Flattened T-waves, prominent U-waves, and/or ST depression may be caused this electrolyte disturbance?
What is potassium?
This electrolyte abnormality would be concerning for lethargy?
What is calcium?
Rehydration involves these two forms.
What is oral and intravenous?
How would this edema be staged clinically?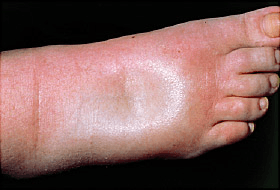
What is 3+?
True or false: This extended release medication may be broken in half prior to administration.
What is true?
Diuretic therapy may be a cause of these two electrolyte abnormalities?
What are sodium and potassium?
This happens when fluid shifts from the intravascular space to the interstitial space.
What is third spacing?
This is the priority intervention for a client who's experiencing prolonged changes from baseline heart rate and blood pressure?
What is notify the physician?
This finding may indicate which electrolyte abnormality?
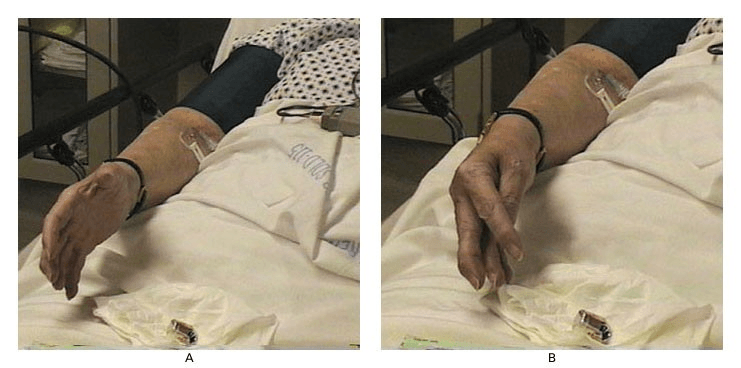
What is calcium?
This electrolyte abnormality would be concerning for tingling and parathesias?
What is calcium
These type of fluid losses cannot be objectively measured.
What are insensible fluid losses?
This finding is associated with what fluid volume disturbance?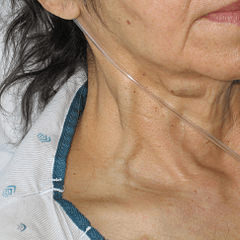
What is fluid volume overload?
This electrolyte disturbance is of concern when caring for a client with alcoholism?
What is magnesium?
These foods can help balance electrolyte loss from loop diuretic therapy.
What are potassium-rich foods?
This laboratory value helps to assess hydration status.
What is urine specific gravity?
This type of dehydration may be associated with hypernatremia.
What is hypertonic dehydration?
This nursing intervention is used to treat hyponatremia.
What is free water restriction?
This serum potassium level would be appropriate for supplemental potassium administration.
What is hypokalemia to normokalemia?
This type of intravenous fluid is appropriate for treatment of hypertonic dehydration.
What are hypotonic IV fluids?
This finding may be with extreme acute hyponatremia.
What is altered mental status?