The basic underlying principle (or assumption) in science, "All _____ events have _____ causes."
What is all natural events have natural causes?
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
What is atomic number.
What is carbon?
Definition of cell theory.
1) Every living organism made of one or more cells
2) Smallest organisms are single cells
3) All cells arise from preexisting cells
This organelle is composed of three major parts (__, __, and __); synonymous to a baseball.
What is the nucleus; nuclear envelope, chromatin, nucleolus.
This step of the scientific method is the result of curiosity while observing a natural event.
What is a question?
This is the reason why atoms react with other atoms to form molecules.
What is to fill or empty the outermost shell; to become inert?
Organic molecules are divided into ___ categories. ___ synthesis builds polymers while ___ breaks them down.
What is 4; dehydration synthesis; hydrolysis?
4 attributes ALL cells share in common.
What are 1) Plasma Membrane, 2) Cytoplasm, 3) Use DNA, 4) Use RNA
The _____ includes the Nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, and vacuoles.
What is the Endomembrane System?
The six characteristics of life.
What are: 1) processing materials/energy, 2) Homeostasis, 3) Respond to Stimuli, 4) Grow/Develop, 5) Reproduce, 6) Evolve.
The specific bond that exists between hydrogen and oxygen in water.
What are polar covalent bonds?
Fructose, glucose, and galactose are ___ of this biomolecule type.
What are monosaccharides; carbohydrates?
___ cells form the bodies of animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
What are eukaryotic?
Forms interconnected series of membrane-enclosed channels; all proteins & phospholipids of cell membranes are synthesized here.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
When designing an experiment, this variable is also known as the response variable. In other words, it responds to your manipulations.
What is the dependent variable?
_____ bonds between water molecules produces _____ which allows insects to "walk" on water.
What are hydrogen bonds: surface tension?
___, rich in hydrogens and carbons, having mostly C-C single bonds, and are solid at room temperature.
What are saturated fatty acids?
4 organelles/structures unique to plant cells.
What are a cell wall, central vacuole, plastids, chloroplasts?
This modifies, sorts, and packages molecules; adding a carbohydrate group to proteins = glycoproteins; breaks some proteins into smaller peptides
What is the Golgi apparatus?
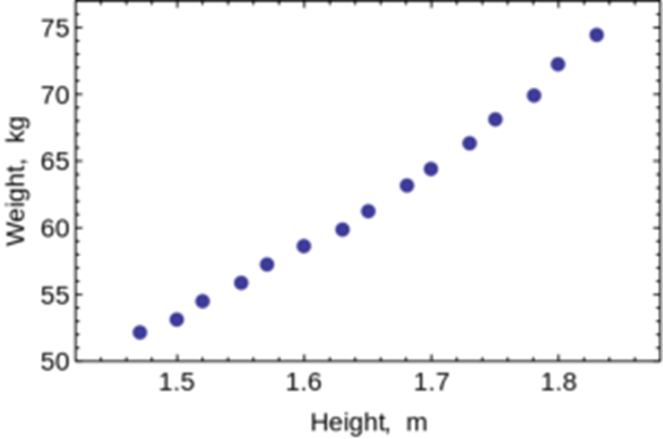
This type of graph is used to evaluate the relationship between two different continuous variables.
What is a scatter plot.
The balance of these two ions determines the pH of a solution.
What are OH- and H+ ions?
20 varieties of these create this class of biomolecule. Each monomer is covalently bonded forming a ___ bond.
What are amino acids; proteins; peptide.
This eukaryotic feature is composed of three types of protein fibers: __, __, and __.
What is the cytoskeleton; microfilaments, intermediate filaments; microtubules?
Occupies 75% of cell volume; provides cellular support (via turgor pressure); maintains water balance; stores hazardous wastes, nutrients, or pigments.
What is the central vacuole?