All food trains begin with this
What is an autotroph?
or
producer, plant
This diagram shows the complex interactions between multiple food chains
Heterotrophs are organisms that cannot make their own food; they are also called this because they must consume other organisms for energy
What is a consumer?
The hawk in this food web
What is a carnivore?
Autotrophs are organisms that have the ability to use photosynthesis to produce their own food, therefore they are also called this
What are producers?
Each step in a food chain is called a this, which shows the organism's position in the energy flow of an ecosystem
What is a trophic level?
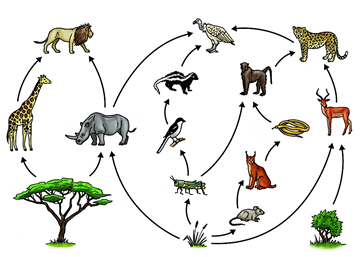
In this food web, the grasshopper is this level of consumer.
What is primary consumer?
These consumers only eat plants
What are herbivores?
The chipmunk in this food web
What is a herbivore?
This is the main source of energy for life on Earth
What is sunlight?
algae --> zooplankton --> minnow -->squid --> whale
In this food chain, this organism is the autotroph
What is algae?
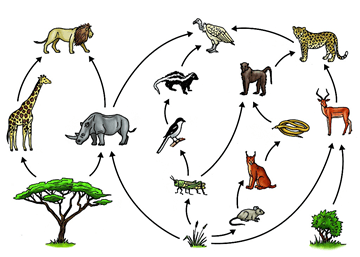
This organism is a secondary consumer.
What is a lion (show)?
or
Vulture, bird, cheetah, bobcat (show)
These heterotrophs eat other animals for energy
What are carnivores?
The deer in this food web
What is a herbivore?
Photosynthesis allows autotrophs to make their own food, and it also removes this from the atmosphere and releases oxygen
What is carbon dioxide?
or
CO2
grass --> mouse --> snake --> hawk
In this food chain, the snake is at this trophic level.
What is a secondary consumer?
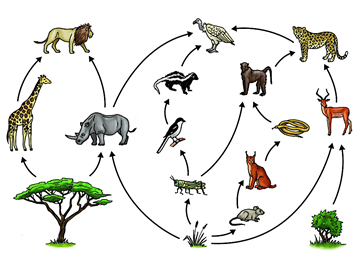
In this food web, the baboon is this level of consumer
What is secondary consumer (show web)?
or
tertiary consumer (show web)
These heterotrophs eat both plants and animals
What are omnivores?
The grouse in this food web
What is an omnivore?
Only 1% or less of this is used by organisms that use photosynthesis
What is the sun's energy?
This level of consumer eats secondary consumers
What is a tertiary consumer?
A producer from this food web
What is flowers, grasses, seeds?
This class of heterotrophs cause decay by breaking down dead matter and returning nutrients to the ecosystem. An example is mushrooms
What are decomposers?
The bear in this food web
What is an omnivore?
On land, green plants are the main autotrophs. In water, these organisms are the main autotrophs
What are algae?
