Proteomics is different genomics in the fact that proteomics can reveal
a. Number of genes characteristics of a species
b. The patterns of alternative splicing
c. The set of proteins present within a cell or tissue type
c. The set of proteins present within a cell or tissue type
Genomics: the study of whole sets of genes and their interactions
Proteomics: the study of large sets of proteins and their properties
Proteome is the entire set of proteins expressed by a cell or group of cells
Which of the following can be duplicated in a genome?
a. DNA sequences
b. Entire Chromosomes
c. DNA sequences, chromosomes, or entire sets of chromosomes
c. DNA sequences, chromosomes, or entire sets of chromosomes
A species of crocodiles migrated to Neverland, where there many ecological niches unoccupied. The species evolved into many different species to fill the diverse array of niches. This is an example of
a. Morphological Isolation
b. Adaptive Radiation
c. Lamarck's Hypothesis of Evolution
d. Temporal Isolation
B. Adaptive Radiation
Adaptive radiation is the diversification of a group of organisms into forms filling different ecological niches.
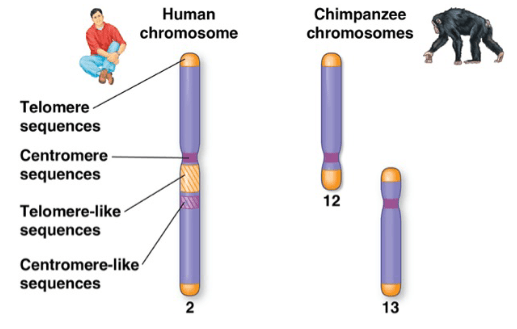
Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, and chimps have 24 pairs of chromosomes. What is the most likely explanation for these differences in human and chimp genomes?
a. During human evolution, two ancestor chromosomes fused end to end
b. During chimp evolution, chromosome duplication occurred
c. During the evolutionary history of chimps and humans, interspecies breeding frequently occured.
a. During human evolution, two ancestor chromosomes fused end to end
All of the following are conditions for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium EXCEPT:
a. No mutations
b. Assortative mating
c. No natural selection
d. Large population size
b. Assortative mating
Assortative mating is when individuals with similar phenotypes or genotypes mate with one another more frequently than would be expected under a random mating pattern. 
Which of the following statements is true regarding Homeotic genes?
a. Homeotic genes are not highly conserved and typically undergone rapid divergence.
b. Homeotic genes are important in controlling the pattern formation of body parts
c. Homeotic genes are most active after an organism has reached adulthood
d. Homeotic genes explain why chimps have one more chromosomes than humans
b. Homeotic genes are important in controlling the pattern formation of body parts
Homeotic genes are highly conserved amongst organisms
Homeotic genes in animals are called Hox genes.
Homeotic genes are associated with development.
Gene density is correctly represented by
a. E. coil have 4,400 genes in their genome
b. S. cerevisiae have a haploid genome size of 12 Mb
c. The human genome is 3 billion base pairs in length
d. Z. mays have 14 genes per million base pairs
d. Z. mays have 14 genes per million base pairs
Gene density is the number of genes in a given length of DNA.
A. Number of genes
B. Genome size
C. Genome size
An organism's fitness is measured by
a. Genetic variation of heritable traits
b. Ability to resist drastic changes in the environment
c. how long it lives a healthy life
d. contribution to the gene pool of the next generation
d. contribution to the gene pool of the next generation
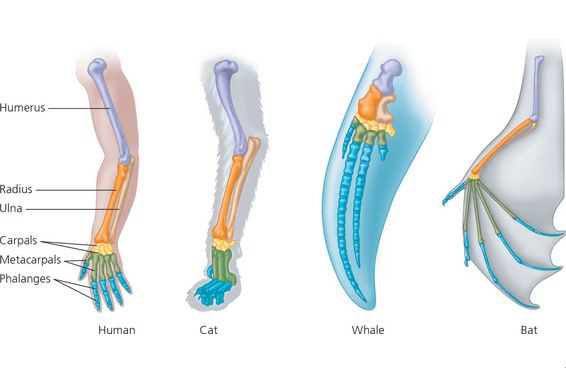
Even though they have become adapted for different functions, the forelimbs of humans, cats, whales, and bats are all constructed from the same basic skeletal elements. This is an example of
