Carbon has an atomic number of 6 and an atomic weight of 12, meaning it has this many protons/electrons/neutrons.
What are 6 protons, 6 electrons, and 6 neutrons?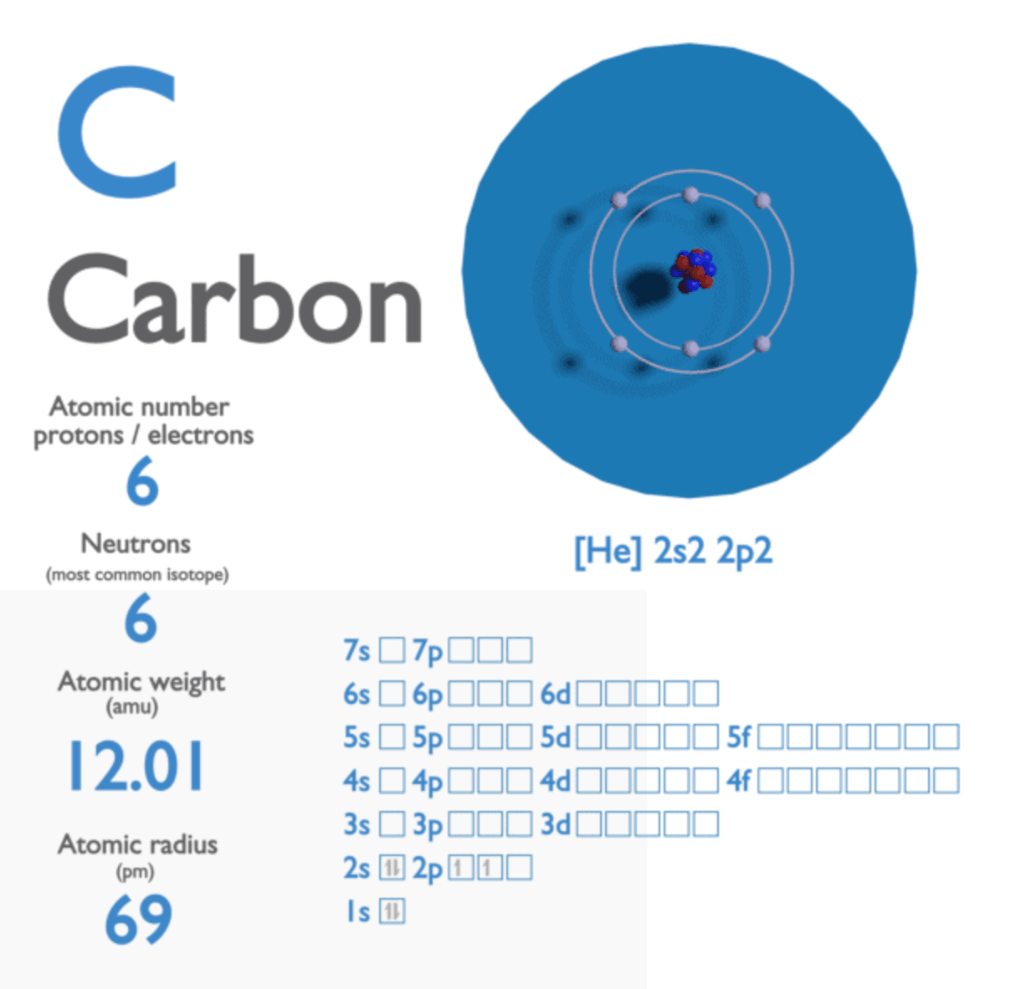
What is glycerol?
The Na/K pump transports these ions in the following order/amounts.
What is 3 Na Out, 2 K In, using 1 ATP?
321 NOKIA!
This is what is occurring to NAD+ in the following reaction.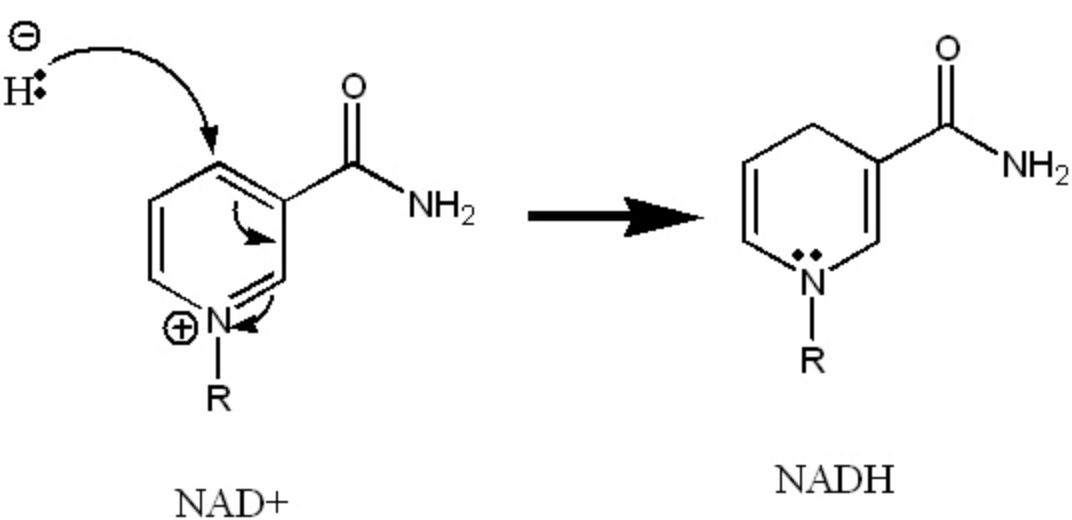
What is reduction?

Positive --> negative = gaining electrons
RIG --> Reduction Is Gaining
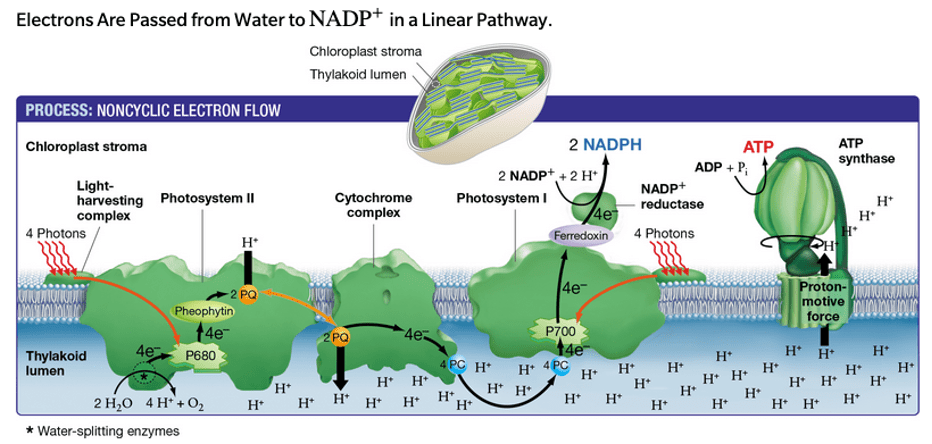
During the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis, H+ ions accumulate in this structure.
