Define: Competition
Answer: When two or more organisms compete for the same resource.
What do the arrows represent in a food chain?
They show the flow of food energy/ represent what eats what in the food chain.
A combination of two or more food chains that show complex interactions is known as a _____________.
Food web
Define: Mutualism
When two organisms benefit each other.
Which of the following is a consumer?
a) Pine tree
b) Squirrel
C) Moss
D) Mushroom
B) Squirrel
Give an example of cooperation.
Example:
A pack of wolves work together to kill and eat a much larger moose.
Every food chain starts with __________________.
Producers/ plants
Which of the following is an example of a decomposer?
A: A bush growing in a field
B: A deer eating bushes
C: An eagle catching a fish
D: A pill bug eating old leaves
D: A pill bug eating old leaves
Give an example of commensalism.
Answers will vary
Snapping turtles eat aquatic plants, worms, and fish. What type of consumer is this organism?
Answer: Omnivore
What interaction is shown in this photo?

Answer: The lions and hyenas are showing competition for food.
Why do all arrows in a food chain point to decomposers?
They gather food energy from everything after it dies.
Which organism should be included in every ocean food web?
a) fish
b) turtles
c) dolphins
d) plants
d) Every food web starts with plants!
Botflies lay their eggs under the skin of large mammals, including humans. The larvae hatch and feed on the flesh of the animal causing a terrible itch. This is an example of _____________________.
Parasitism
What is the primary source of energy for all food webs?
The sun
Carpenter ants live in colonies of hundreds of related females. They work together to carve out a nest in old wood. This example best illustrates _______________.
Answer: Cooperation
Which is the correct progression in the food chain?
A: Grass-> deer-> wolves
B: deer-> grass-> wolves
C: grass-> wolves-> deer
D: wolves-> deer-> grass
A: Grass-> deer-> wolves
Which animal in this food web is an omnivore?
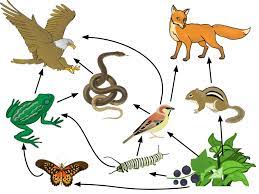
The sparrow eats caterpillars and plant berries/seeds.
Cowbirds follow cows around and feed on ticks and other bugs attracted to the cows. The cows enjoy being cleaned. This is an example of _____________.
Mutualism
Students designed an experiment using a closed terrarium ecosystem. It contained snails and small plants, received plenty of sunlight, and had soil for the plants to root. Why does the ecosystem need sun to stay in balance?/how-to-make-terrariums-848007-24-21db49b28a3d45a69737a3a538bd10db.jpg)
The plants use sunlight to produce food and oxygen for itself and the snail.
Give an example of a predator/ prey interaction.
Answers will vary
The islands of Hawaii had no mongooses until they were brought in to control rat populations. What was the effect on native bird populations?

Native birds decreased because of the new predator.
What process forms the foundation of every food web?
Photosynthesis: it is the start of food energy in the web.
Mistletoe seeds stick to tree trunks. The plant grows on the trunk, and its roots penetrate the wood allowing to take water and nutrients from the tree. This is an example of _________________________.
Parasitism
Which interaction best describes the relationship between the owl and snake in this food web?
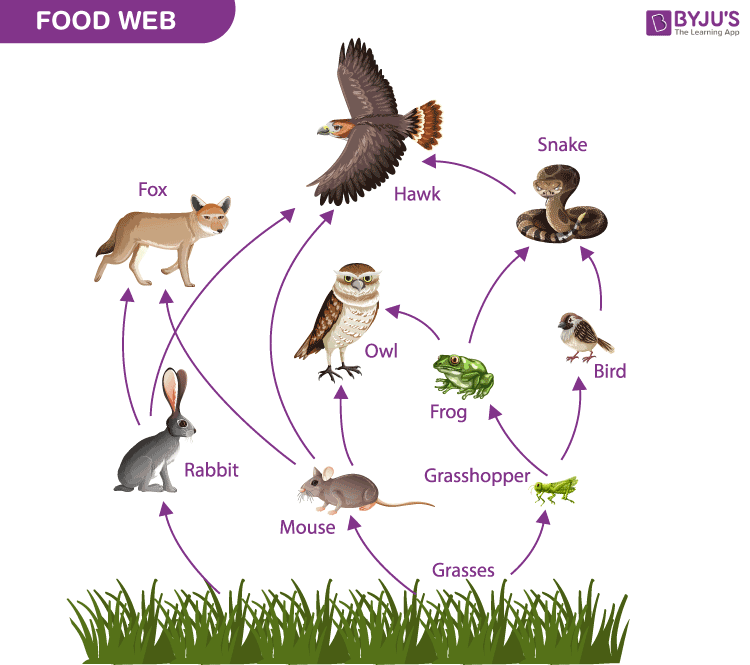
Answer: Competition