Give two reasons why the U.S. has only two major political parties.
Acceptable answers: Single-member districts; strategic voting; ballot access; path dependence, funding
Give two reasons why business groups are often more influential in lobbying than diffuse citizen groups.
Collective action advantages; concentrated benefits; more resources; expertise; lower coordination costs
Why do campaigns spend so much effort on mobilizing their base rather than changing minds?
Acceptable answers: mobilization easier than persuasion, polarized electorate, party ID is stable, turnout is low, reliable supporters matter, could mobilize the other side the other way
What are two reasons why people rely on cues from political leaders when forming opinions?
Acceptable answers: low information, trust in in-group elites, heuristics, cognitive shortcuts, partisan identity, lack of time to evaluate issues.
During the 1930s, many Black voters shifted from the Republican Party to the Democratic Party; by the 1960s this change stabilized.
What concept does this describe and what signals it has occurred?
A partisan realignment; durable shifts in coalition composition and issue alignment
A local environmental group cannot get people to attend meetings unless they offer free pizza and merch. Which solution to collective action are they using?
Selective incentives
When evaluating a sitting president, many voters focus on inflation and employment rather than detailed policy positions.
Which voting model is this?
Retrospective/economic voting
A nightly news broadcast spends 10 minutes covering immigration. Afterward, viewers say immigration is the most important national problem. Which concept explains this?
Agenda-setting: Media changing which issues viewers think are most important
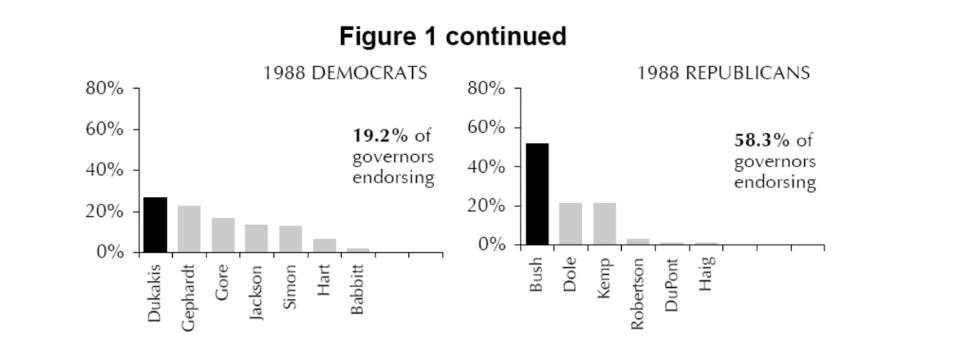
What primary-based phenomenon does this graph illustrate, and what is one critique of this phenomenon for democratic accountability?
The invisible primary — early elite endorsements shape viability. Critique: insiders decide before voters; weakens democratic accountability.
What is astroturf lobbying and what is one pluralist critique of it?
Astroturf = fake grassroots campaigns. Pluralist critique: it distorts real public opinion and gives organized interests unfair influence.
What is one proposed primary reform and a pro and con of it?
Examples: ranked choice voting, approval voting.
Pros: may broaden participation, allow more moderates to win, stop fears of "vote-splitting"
Con: tougher for voters to understand, low information voters, doesn’t increase moderate candidates, etc.
What media effect did this ad demonstrate, and how did it impact public opinion?

Priming — the ad made crime the key lens for judging candidates, boosting crime’s salience in incumbent evaluations.
Didn't change opinions, but changed which issues people thought about more when evaluating candidates