What is the thylakoid lumen?
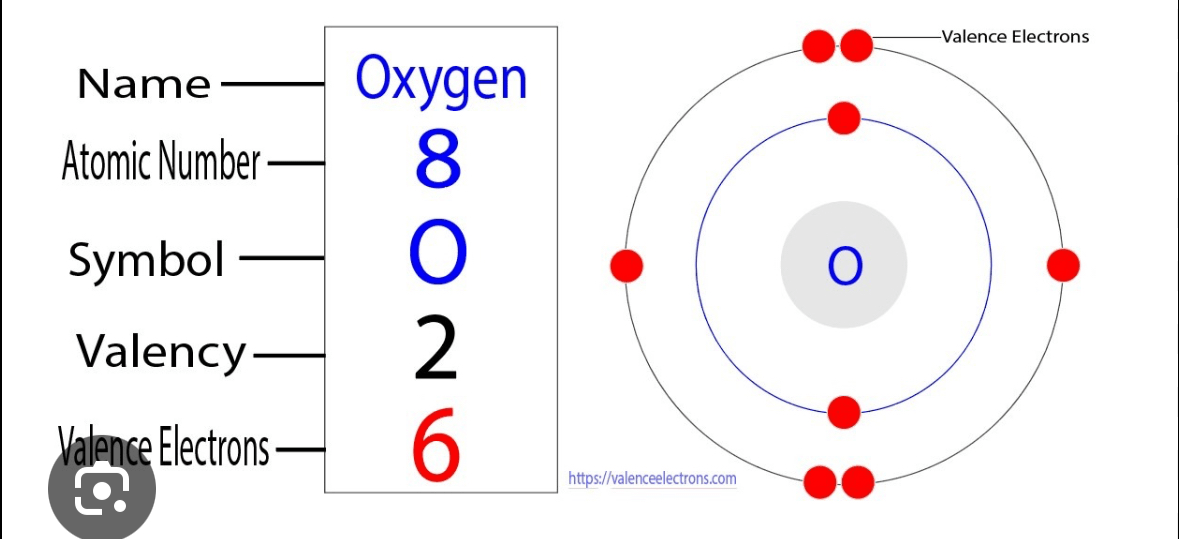
This is the valence of the following oxygen atom.
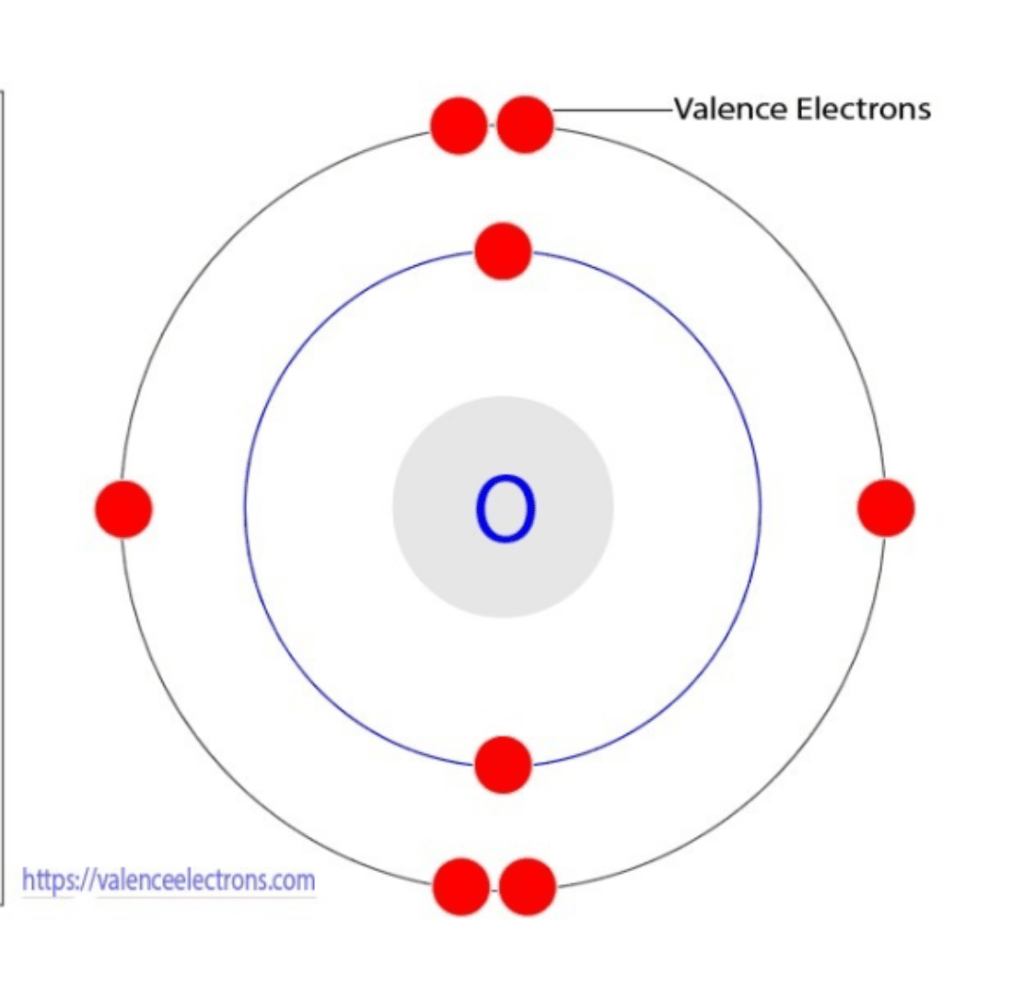
What is 2?
Cholesterol has this effect on the membrane at higher temperatures.
What is decreases membrane permeability?
