In which of these force diagrams are ALL of the horizontal and vertical forces balanced?
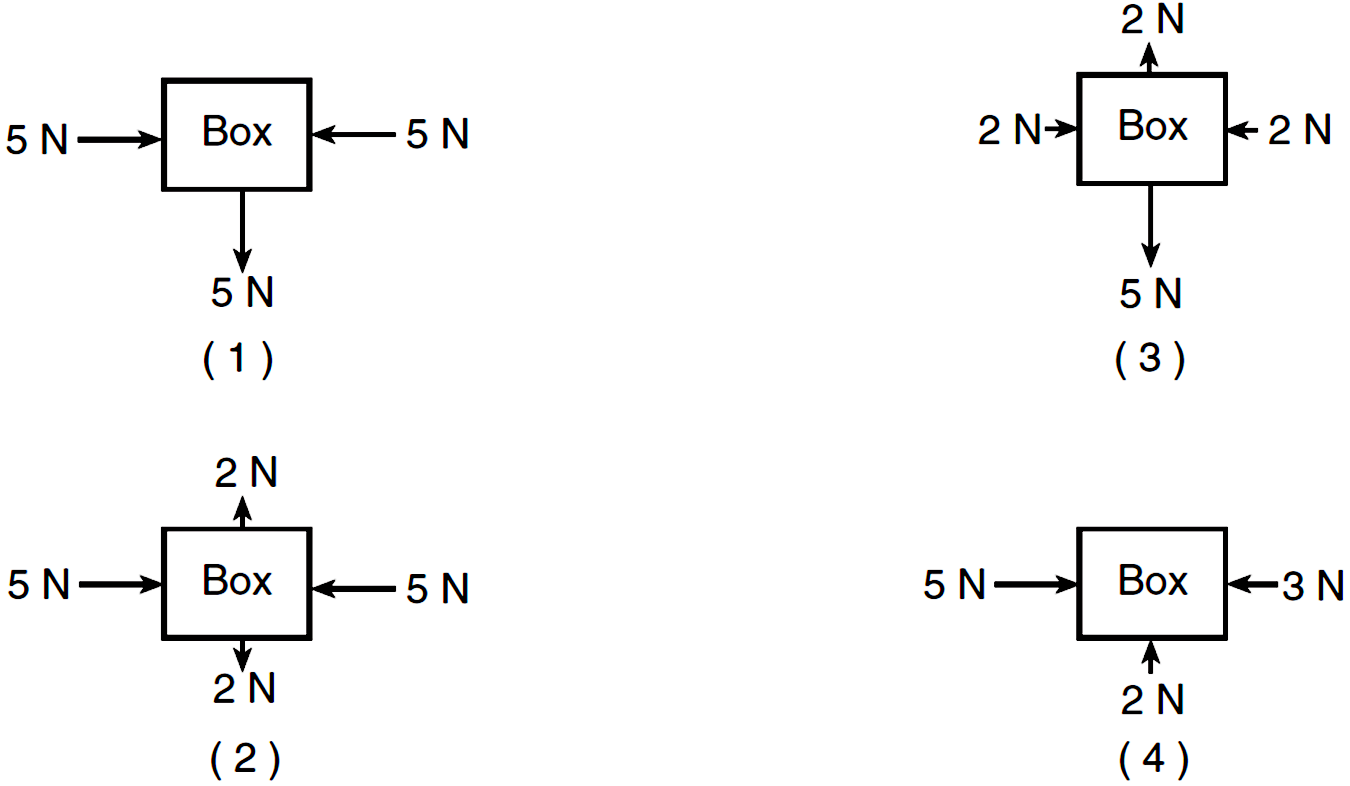
Number 2
What is the equation to work out speed (v)?
v = d / t
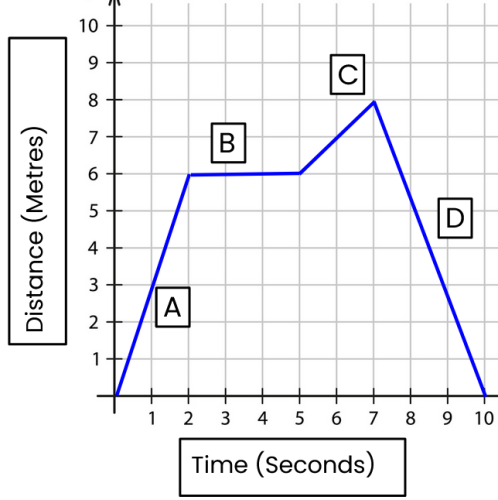
In which section is the object stationary?
