Einstein’s theory that mass and energy are different forms of the same thing, that amounts of mass and energy may each be expressed in terms of the other.
What is the Theory of Mass-Energy Equivalence?
The weakest of the forces, but operates over the longest distances.
What is the gravitational force?
A field caused by a magnet or current carrying wire.
What is a magnetic field?
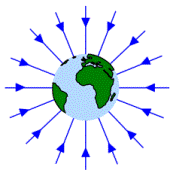
What is a gravitational field?
A push or a pull
What is a force?
Energy is never created or destroyed, only changed from one form to another.
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
This force operates over very small distances - holding the protons of an atom together.
What is the strong nuclear force?
A field around any charged object.
What is an electric field?

What is an electric field around a positive charge?
One end of a magnet, identified as either north or south
What is a pole?
Isaac Newton's theory that all objects with mass attract all others, with a force that is inversely proportional to the distance squared.
What is the Law of Universal Gravitation?
This force is the agent for Beta decay.
What is the weak nuclear force?
A field around any object possessing mass.
What is gravitational field?
What is an electric field around a negative charge?
A geometric description of the way one object exerts a force on another.
What is a field?
Albert Einstein's theory of gravity; an explanation of gravity in terms of acceleration and the curvature of spacetime around an object.
What is the General Theory of Relativity?
This force directly affects your life on a daily basis
What is the electromagnetic force?
In this field, the force always moves from north to south
What is the magnetic field?

What is a magnetic field around a bar magnet?
When a neutron in the nucleus of an atom spontaneously converts into a proton, emitting an electron and a neutrino in the process.
What is beta decay?
The principle that an electric current generates a magnetic field that is proportional to the strength of the current.
What is Ampere's Law?
Name the 4 forces in order from strongest to weakest.
What is: Strong nuclear, electromagnetic, weak nuclear, gravitational?
In this field, ask "What would a positive do?"
What is the electric field?

What is a magnetic field around a current carrying wire?
A term for substances that spontaneously undergo nuclear decay, producing nuclear radiation in the process.
What is radioactive?