A type of fibrous protein that makes up the majority of the cortex of hair.
What is keratin?
Determines composition of elements in a sample.
What is neutron activation analysis?
Name of protein that composes the hair shaft.
What is keratin?
The importance of hair as trace evidence in criminal investigations was recognized during this time period.
What is the late 1800's?
Straight or wavy hair that can be blonde, red, brown, or black.
What is European hair?
List the 5 types of medulla patterns.
What are continuous, interrupted, fragmented, solid, and none?
Identify the structure being labeled in the top box on the left.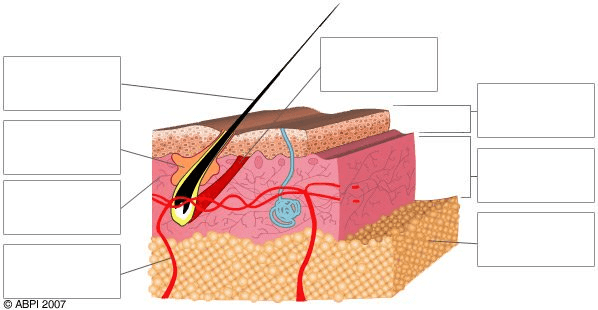
What is the hair shaft?
Allows the side-by-side analysis of samples, such as of hair or fibers.
What is comparison microscope?
Central core of a hair fiber.
What is medulla?
3 layers of the hair.
What are medulla, cortex, and cuticle?
Number of hair follicles humans are born with and only 2% are found on the head. This is the largest number of hair follicles a human will ever have because the density of hair decreases as a person ages.
What is 5 million?
Straight dark or black hair.
What is Asian hair?
This type of medulla pattern is broken at regular intervals. ___ ___ ___ ___
What is interrupted?
Identify the item being identified in the second box on the left.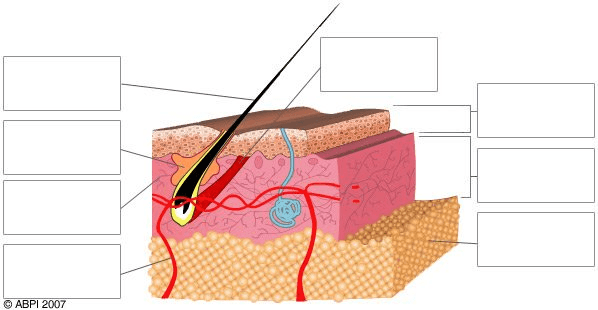
What is a sebaceous gland?
The region of a hair located outside of the medulla containing granules of pigment.
What is the cortex?
Actively growing root or base of a hair containing DNA and living cells.
What is a hair follicle?
Innermost, can be hollow, missing, fragmented, segmented, continuous or doubled part of hair.
What is medulla?
Three stages that hair proceeds through as it develops.
What are the anagen stage, the catagen stage, and the telogen stage?
Kinky, curly, coiled, dark black hair.
What is African hair?
This type of medulla pattern has no pigmentation in the medulla.
What is none?
Identify the pink layer labeled in the 3rd box on the left.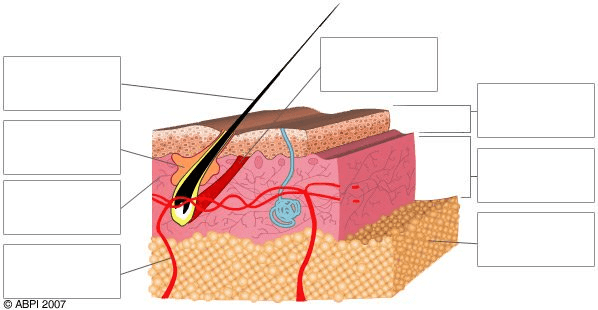
What is the dermis?
The tough outer covering of a hair composed of overlapping scales.
What is the cuticle?
Connects an individual or thing to a certain group.
What is class evidence?
Largest part of hair shaft in humans; contains most of the pigment.
What is melanin?
Stage of hair lasting 1,000 days with active growth.
What is the anagen stage?
Name 3 regions of hair located above the shoulders.
What are head hair, eyebrows/eye lashes, and beard/moustache hair?
This type of medulla pattern is an unbroken line of color. ________________________________
What is continuous?