B
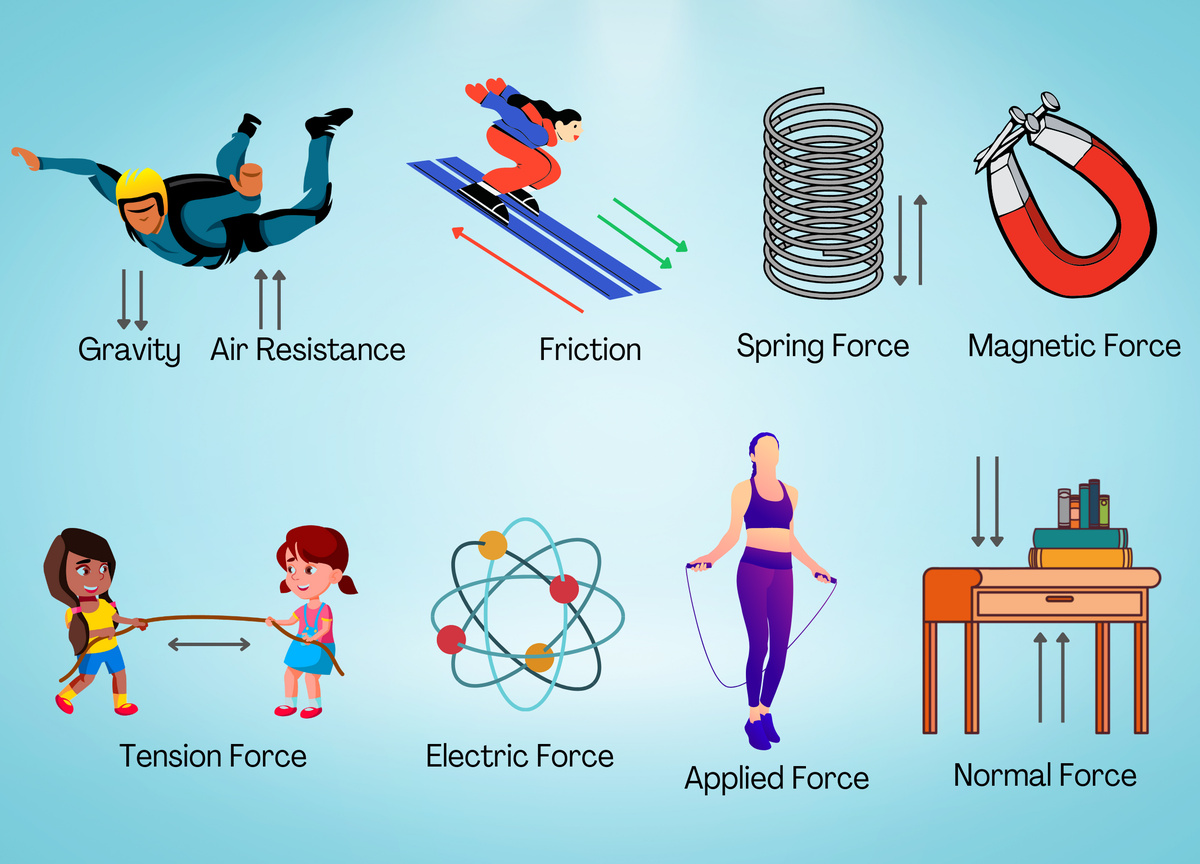
Name 3 different types of forces.
How many laws of motion are there?
3
Which of these wagons would be accelerating faster (if their mass is the same)?
The one with 90N of force on it. Because it has a greater net force on it, which would causes a greater acceleration.
An acceleration is a change in... what?
Speed
Which of these has the greatest speed?
