What is an example of a human-made, mass structure?
answers may vary:
e.g. concrete barrier
What is measured in Newtons
Weight
You need to provide ____________ and ______________ when describing a force.
Magnitude and direction
When you twist your ankle at a soccer game this is an example of what type of failure?
Torsion failure
State the condition necessary for the stability of a structure.
The centre of gravity must be within the space of support
Which state(s) of matter have no fixed volume?
What is viscosity?
A measure of a fluid's resistance to flow
When an object's density increases, what happens to its buoyancy?
It decreases
What is the most likely reason that a mass structure would fail?
It's weight causes the foundation below it to shift and sink.
What is the definition of mass and what are the units in which it is measured?
The amount of stuff that an object contains. Measured in kilograms.
What are the four internal forces?
What is important about graphite when it comes to type of material strength.
It has a very low shear strength, which allows it to leave marks on a page and makes it good material to use in pencils for writing.
This part of an arch carries the load and prevents the arch from spreading out
The abutments
What is a fluid? Which state(s) are fluids?
a substance that has no fixed shape and can flow freely
liquids and gases
Which fluid has a greater viscosity - one with a flow rate of 10 m3 / s or one with a flow rate of 1 m3/s - explain your answer.
the one with flow rate of 1 m3/s because it that means it has a slower flow rate which means it has a higher viscosity since it is more resistant to flow
What must be true about the buoyant force acting on an object immersed in a fluid in order for the object to float?
It was great than the force of gravity acting on the object
This is an example of a natural frame structure
spider web
What happens to mass when you go to the moon?
It does not change.
When a person sits on a chair while twisting a jar of pickles, the chairs of leg are under ______________ and the lid of the jar under _______________
Compression, torsion
Name an example of a material with very high tensile strength and an example of a material that has very high torsion strength.
Tensile strength: steel
Torsion strength: rubber
Name three examples of cantilevers in the real world
balconies, construction cranes, shelving and some furniture, stadium roofs
Name two examples of hydraulic systems and two examples of pneumatic systems
hydraulic: water towers, hydraulic lifts, syringes, circulatory system
pneumatic: jackhammers, air breaks, respiratory system
0.0741 m3 / s
Solution:
3 hours x 60 min/hour x 60 sec/hour = 10 800 seconds
Flow rate: Volume of fluid passing/ time
= 800/ 10800 = 0.0741
Would an object that has a mass of 0.8 kg and a volume of 1000 cm3 have a positive, neutral or negative buoyancy in water? Explain.
it would have a density of 0.8 g/cm3 which is less dense than water which has a density of 1g/cm3 so it would have a positive buoyancy in water.
What are three key facts about shell structures?
Strong and hollow
Make great containers
Use their outer layer for support
What does the gravitational force between two objects depend on?
the mass of the two objects and the distance between them?
What is deformation and how does it arise?
What are the three parts of the definition for the centre of gravity? Is it always located deep inside a structure?
1) the point around which a structure's mass is equally balanced
2) the point at which mass of entire object seems to be concentrated
3) the point directly acted on by the force of gravity
No, depending on the shape and mass distribution of an object, it can be outside of it
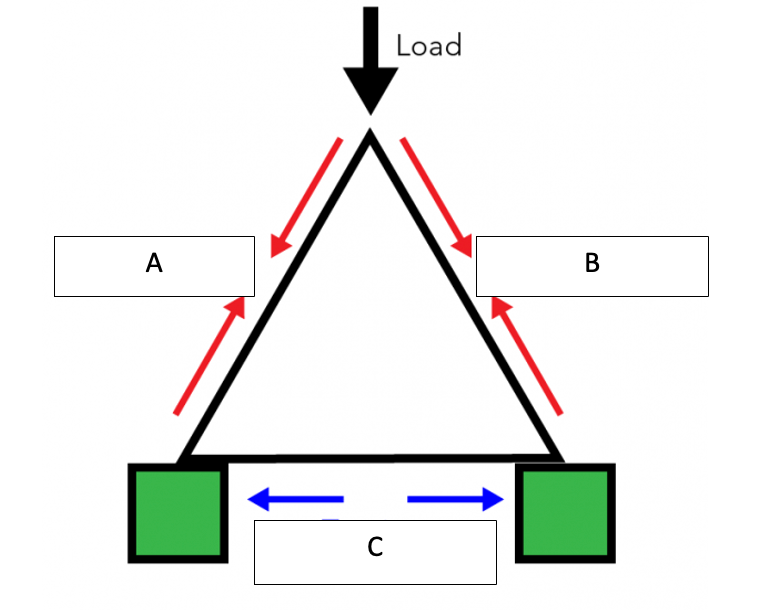
Label A, B and C to describe how a triangle transfers force
Compression, Compression and Tension (the two sides gets squeezed together and the bottom gets stretched)
What is Pascal's Law?
States that the pressure exerted on a fluid will be evenly distributed throughout the fluid.
How does increasing the temperature a liquid affect its viscosity? Explain.
What does Archimede's principle state?
Archimedes’ principle states that the upward, buoyant, force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
What are the four characteristics of aesthetic design?
Keep it simple
Interesting colours and textures
Carefully arranged shapes
Symmetry
Weight is measured with a ______________ and mass is measured with a _________________
Spring scale or force meter, balance
The weight of the pillars of a building is a ___________ load while the weight of the people in the building is a _______________ load.
static, dynamic
Would a sports car or a truck be more stable? Explain why.
