How do we render aid for first degree burns?
Run cool water for 10-15 min
What is the universal sign for choking, and what aid do we render to a person choking?
Heimlich Maneuver
What is hands only CPR?
100/min Compressions only CPR
What does CPR stand for and how do you spell it correctly?
cardiopulmonary resuscitation
The patient is experiencing tachycardia, hypotension, pallor, cold, cyanotic skin, and confusion. What might this person be experiencing?
a hemorrhage
What is a common brain injury for athletes?
Concussion
What aid do we render for third degree burns?
Call 911 and place cool, clean bandages
Injury that consists of a stretching or tearing of ligaments
sprain
What is the lifesaving device used during CPR?
AED.
What's another way to say second degree burn?
partial thickness burn
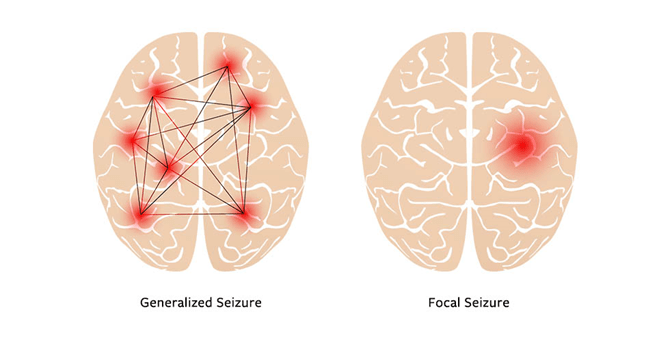
What's the difference between a focal and a generalized seizure?
A focal seizure is focused to one part of the brain, whereas a generalized seizure is more so the entire brain.
How long should a person with a concussion not consume alcohol and why?
48 hrs so their LOC can be assessed
What is a brief loss of consciousness caused from inadequate blood flow to the brain?
fainting
What does AED stand for?
Automated external defibrillator
What does RICE stand for?
Rest
Ice
Compression
Evelvation
What is a CI for a third degree burn and why?
Never run cold water over a third degree burn because it can cause tissue damage or hypothermia
Never give them anything to eat or drink
Name three categories of allergens.
insect bites, insect stings, food allergies, latex, medications
What's the class of medications used to treat allergies?
antihistamines
Why do we raise burns and bleeding injuries above the heart?
To decrease blood flood and inflammation to the area
What is a CI for a penetrating head trauma?
Never remove the object
What is the best way to determine the cause of a poisoning and what kind of things may be clues? (need 3)
Check the scene
Empty pill bottles, drug paraphernalia, open medicine cabinet, chemical bottles, etc.
Identify some risk factors for choking
hx of stroke, dentures, weakened esophageal muscles, eating too quickly
a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body loses too much blood or fluids resulting in hypoperfusion
hypovolemic shock
How many phases are there to a grand mal seizure. what are they and describe each?
2 phases: tonic/clonic
1st-superficial, epidermis
2nd-dermis, blisters
3rd-subcutaneous layer and affects nerves, blood vessels, muscle, and bone