Identify what the bottom box on the left is pointing to.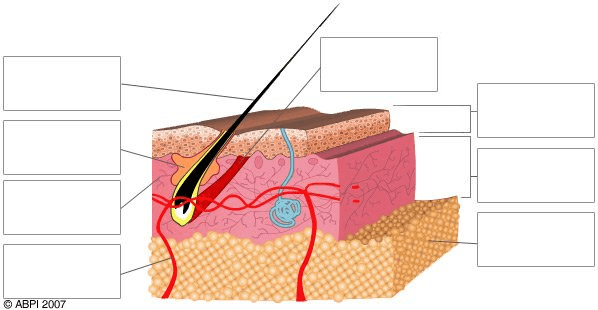
What is a capillary?
This identifies a particular person or thing.
What is individual evidence?
Bits of pigment found in the cortex of a hair.
What is melanin granules?
Transparent outer layer made of scales.
What is the cuticle?
Stage of hair development when hair follicles are dormant and hair is easily lost.
What is the telogen stage?
This hair has a double medulla.
What is beard hair?
This type of medulla pattern is unevenly spaced.
_________ _ _ _ _ ___________ __ _ __________
What is fragmented?
Identify the top, dark brown layer of the diagram.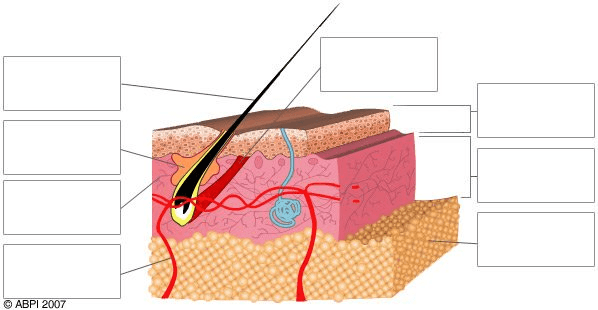
What is the skin surface?
Small amounts of physical or biological material found at a crime scene.
What is trace evidence?
With this type of evidence a follicle is present.
What is individual evidence?
Name the 2 main parts of a single hair.
What are the follicle and shaft?
Stage of hair development when hair grows, changes, and possibly turns grey.
What is the catagen stage?
This type of hair shows buckling.
What is pubic hair?
This type of medulla pattern fills the medulla and cortex.
What is solid?
Identify the top box on the right.
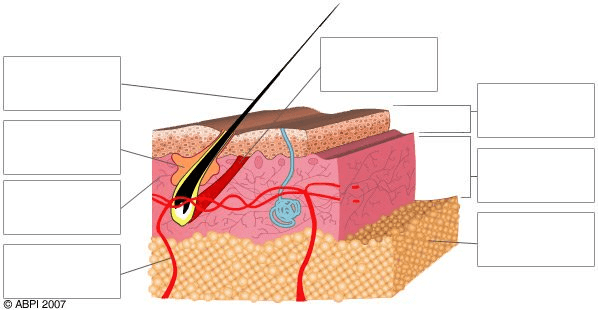
What is the epidermis?
When blood and tissue is attached to a hair follicle it is called this. It can be analyzed for blood type, DNA, and toxins.
What is a follicular tag?
In this type of evidence no follicle is present.
What is class evidence?
The end of a follicle has a network of these to supply nutrients to feed the hair and help it grow.
What are blood vessels?
A person's body can absorb these and incorporate it into the hair.
What are chemicals?
Hair that is very dense.
What is fur?
Identify the lowest layer in the diagram marked by the last box on the right.
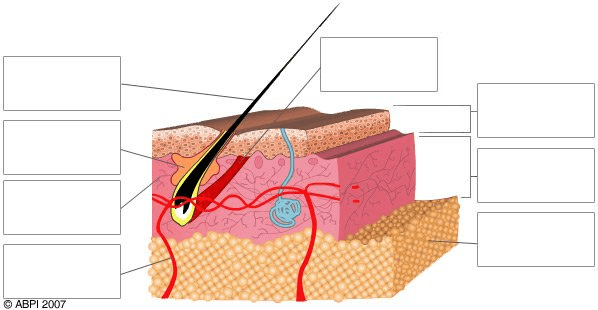
What is the sub-cutaneous layer?
Type of hair that is blunt and may have frayed ends.
What are arm and leg hair?