The sports car because it has a lower centre of gravity and relatively wider base of support. Also it is designed to have it's weight evenly distributed, unlike the truck.
Name two reasons why symmetry important for stability. Then, considering the diagram, explain why this is not always true. 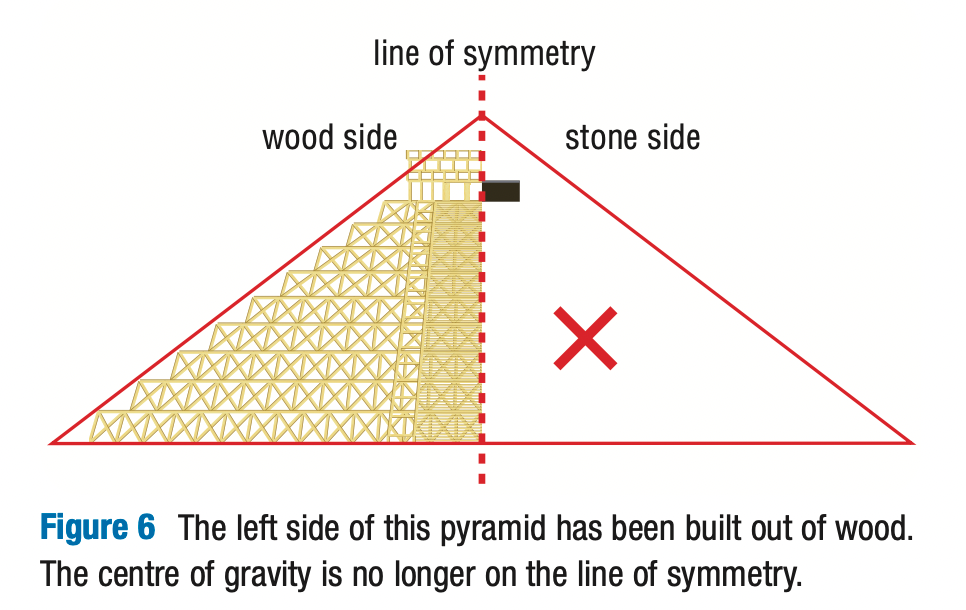
1) a symmetrical structure usually has its weight more evenly distributed
2) the line of symmetry sometimes helps you find the centre of gravity
No this is not always true, sometimes the weight of a symmetrical structure is NOT evenly distributed.
What is the difference between adhesion and cohesion?
Adhesion is a measure of how strongly particles of a fluid are attracted to another substance (e.g. walls of the container) while cohesion is a measure of how strongly particles in a fluid are attracted to each other.
Name factors that lead to a higher fluid viscosity
greater adhesion
greater cohesion
greater concentration
larger particle size
lower temperature (liquids)
Name five examples (combination of natural and human-made) that use changes in density to change their buoyancy
Submarines, Sperm whales, Fish, Scuba divers, Hot air balloons
What must designers consider when choosing materials for a structure (must name all four from the unit)
cost, appearance, environmental impact, energy efficiency
Calculate the weight of an object on Earth if its mass is 900g. State the formula and explain how you got the final answer.
F = m x 9.8 , where F= force of weight in Newtons and m =mass in kilograms
First convert 900g to 0.9 kilograms. Then, plug it into the formula:
F= 0.9 x 9.8 = 8.82 N (final answer must be in Newtons!)
What is the difference between a static and a dynamic load? Provide an example of each.
A static load is a permanent and non-changing external force acting on a structure (e.g. gravity), while a dynamic load is a non-permanent and changing external force acting on a structure (e.g. the force of wind or snow hitting the roof of a building).
Why is car design a great example of a type of material failure being put to good use? Name the type of failure and how it is used.
The fronts and backs of cars are designed to bend and buckle during a collision in order to absorb most of the impact. The car gets badly damaged but the occupants are less likely to be seriously hurt.
What are the three strategies that engineers, designers and architects use to make structures stronger?
1. Distribute the load throughout the structure so that no single part is carrying most of the load.
2. Direct the forces along angled components so that the forces hold pieces together instead of pulling them apart.
3. Shape the parts to withstand the specific type of force they are likely to experience.
Name three key differences between hydraulic and pneumatic systems
hydraulic uses liquid, pneumatic uses gas
hydraulic is more powerful and has no delay in action however it has heavier hoses
pneumatic can be used where there is no electricity and has lighter hoses
What happens to the viscosity of a solution of water and salt when you boil it? Explain.
Boiling the solutions causes the liquid to evaporate which increases the concentration of the remaining liquid. The more concentrated a fluid is the greater its resistance to flow and thus the greater its viscosity.
Use detailed scientific vocabulary to explain how a cruise ship floats in the ocean
A cruise ship floats in the ocean due to buoyancy, based on Archimedes' principle, which states that an object submerged in a fluid is acted on by an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the displaced fluid. Despite its size and weight, a cruise ship displaces a large volume of water, generating a large buoyant force that opposes gravity. In addition, the ship's average density (mass divided by volume) is less than that of the water it displaces. This is achieved by designing the hull to be largely hollow, reducing the ship's overall density and ensuring it remains afloat.