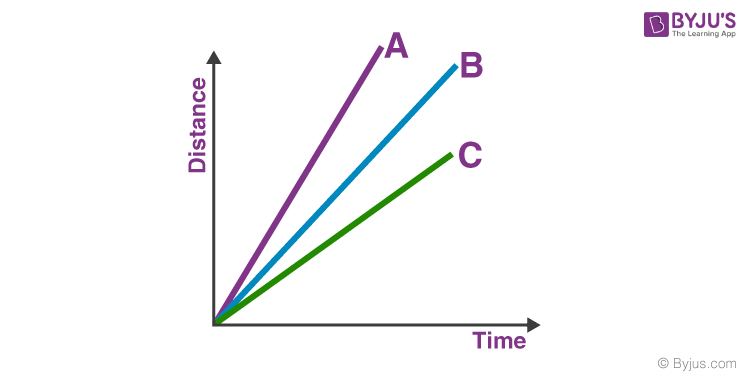
A (the steeper the line, the greater the speed)
What type of forces oppose the motion of an object?
Friction and drag forces
What is the net force acting on the hot air balloon? (remember units and a direction)
2500N - 2200N = 300N upwards
Calculate the average speed of a sailfish that travels 248 metres in 8 seconds.

v = d / t = 248 / 8
v = 31m/s
(about 110km/h)
Describe the motion represented by each of these distance-time graphs.
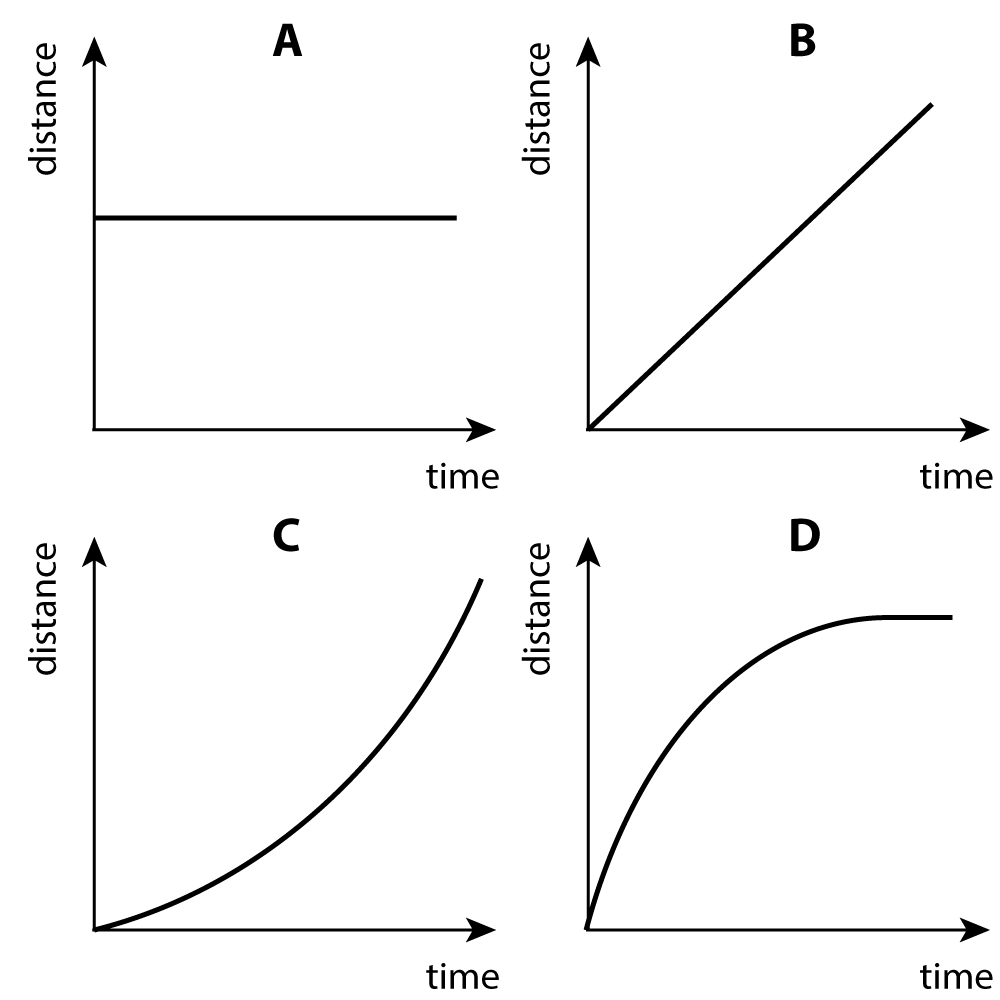
A - stationary
B - constant speed
C - accelerating
D - decelerating
Calculate the weight force of Zorba, who is the heaviest dog to have existed at 156kg. (g=10m/s2)

W = m x g
W = 156 x 10
W = 1560N
Which of the following is an example of Newton's first law of motion?