a. Convergent evolution
b. Vestigial structures
c. Homologous structures
d. Co-evolution
C. Homologous structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of sharing a common ancestor.
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is useful in that it allows scientists to
a. predict the number of individuals that are heterozygous at a particular locus
b. measure the amount of mutations occuring in a population
c. prove that genetic drift has occured to a population
d. provide evidence that an evolutionary force is acting on a population.
d. provide evidence that an evolutionary force is acting on a population.
The Hardy-Weinberg equation describes a population that is NOT evolving. Thus, if the calculated frequencies differ from the actual frequencies of alleles/genotypes than the population is evolving.
Which of the following characteristics are only associated with retrotransposons?
a. Existing in multiple copies in the genome
b. Capable of movement within the genome
c. Mutations arising when it moves
d. Moves via a RNA intermediate
D. Moves via a RNA intermediate
Transposable elements
- Stretches of DNA that can move from one location to another in the genome.
- Barbara McClintock provided the first evidence with her corn experiment, transposable elements disrupted predicted kernel color pattern.
- Includes transposons and retrotransposons.
Transposons
- Move via DNA intermediate.
- “Cut and paste” or “Copy and paste” mechanisms.
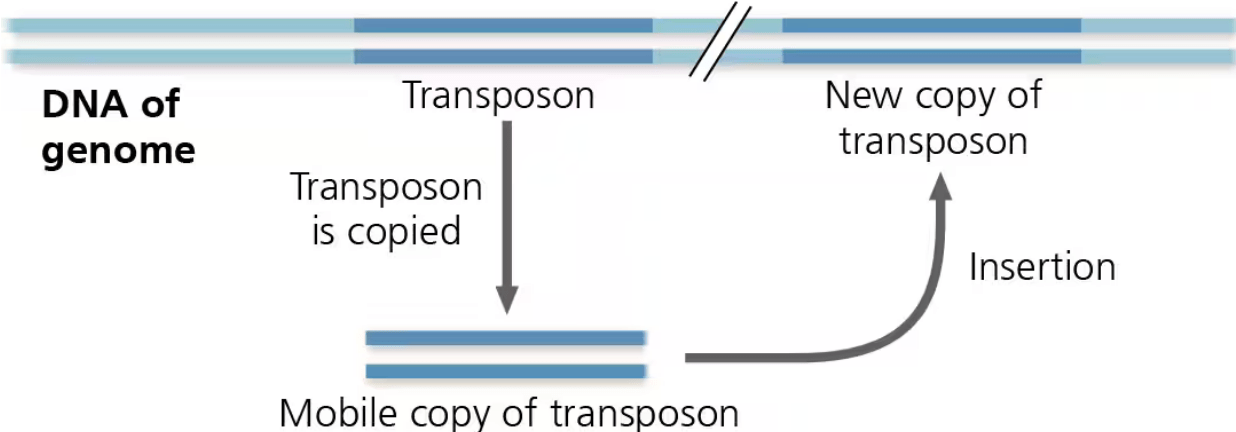
Retrotransposons
- Move via RNA intermediate.
