When group interests conflict with an individual interest, a(n)________ occurs?
Collective action problem
How do we measure political ideology?
The conservative-moderate-liberal spectrum.
What is gerrymandering?
Attempting to use the process of re-drawing district boundaries to benefit a political party, protect incumbents, or change the proportion of minority voters in a district.
What are Government actions that affect countries, corporations, groups, or individuals outside America’s borders?
Foreign policy
A form of government that divides sovereign power across at least two political units is called:
Federalism
What is the prisoner's dilemma?
is a classic game theory scenario where two individuals, acting in their own self-interest, may choose not to cooperate even if it would lead to a better outcome for both of them. (Squeal or snitch)
What is the difference between solidary benefits and purposive benefits?
Solidary: Satisfaction is derived from the experience of working with like-minded people, even if the group’s efforts do not achieve the desired impact.
Purposive: Satisfaction derived from the experience of working toward a desired policy goal, even if the goal is not achieved.
What is the difference between constitutional authority and statutory authority?
Constitutional is powers derived from the provisions of the Constitution that outline the president’s role in government. Statutory is Powers derived from laws enacted by Congress that add to the powers given to the president in the Constitution.
What is isolationism?
The idea that a country should refrain from involvement in international affairs.
What is a Presidential caucus?
A local meeting in which party members select a party’s nominee for the general election.
The three principles that make up the primary framework of the constitution are:
federalism,separation of powers, and individual rights
What are the three tests for evaluating discrimination? What types of discrimination do these cases involve?
Strict Scrutiny Test: "suspect classification" (race, ethnicity, religion, or national origin)
Intermediate Scrutiny Test: Sex or gender equality
Rational Basis Test: Age, economic status, and others
What is oversight? And its two types?
Congressional efforts to make sure that laws are implemented correctly by the bureaucracy after they have been passed. Police patrol and fire alarm.
What is internationalism?
The idea that a country should be involved in the affairs of other nations, out of both self-interest and moral obligation.
What is affirmative action?
Steps taken to increase the representation of women and minorities in areas of employment, education, and culture from which they have been historically excluded. When those steps involve preferential selection—selection on the basis of race, gender, or ethnicity—affirmative action generates intense controversy.
__________, or the use of words to express your feelings or views about the government, is the most protected form of expression.
Political speech
What is Duverger's Law?
When a democracy uses a winner-take-all or first-past-the-post system, a two-party system is also likely to develop. In other words, when an election results in the victory of just one candidate, whether or not that candidate has earned the majority of the vote, two political parties are likely to dominate the political landscape.
What is principal-agent theory?
A theoretical framework that focuses on the relationship where one party, known as the "Principal," delegates tasks to another party, called the "Agent," for execution, often leading to challenges due to potential misalignments in decision-making between the two parties.
What is a signing statement?
The President can express their views on a bill and influence the court specially used in foreign policy and the Torture Ban in those case.
What is cloture?
A procedure through which the Senate can limit the amount of time spent debating a bill (cutting off a filibuster) if a supermajority of 60 senators agree.
The Constitution is a short document. Many of the descriptions of government institutions and rules described in the Constitution are short and/or vague. How do we know which specific actions are allowed by the Constitution and which specific actions are prohibited by the Constitution? In class lectures, we discussed three specific ways by which we better understand what the Constitution truly means.
history/prior actions/precedent
court cases/rulings/legal precedents
laws passed by Congress/ legislation/acts of Congress
What is the median voter theorem?
In a multi-party system, the party that is closest to the median voter’s preferences will win the election. That means if voters and parties are distributed on a one-dimensional spectrum according to their preferences (i.e., preferred parties placed closer to the voters), the party that is closest to the median voter will be able to capture the majority of the votes and win the election.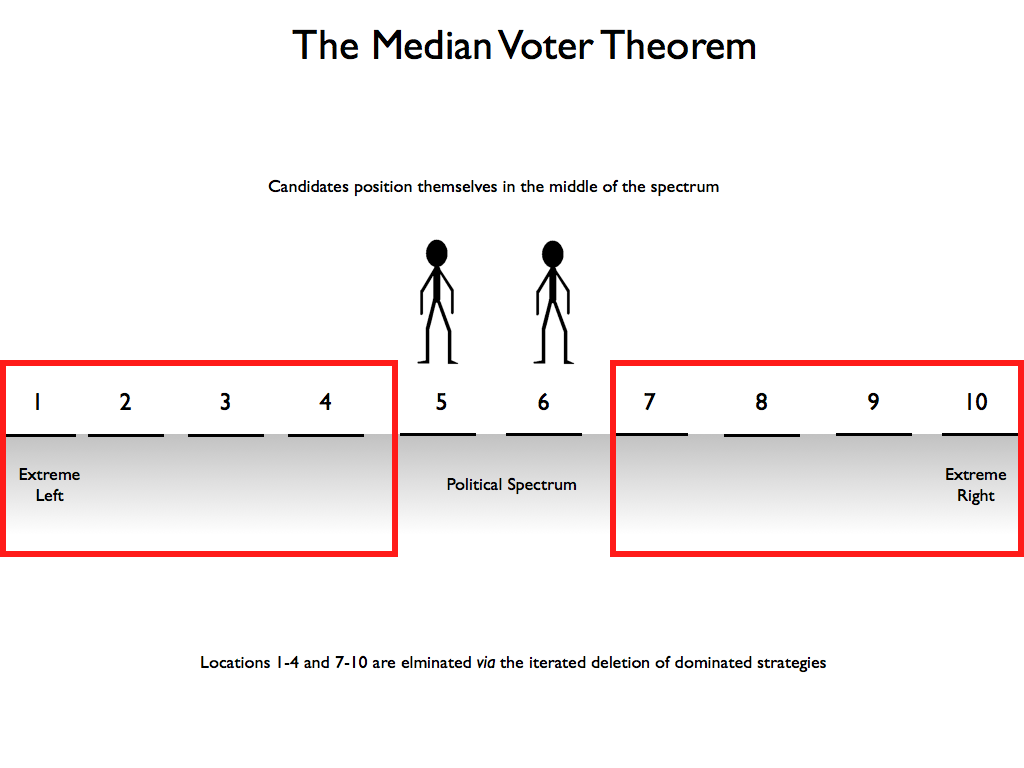
What is the nuclear option?
A parliamentary procedure that allows the Senate to override a standing rule by a simple majority, avoiding the two-thirds supermajority normally required to invoke cloture on a measure amending the Standing Rules.
What are the powers of Congress in foreign policy?
Can declare war
Senate must approve Defense nominees
Treaties take effect only if approved by the Senate
Can overturn orders and findings with legislation
Makes policy using “power of the purse” (annual budget)
What is the difference between civil liberties and civil rights
civil liberties- involve limits on government action
Civil rights- involve protection from discrimination by either government or individuals