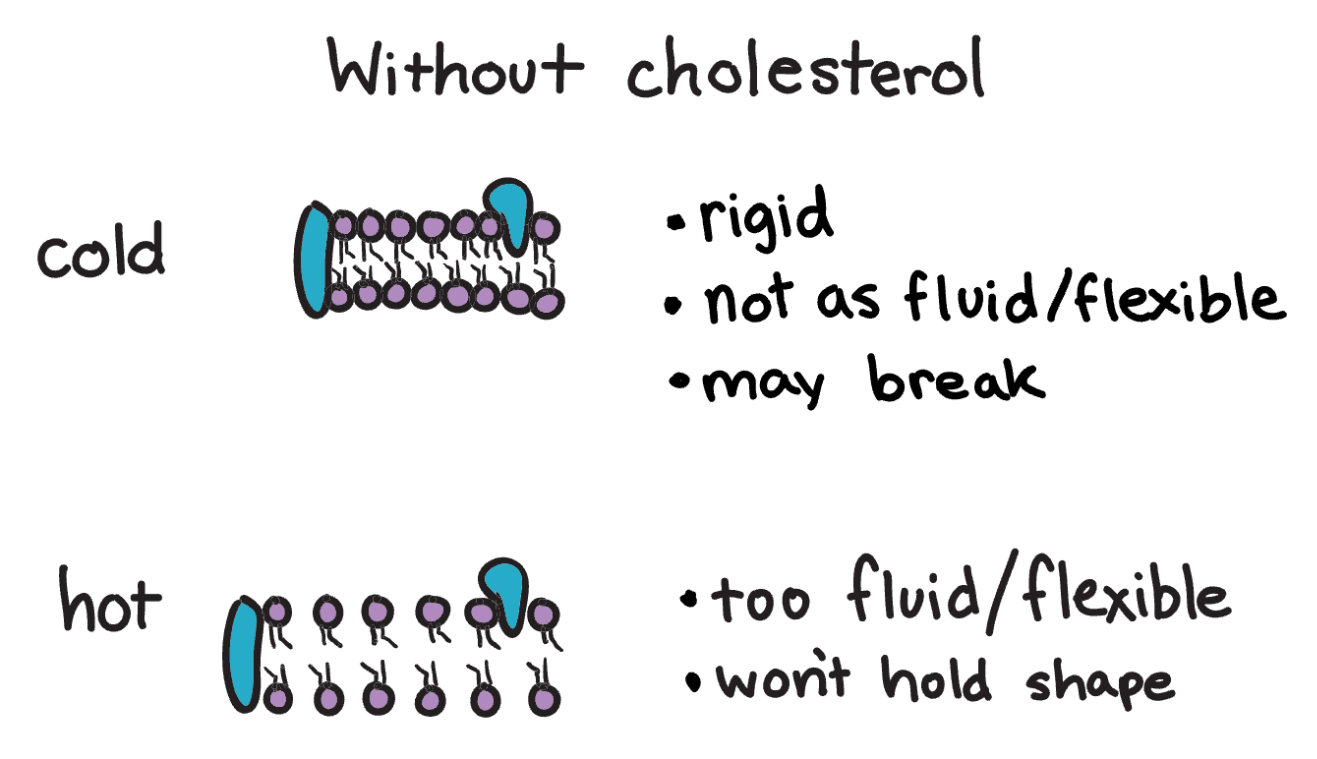
The hydrophobic amino acids of the Na+/K+ pump, a protein, come into contact with this portion of the phospholipid bilayer.
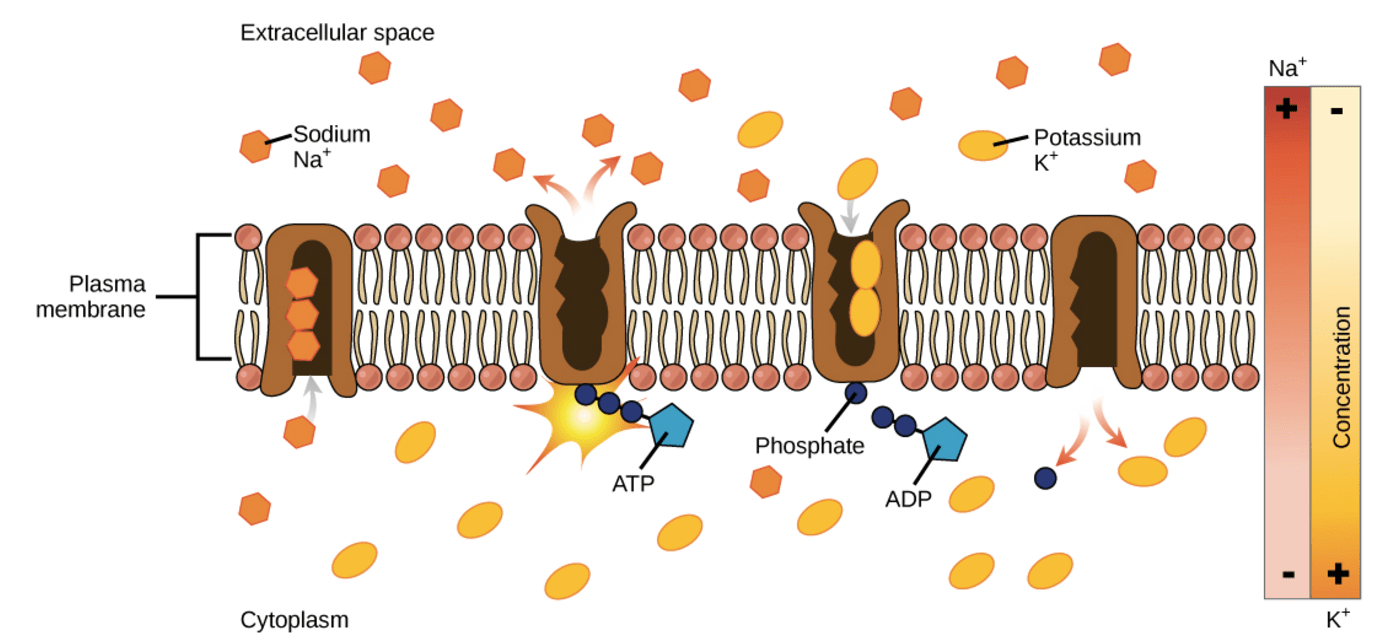
What are hydrocarbon tails?

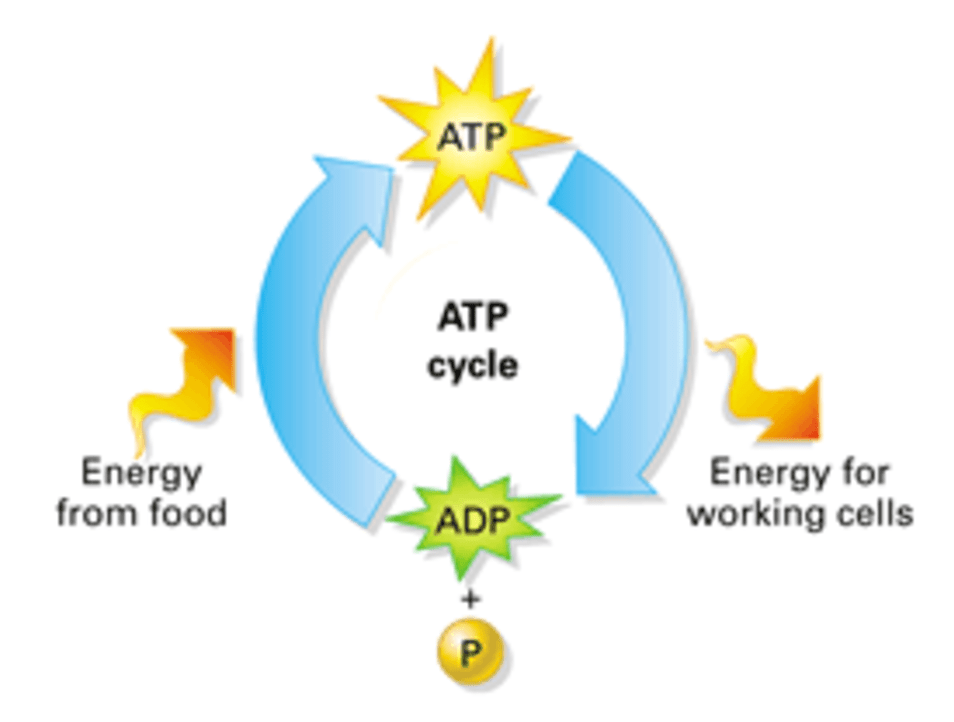
ATP is an example of this kind of energy.
