A herbivore is a producer organism.
False
What is a consumer?
An organism that depends on other organisms to obtain their energy/food. E.g. Zebra
What is a food chain?
A representation of the flow of nutrients and energy.
Is there more than one types of dichotomous key?
Yes, list and branched.
All introduced species become invasive species.
False.
Name an invasive species and 1 impact that it has had on its environment.
Answer will vary.
A herbivore is an organism that consumes only plants.
True
What is a producer?
Something that produces/makes its own energy/food. Eg. plants
What is a food web?
A collection of all food chains present in an ecosystem.
Is this a good dichotomous key? How do you know?

No, it uses subjective language (it is not specific enough).
If an organism is removed from an environment, there will be no effect on the remaining food web/chain.
False.
Name an invasive species and a control mechanism that may be used to reduce its impact on its environment.
Answers will vary.
Energy and matter are the same thing.
Energy - enters the food web from the sun, transfers up the food chain in one direction.
Matter - enters food webs from small molecules that are turned into bigger molecules and is continuously recycled by decomposers.
An apex predator is an organism with no natural predator.
What do arrows in a food chain and web mean? and what direction must they be pointing?
They show the direction that energy travels in a system.
They always point to the organism that does the eating/gains the energy.
What is missing in this dichotomous key?
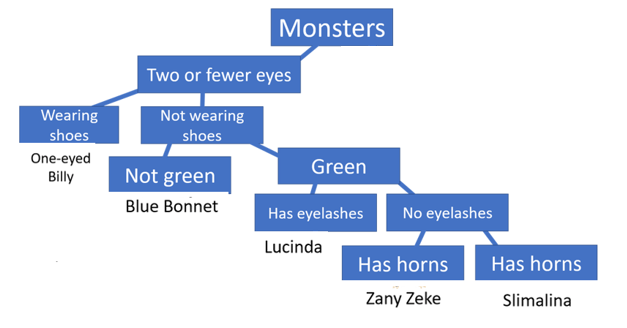
A second branch from monsters.
Biotic factors are just as important as abiotic factors.
True
Are all control mechanisms good at only impacting the invasive species? Or can they impact the environment in other ways too? Explain.
Answers will vary.
An ecosystem needs both heterotrophs and autotrophs to become stable.
True.
The secondary consumers generally preys on at least one herbivore.
Is this food chain correct?
Sun > grasshopper > lizard > snake > decomposer?
If yes, how do you know?
If no, what is wrong with it?
There is no producer.
Identify this organism in the following dichotomous key. 
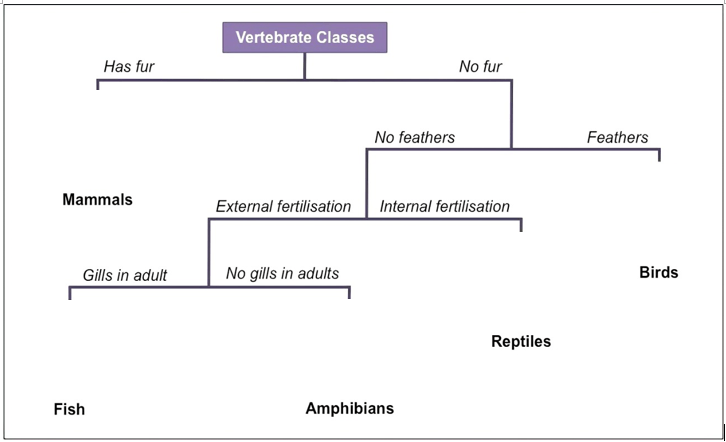
A dichotomous key must be able to organise all given organisms.
True
Why are we learning this unit?
So that we can analyse how the sustainable use of resources is relevant to how they cycle through earth systems.
Classification is not an everyday necessity.
False
Describe what an autotroph and heterotroph are.
Autotroph - makes its own nutrients to meet energy needs.
Heterotroph - consumes other organisms to gain energy to meet its needs.
What is wrong with this food web?