a) A soccer ball will not move until it is kicked.
b) A car accelerates when the driver steps on the gas pedal.
c) A rocket launches into space.
d) A balloon deflates when air escapes from it.
a) A soccer ball will not move until it is kicked.
First law states that an object that is not moving will not move until a force is applied to it and an object that is moving will not stop moving until a force is applied to it.
Label the forces acting on this plane.


Calculate the acceleration of these skydivers who go from 0m/s to 32m/s in their first 4 seconds of free-fall. Why do they start to decelerate after pulling the parachute?

Change in speed = 32 - 0 = 32m/s2
Change in time = 4s
a = v/t = 32/4 = 8m/s2
They decelerate as the upward drag force increases when the parachute is released. This means the net force is in the upward direction.
Calculate the speed of the object between 8 and 10 seconds.
Change in distance = 40 - 30 = 10m
Change in time = 10 - 8 = 2s
v = d / t = 10 / 2 = 5 m/s
A car with a mass of 1500kg accelerates at 12m/s2 what is its overall force?

F = m x a
F = 1500 x 12
F = 18000N
Using Newton's First Law, explain why a person falls forward when their car suddenly stops.
The first law states that an object that is moving will keep on moving until a force acts on it. When a car comes to a sudden stop, the people inside the car want to keep moving.
What is the net force on this object and in what direction?
What does this mean about its motion?
And why can we ignore the weight and normal forces acting on it?
Net force: 40N to the right -->
Motion: accelerating to the right
Ignoring weight and normal force: because they are balanced so there is no vertical movement.
Calculate the acceleration of a plane that goes from 70m/s to stationary (0m/s) in 10 seconds. What is it's acceleration? (Remember to show your working and to include units!)
Change in speed = end speed - start speed
Change in speed = 0 - 70 = -70m/s
a = change in speed / time
a = -70 / 10 = -7 m/s2
In which section is the object travelling the fastest. Calculate the speed it is travelling in this section.
B (because it is steepest).
Change in distance = 4-1 = 3m
Change in time = 3-2 = 1s
v = d/t = 3/1 = 3 m/s
What is the difference between mass and weight?
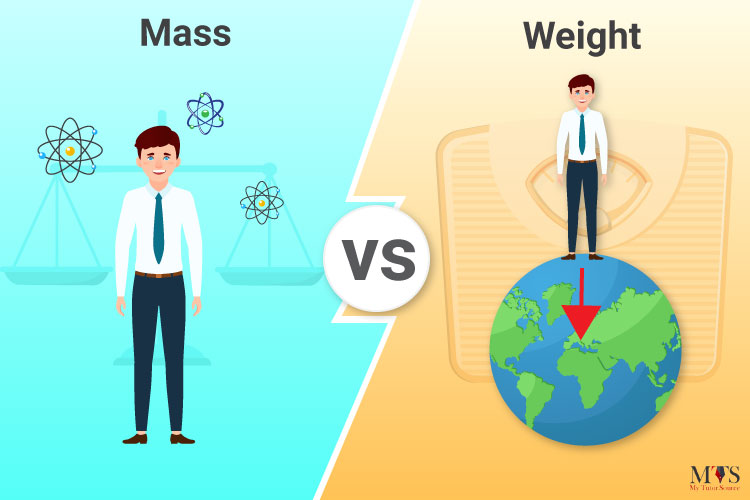
Mass is the amount of matter that makes up an object. It is measured in kilograms (kg) and is constant (does not change depending where something or someone is).
Weight is the force on an object due to gravity. It is measured in Newtons (N) and changes depending on the strength of gravity.
How does Newton's Third Law explain this?
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction (forces come in pairs). The force put on the canon ball is also put on the canon in the opposite direction, causing it to move backwards with an equal amount of force.
Because the canon has a greater mass than the canon ball it doesn't accelerate as fast.