What are the three types of cell membrane proteins? Draw them!
Peripheral (outside), integral (inside), transmembrane (across)
What are the 4 types of bone cells? What does each do? Where are they located?
osteogenic cell (stem cell, can become osteoblast or osteoclast, outside & inside)
osteoclast cell (breaks down bone to release calcium, inside)
osteoblast cell (form new bone from calcium, in matrix)
osteocyte (maintains bone tissue, outside)
Neurons communicate to certain muscles at the _____________ .
Neuromuscular junctions
Intercalated discs on cardiac muscles connect via ________ which allows the heart to contract rhythmically.
gap junctions
What is the difference between lysosomes and peroxisomes?
peroxisomes: contain catalase to break down hydrogen peroxide
lysosomes: contain cellular digestive enzymes to remove physical wastes
Categorize these processes under the correct category of active or passive transport.
Endocytosis, diffusion, osmosis, exocytosis, facilitated diffusion, pinocytosis, phagocytosis
Active: endocytosis, exocytosis, pinocytosis, phagocytosis
Passive: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
What structure on the outer surface of the bone turns into a tendon and connects bone to muscles?
periosteum
____ binds to _____ which then exposes the binding site for the myosin head.
calcium, troponin
The structure that allows a fetus to bypass the liver is ________ which becomes ________ after birth.
ductus venosus; ligamentum venosum
Which sweat gland secretes directly into the hair follicle?
apocrine sweat gland
What is the mnemonic for the skin layers (superficial to deep)? What are the layers?
Come, Let's Get Sun Burned! Stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum basale.
Synovial joints are _____ movable. In the joint capsule, the cavity is filled with ___________ which helps with __________.
freely moveable, synovial fluid, lubrication
Describe the sliding filament theory!
It is good to familiarize yourself with the key players in each step, so you could quickly recognize the answers on the exam.
The innermost layer of an artery is called ________ which is __________ epithelium. The thin layer of cells allows quicker diffusion of ______, ______, and hormones.
tunica media, simple squamous; gases, nutrients
Describe tetanus.
Infection by bacteria Clostridium tetani. Produces toxin that causes involuntary muscle contraction. Leads to respiratory failure.
What type of epithelium is found in the trachea? What is the purpose of the cilia?
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium; move mucus
Where do you find intramembranous ossification? Endochondral ossification?
flat skull bones, long bones
What's the difference between antigen and antibody? Draw and explain!
Antigen on all cell surfaces - helps tell self from non-self. Antibodies free-floating proteins or receptors on WBCs that bind to specific antigens. Our body produces antibodies!
What's the difference vasodilation and vasoconstriction? How do these processes happen?
enlarging of blood vessels, reducing blood vessel diameter; work of precapillary sphincters (arteriole --> capillary)
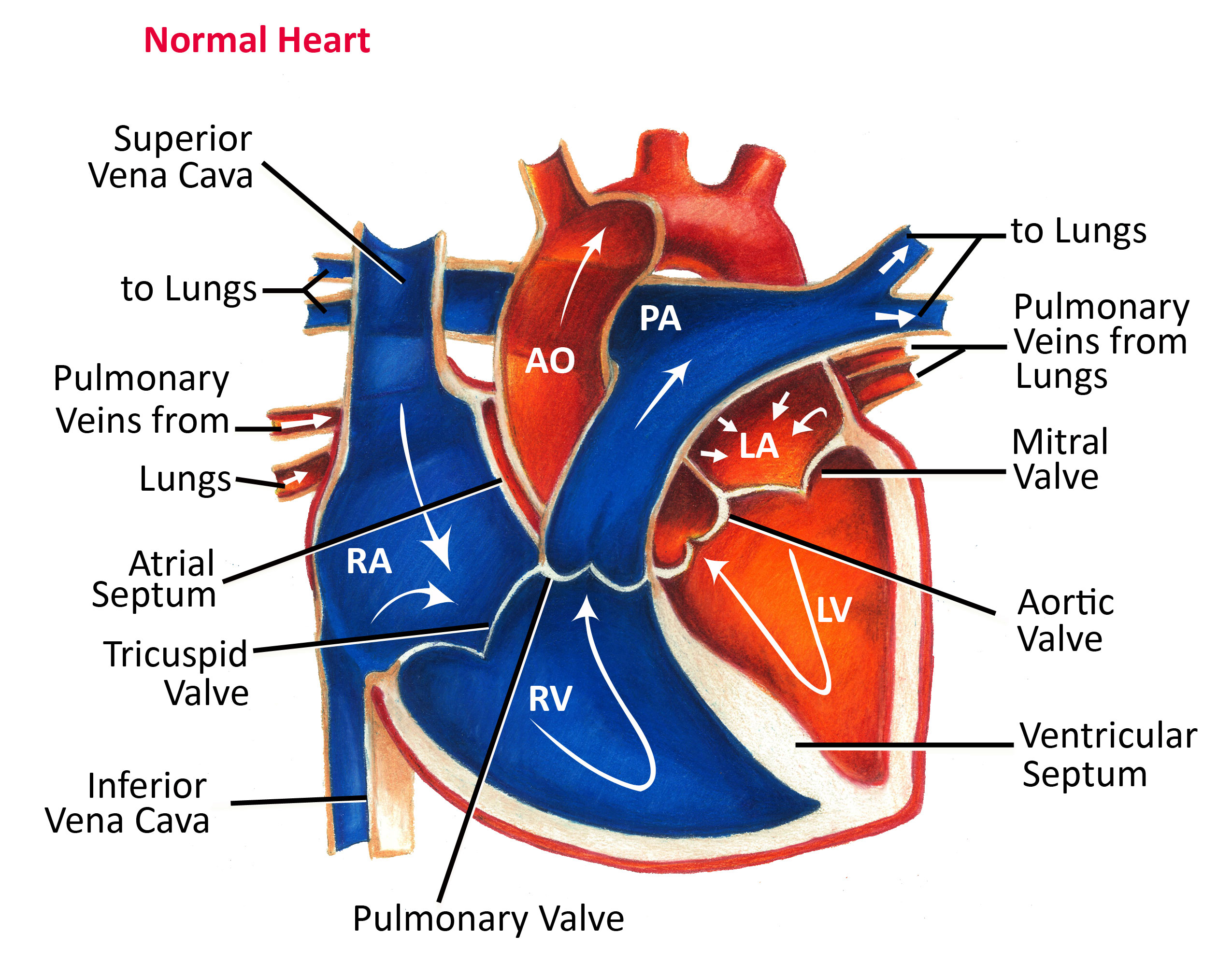
Walk me through the structures of the heart as blood flows through it! Draw & label!
Where do you find apocrine sweat glands? Merocrine sweat glands?
axillae, groin and nipples; everywhere
What type of joint is the shoulder and hip joint? Why is it the weakest joint?
Synovial - ball and socket; lots of mobility, least amount of stability
What blood type is this?

B+
Main structure difference between arteries and veins?
valves!
Draw an EKG and explain what happens at each step.