What is potential energy?
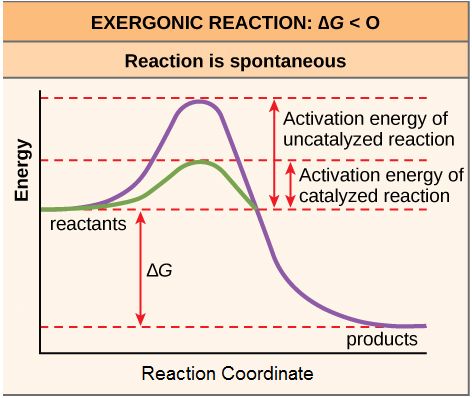
Enzymes have this affect on the activation energy of a reaction.
What is reduces activation energy?
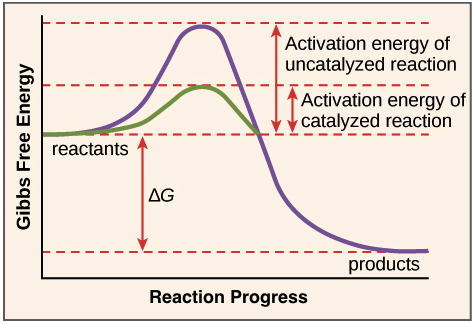
**∆G doesn't change!!**
These occur when water surrounds ions or molecules and causes it to go into solution.
What are hydration shells?
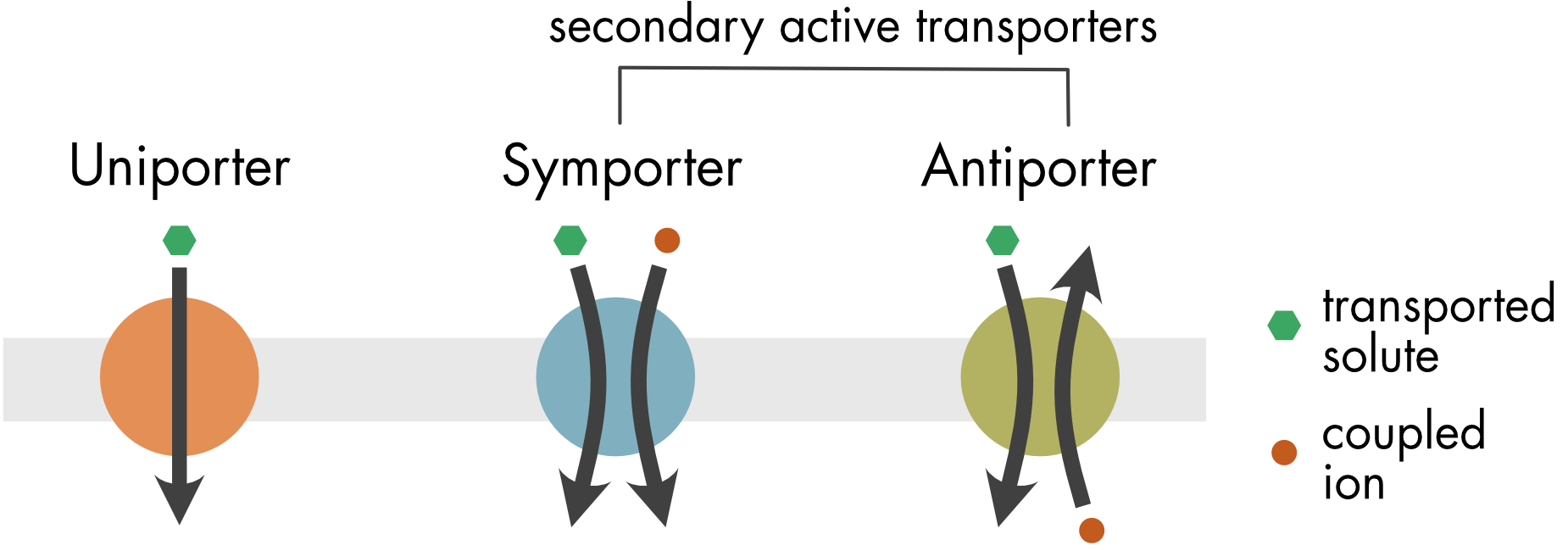
Proteins that move two molecules in opposite directions across the membrane are called this.
What are antiporters?
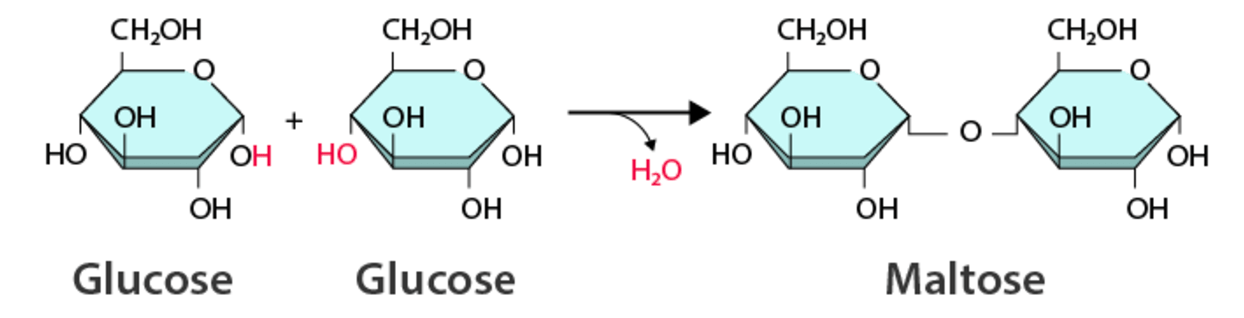
When two macromolecules are joined together by a dehydration reaction, this many atoms are absent from the final product.
What are 2 H's and 1 O?
This is the number of the organelle that is in charge of protein production.