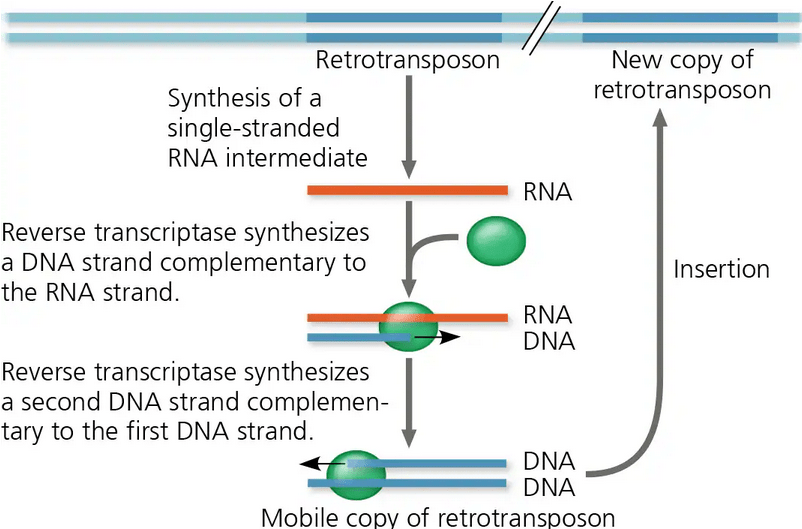
Which of the following statements correctly describes one characteristic of a multigene family?
a. A multigene family includes genes whose sequences are very similar and that probably arose by duplication.
b. A multigene family includes a highly conserved gene found in a number of different species.
c. A multigene family includes multiple genes whose products must be coordinately expressed.
a. A multigene family includes genes whose sequences are very similar and that probably arose by duplication.
Multigene families are collections of genes with identical or very similar genes.
Which of the following is true regarding genetic variation?
a. Natural selection creates genetic variation
b. In response to changes in the environment, genetic variation increases
c. Sexual reproduction tends to decrease genetic variation due to organisms producing haploid cells.
d. For a population to evolve by natural selection, genetic variation must already be present.
d. For a population to evolve by natural selection, genetic variation must already be present.
All of the following occur in populations evolving EXCEPT:
a. The majority of traits acquire during an individual's lifetime is passed on.
b. The population has variation of heritable genetic information.
c. The environment cannot support all of the offspring produced.
d. Specific heritable traits increase the fitness of offspring
a. The majority of traits acquire during an individual's lifetime is passed on.
Answer choice A is referring to Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck's Hypothesis:
- Species evolve through use and disuse of body parts and the inheritance of acquired characteristics.
- Example: Ancestor giraffes used their necks often to reach leaves high up. The necks of these ancestor giraffes grew during their lifetime as was passed on to offspring.
Darwin's two observations:
- Members of a population often vary in their inherited traits
- All species can produce more offspring than the environment can support, and many of these offspring fail to survive and reproduce
Darwin's two inferences:
- Inherited traits give them a higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals
- This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to the accumulation of favorable traits in the population over generations
For the Hardy-Weinberg equation, why is the "2" needed for 2pq?
a. The organisms are diploid (2n)
b. 2pq is referring to the genotypic frequency and not allelic frequency
c. It is assumed that the population is not mutating
d. Heterozygotes can come about in two ways
d. Heterozygotes can come about in two ways

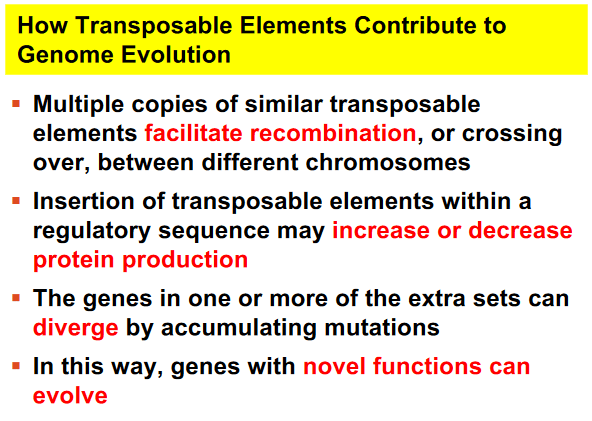
All of the following are ways transposable elements contribute to genome evolution EXCEPT:
a. Facilitate recombination, or crossing over, between different chromosomes
b. Insertion in regulatory sequences can increase or decrease gene expression.
c. One of the genes present in multiple copies can diverge by accumulating mutations
d. False pairing during metaphase I can lead to nondisjunction events.
d. False pairing during metaphase I can lead to nondisjunction events.
