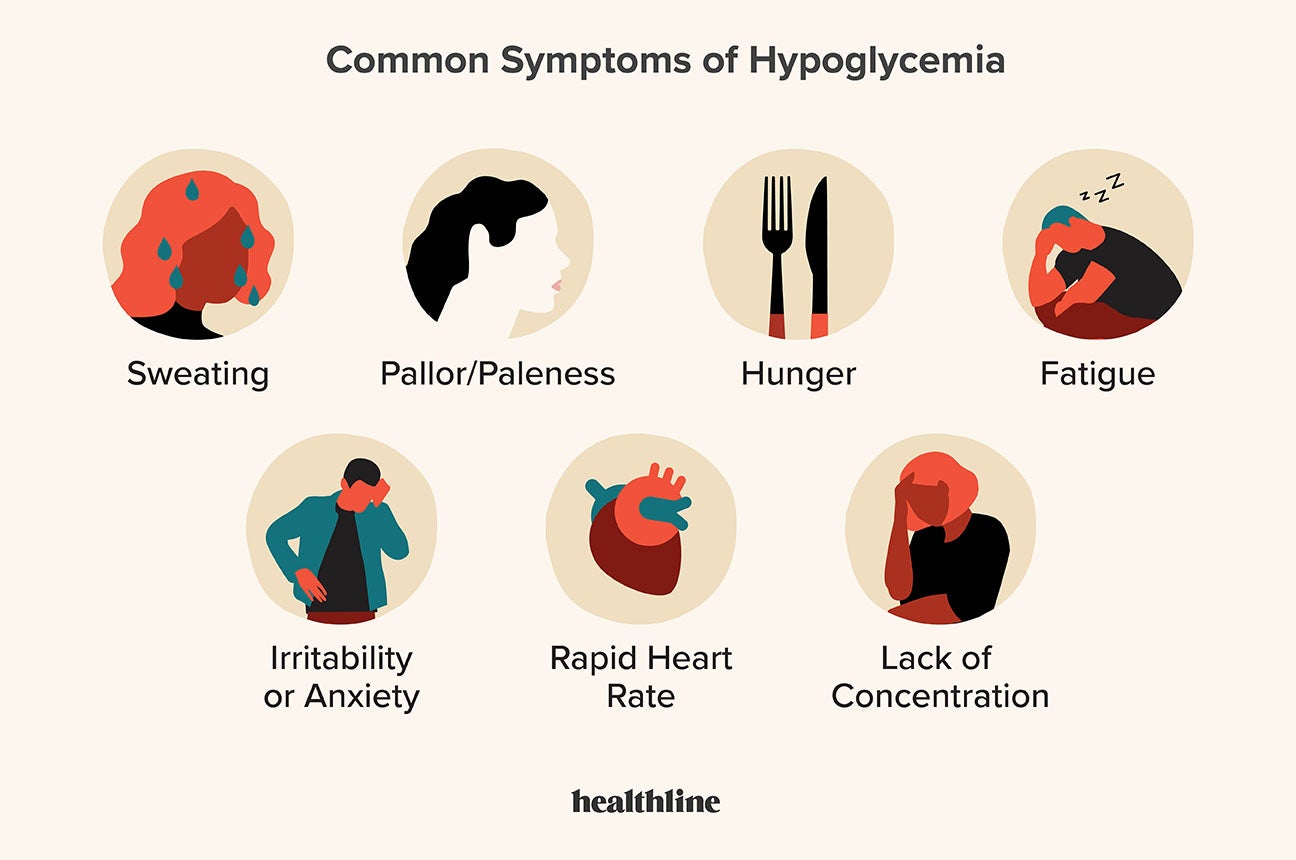
Signs and Symptoms of HYPOglycemia
Failure to produce growth hormone causes
Dwarfism
What is atelectasis
VS
pulmonary edema
VS
pneumonia
COLAPSE of alveoli
fluid inside from fluid shift is pulmonary edema
mucus from infection is pneumonia
explain why there is pain during a myocardial infarction
diminished blood flow causes a lack of oxygen, tissues then begin to die
bonus points... what is the lab value associated with this?
Explain the difference in
Osteoporosis
Osteoarthritis
Osteomyelitis
Osteoporosis - Damage to bones
Osteoarthritis Damage to joints
Osteomyelitis Bone infection
facial droop
slurred speech
confusion
is it ischemic or hemorrhagic?
risk factors
What are Kussmaul respirations
extreme labored breathing in effort to rid body of Carbon Dioxide (acid)
associated with fruity acetone breath
how do you know if your patient has Steatorrhea or constipation
Steatorrhea - fatty, foul smelling, white stools
constipation- more than 3 days
how do you get it?
types of anemia
Iron deficiency
Pernicious anemia (autoimmune b12 deficiency)
Sickle cell (genetic - abnormal shapes)
Aplastic (bone marrow impaired)
biggest complication of hyperparathyroidism?
kidney stones!!!!
High retention of calcium due to the over secretion of PTH
excess calcium is excreted in the kidneys - causing stones
Explain Rheumatoid Arthritis
Autoimmune disorder
Causes exacerbations and remissions of synovitis, cartilage destruction and erosion, ending with fibrosis and calcification and ankylosis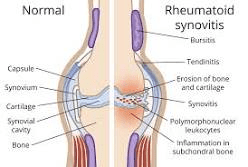
Your patient presents with
air trapping
barrel chest
clubbing of the fingers
shortness of breath
Productive cough
You are concerned for
COPD
Explain Diabetic Ketoacidosis
sugar is too high/uncontrolled
no insulin to help absorb glucose
body uses fat for energy
fat breakdown/biproduct is ketones
Ketones build in blood - altering PH to Acidosis
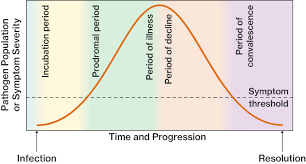
Phases of infection
Normal lab values for
blood pH
Sodium (Na)
Potassium (K)
Chloride (Cl)
Calcium (Ca)
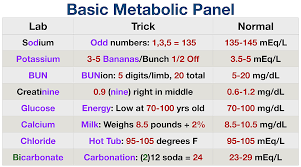
blood ph - 7.35-7.45
signs and symptoms of Cushing's disease
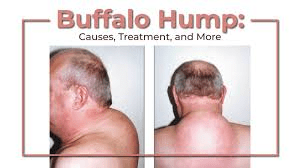
Buffalo hump, moon face, thin limbs, bruising, hyperglycemia, facial hair
too much cortisol
TOO cushy with cushings.