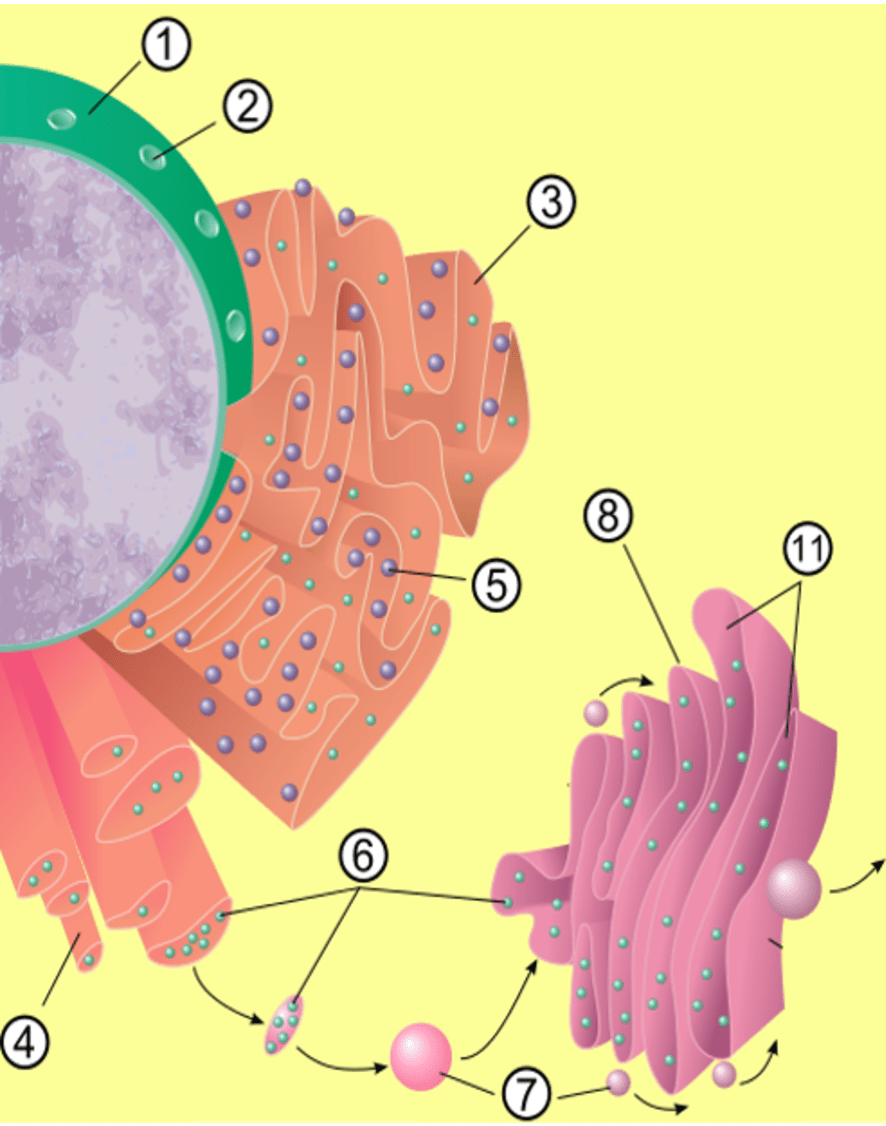
What is 3 (rough endoplasmic reticulum)?
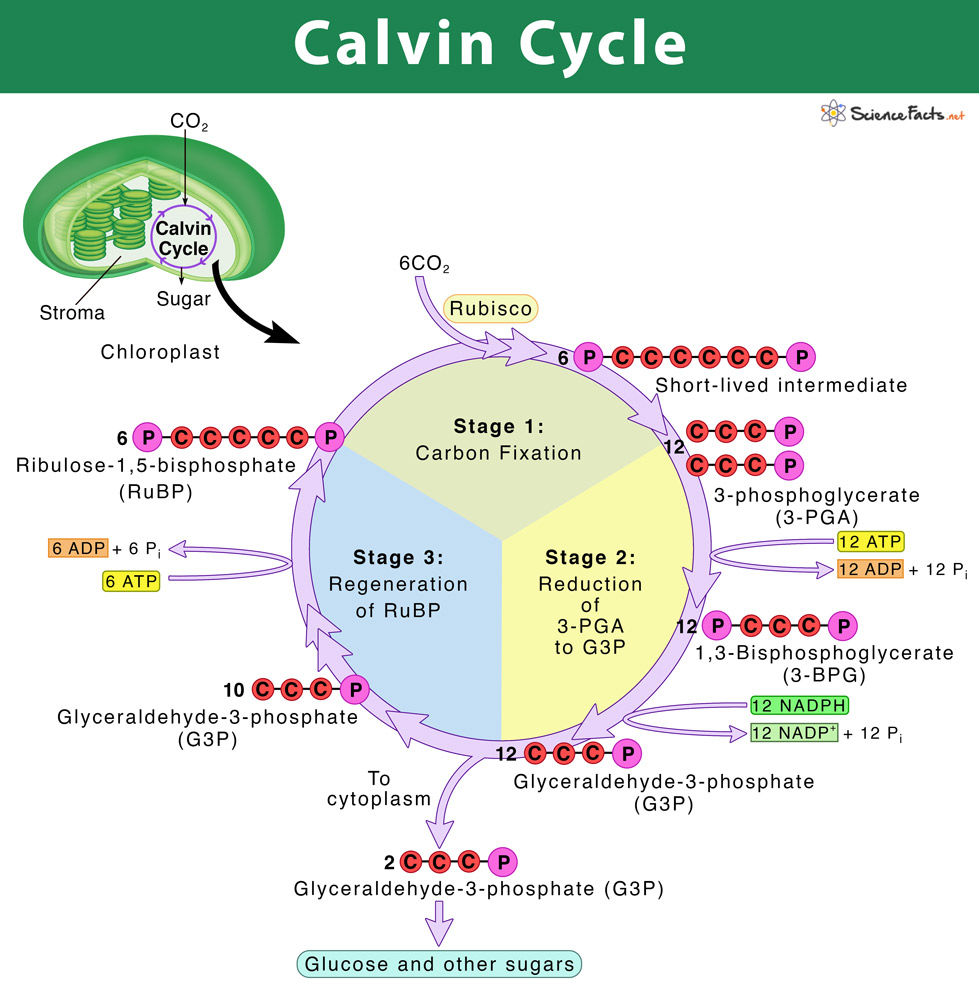
These are the three phases of the Calvin Cycle.
What are fixation, reduction, and regeneration?