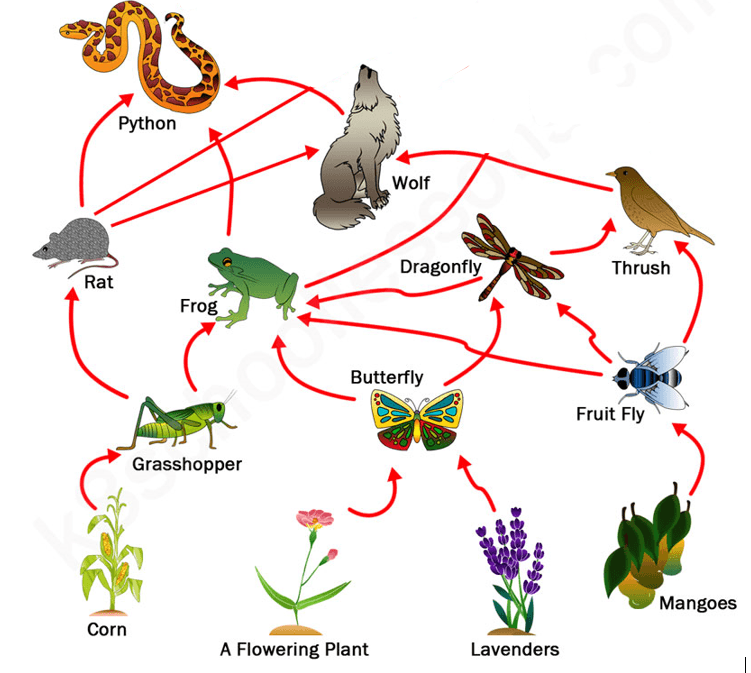
It is missing the apex predator.
Identify beetle D.
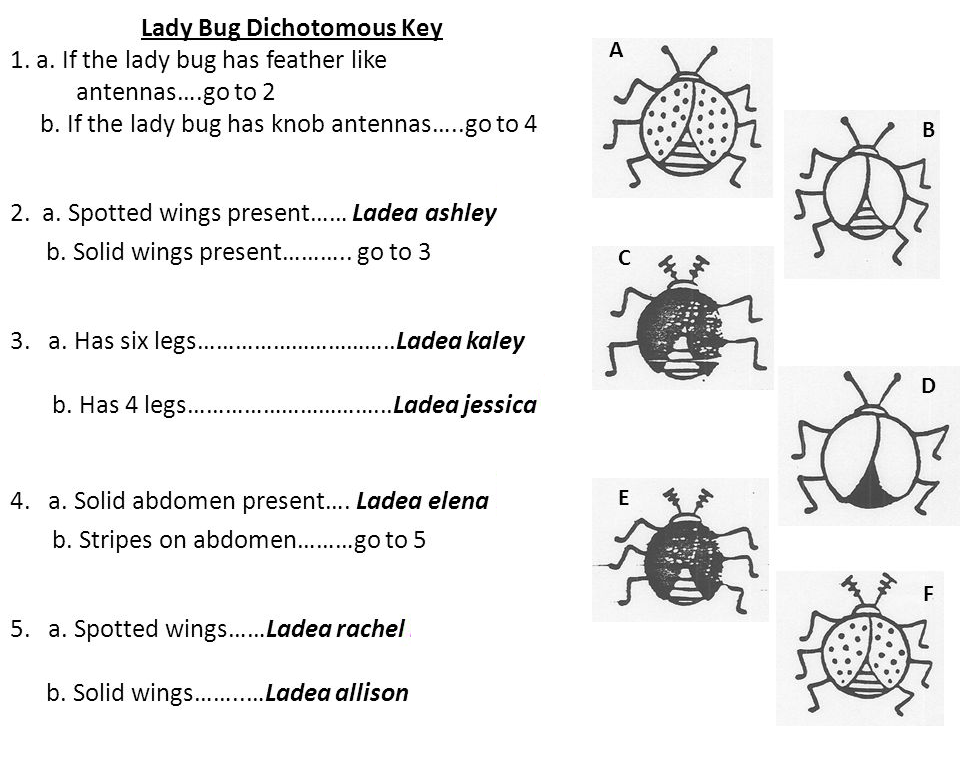
Ladea Elena
Food webs never change no matter the influence (change of season, temperature, etc).
False.
What is subjective language, and why does it impact the effectiveness of a dichotomous key?
It is not specific enough. Being non-specific allows the user to 'interpret' their own meaning and base a classification off of opinion rather than fact.