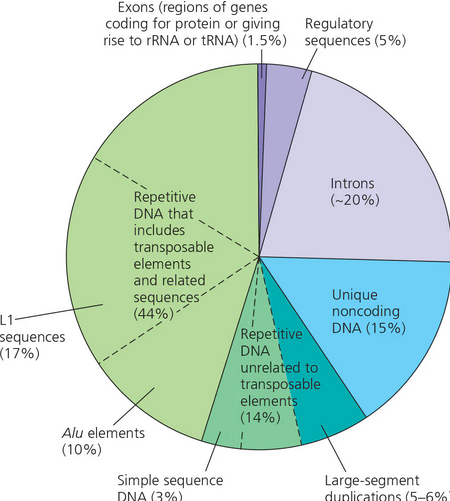
Most of the human genome is made up of
a. Introns
b. Regulatory sequences
c. Exons (unqiue protein-encoding genes)
d. Unqiue noncoding DNA
e. Repetitive DNA sections related to transposable elements
f. Repetitive DNA unrelated to transposable elements
e. Repetitive DNA sections related to transposable elements
From Darwin's book "The Origin of Species", he explained what 3 broad observations?

Under the influence of natural selection, what is the correct order of events?
1: Well-adapted individuals leave more offspring than do poorly adapted individuals.
2: A change occurs in the environment.
3: Genetic frequencies within the population change.
4: Poorly adapted individuals have decreased survivorship.
2 → 4 → 1 → 3
In a Hardy-Weinberg population with two alleles, A and a, that are in equilibrium, the frequency of the allele a is 0.3. What is the frequency of individuals that are heterozygous at this locus?
a. .21
b. .09
c. .49
d. .42
q= .3
p+q=1
p=1-q
p= .7
Heterozygous= 2pq
= .42
During meiosis, an error occurs resulting in an extra copy of a chromosome. How can an extra copy facilitate evolution?
Over time, mutations can accumulate in the extra sets of genes and allow evolution of novel functions.
Evolution of genes with novel functions
- Gene duplication and subsequent divergence can lead to proteins being produced with completely different functions.
- As long as one copy of genes retain their original function, the duplicated genes can take on new functions.
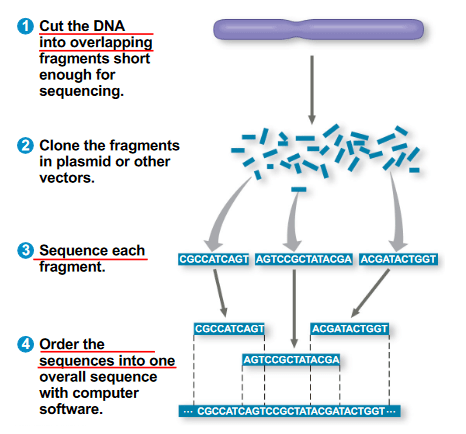
What are the 4 steps of the whole-genome shotgun approach to sequencing
Explain Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection
Darwin's theory emphasized that populations vary and allele frequencies change over time.
If some heritable traits are advantageous, individuals with these traits will produce more offspring that survive to reproduce, and this will increase the frequency of these traits in
the next generation
After exposing a population of bacteria to penicillin (an antibiotic), within six months the bacteria are resistant to penicillin. Explain how the bacteria evolved.
Some drug-resistant bacteria were present at the start of treatment, and natural selection increased their frequency.
Reminder about natural selection/ evolution:
- NS does NOT create individuals with favorable traits. Rather, NS favors individuals that were ALREADY present.
Harmful mutations occur in both diploid and haploid organisms. Would we expect to find more harmful mutations in diploid or haploid organisms? Explain Why
There are more harmful mutations in populations of diploids than in populations of haploids, because the mutations are protected from selection in diploid heterozygotes.