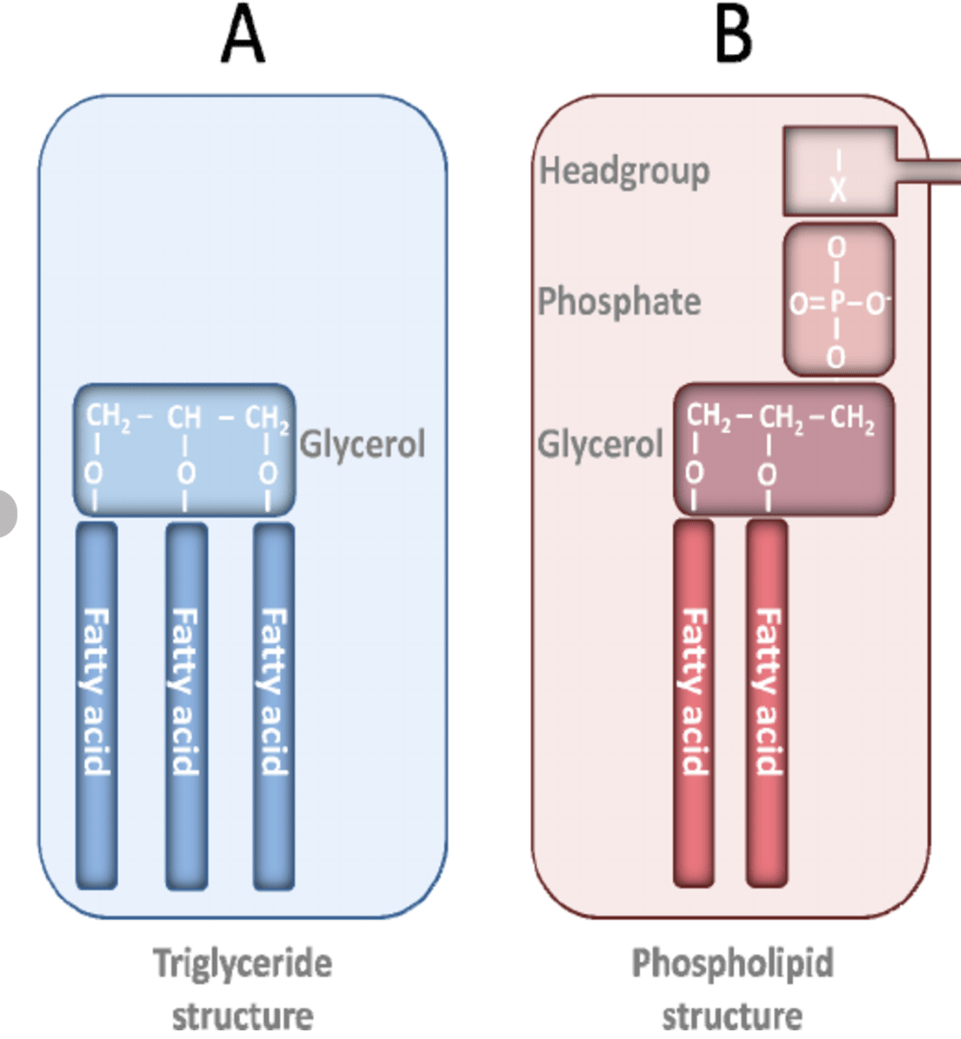
Fatty acids contain this functional group.

What are carboxylic acids (COOH)?

This type of active transport couples the energy of a molecule moving with its gradient to power the movement of another molecule against its gradient.
What is secondary active transport?
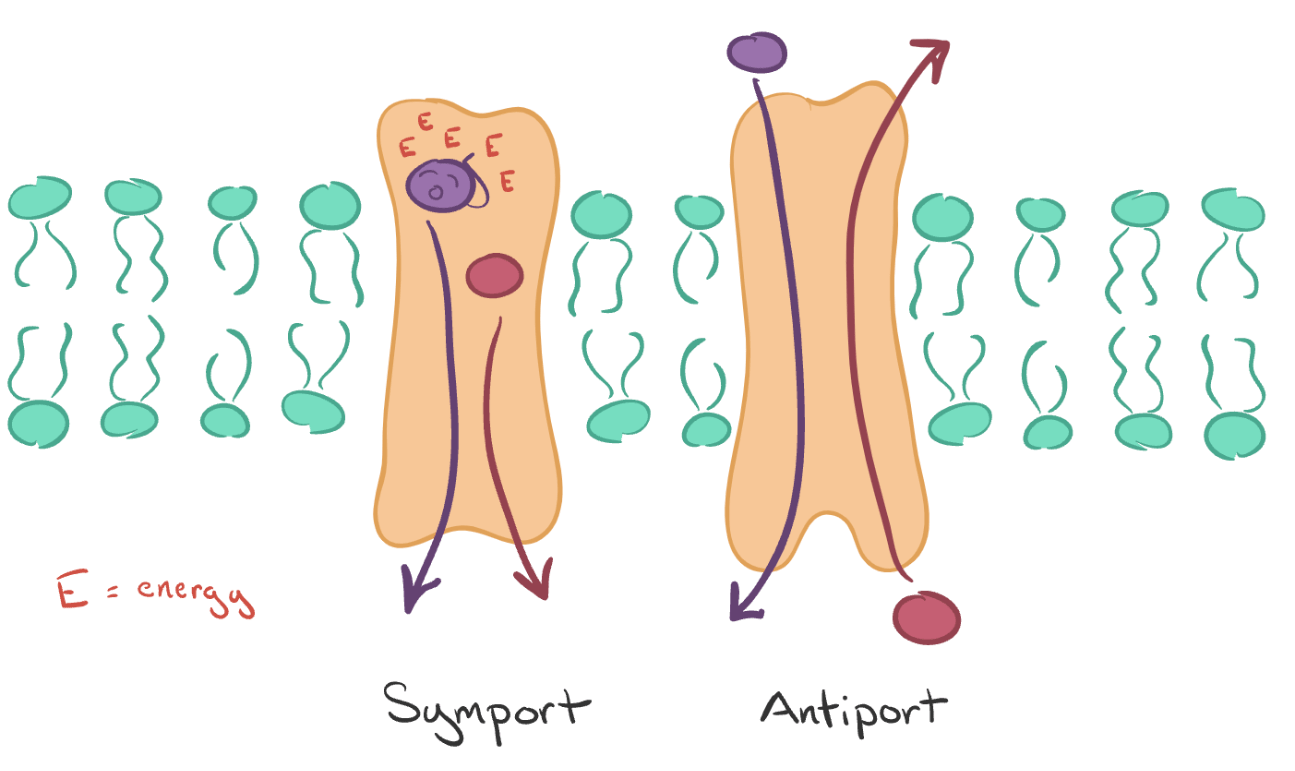
Kind of like it's "hitching a ride"
When a cell is in this type of solution, water will exit the cell and cause it to shrivel.
What is a hypertonic solution?
 Example: pouring salt on a slug causes it to shrivel up :(
Example: pouring salt on a slug causes it to shrivel up :(
This type of regulation occurs when the active site of an enzyme becomes available to the substrate when a regulatory molecule binds to a different site on the enzyme.
What is allosteric activation?

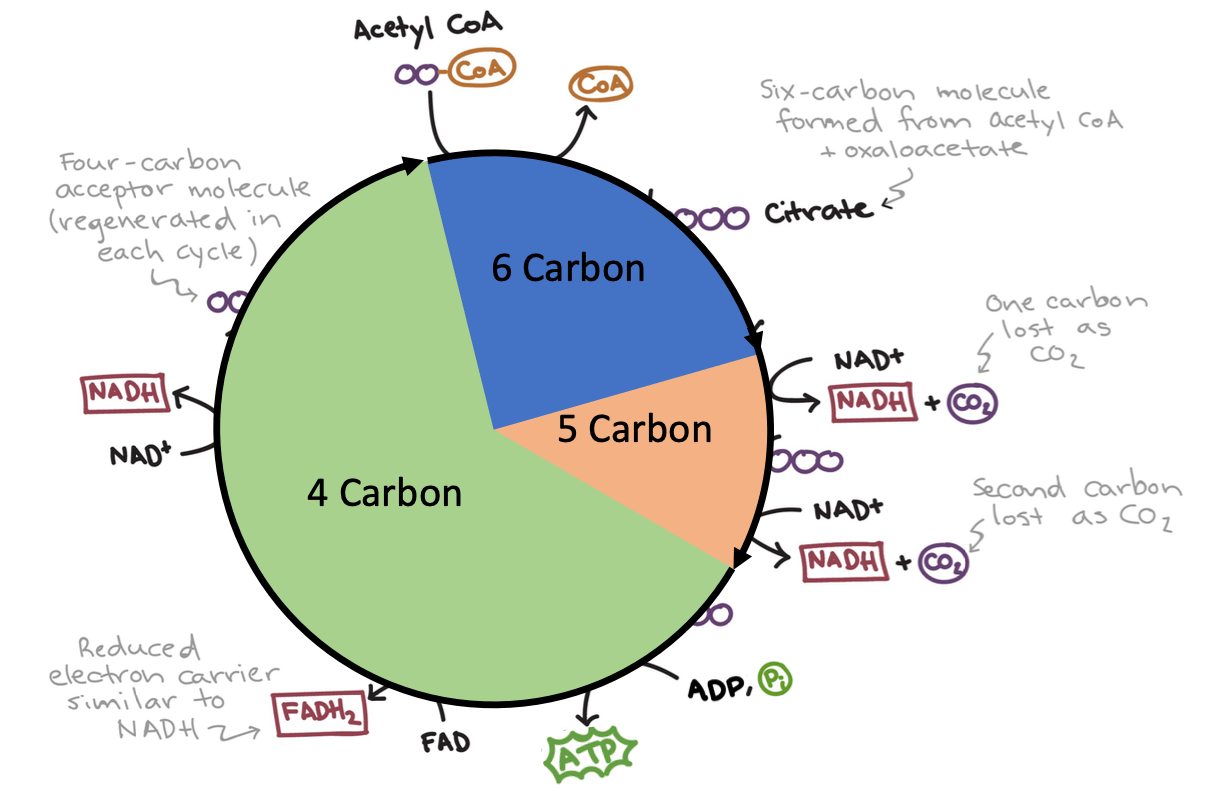
These are the 4 inputs of the CAC (including amounts).
What is 2 Acetyl-CoA, 6 NAD+, 2 FAD, and 2 ADP?
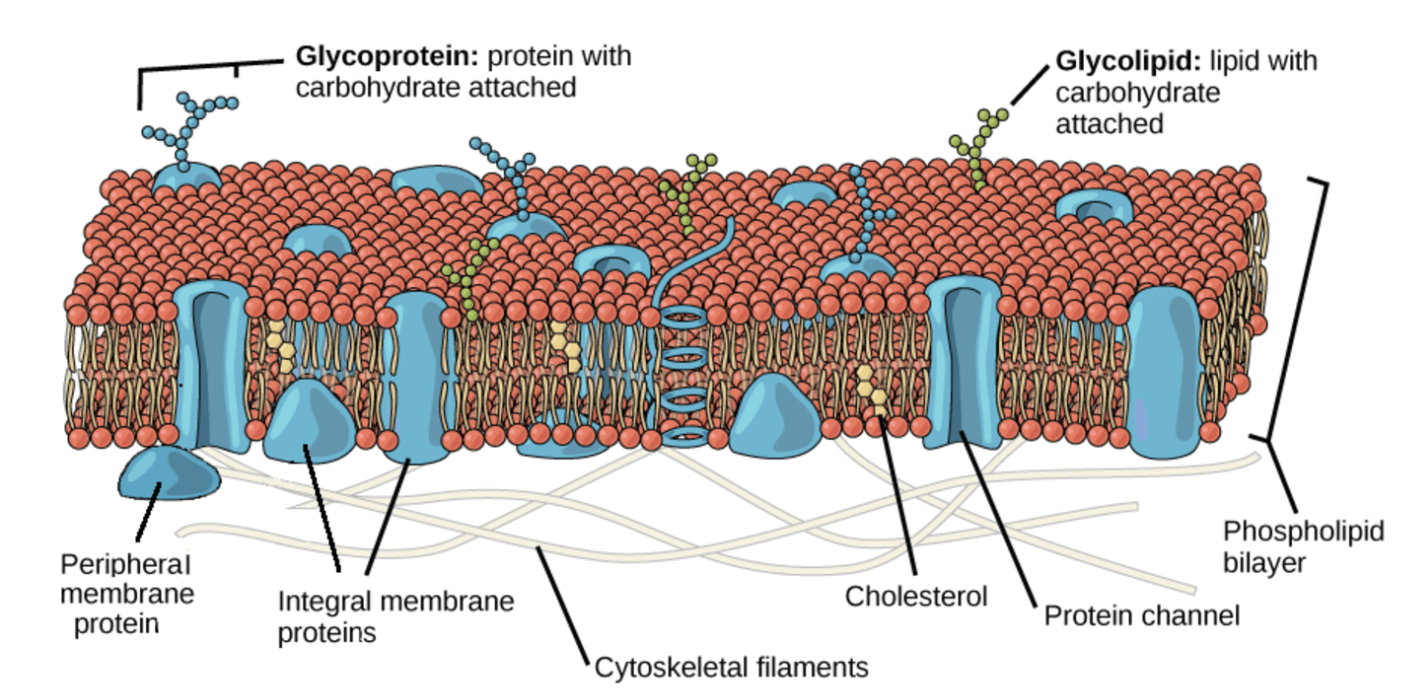
The yellow dots in this plasma membrane represent this.
What is cholesterol?
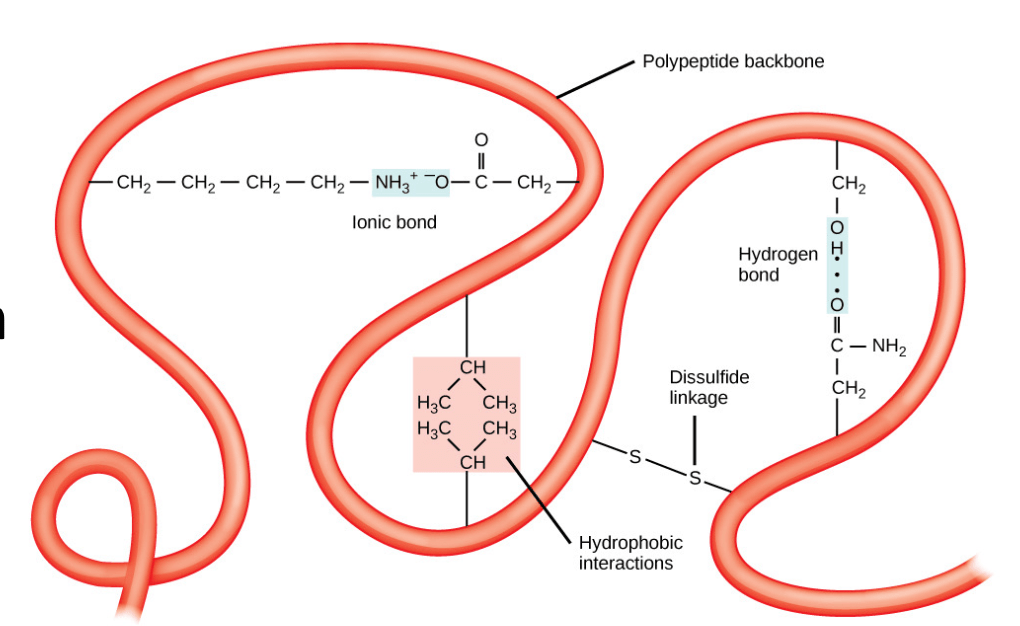
Sulfur can be found in this macromolecule.
What are proteins?
This term refers to the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
What is osmosis?
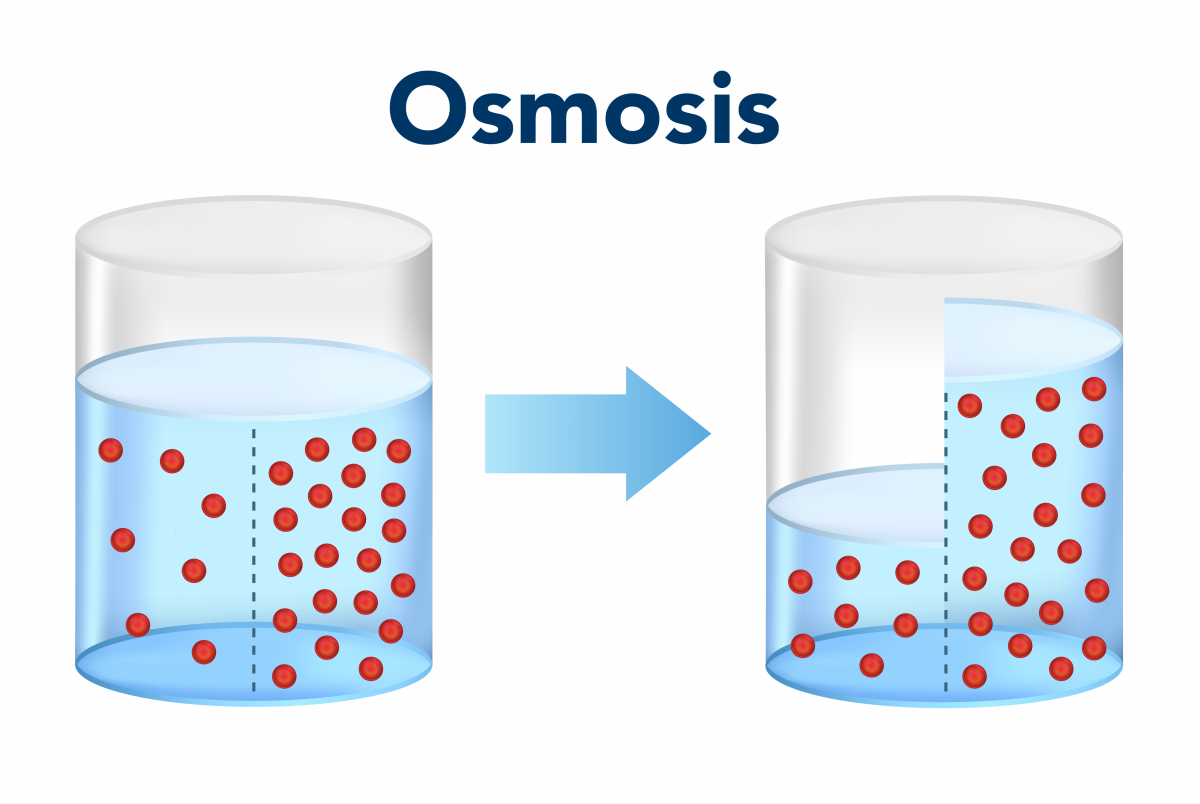 "Water wants to go where the party is"
"Water wants to go where the party is"
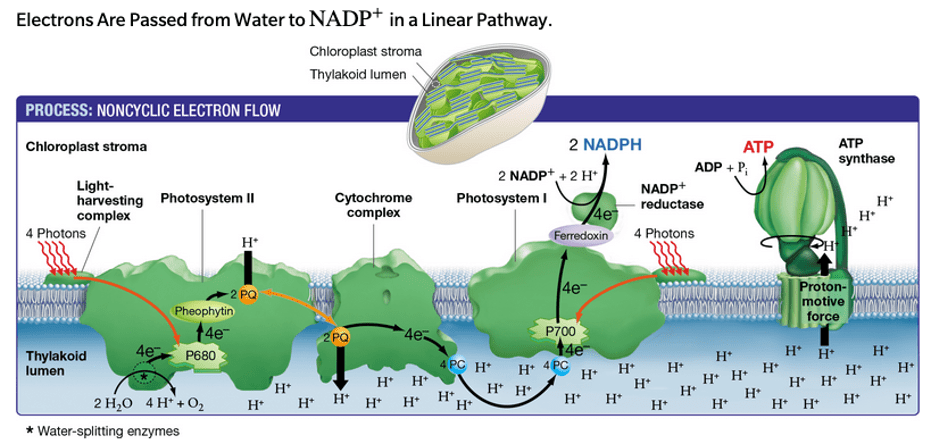
During the light-dependent phase, H+ ions return to the stroma (along the proton gradient) via this transmembrane enzyme.
What is ATP synthase?
Exergonic reactions can be identified by this change in ∆G.
What is negative?