This happens to the thermal energy when a sample is cooled.
What is decreases?
Volume.
What is the amount of space an amount of matter takes up?
This is the direction of your slope if you are graphing a plate of chicken tenders that were taken out of the oven and placed on the counter.
What is downwards?
This is the direction the energy is flowing.
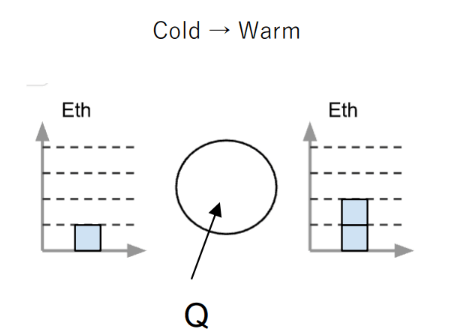
What is into the system?
This is the side with more mass.
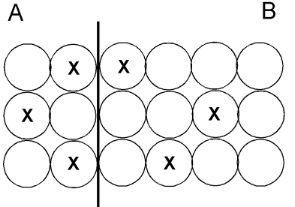
What is side B?
In an energy bar chart, my Eth column will go in this direction if my sample is being heated up.
What is up?
Variables.
What is a letter or symbol that represents a specific value? It stands for something else.
This is the term for the state that a hotter and cooler object strive for when brought together.
What is thermal equilibrium?
This is how the after chart would look if the object was put over an open flame.
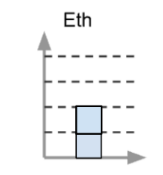
What is 3 or more blocks high?
This is the side with more thermal energy.
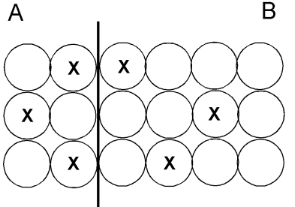
What is they are equal?
These are the three ways thermal energy can be transferred.
What is radiation, conduction, and convection?
Units.
What is the standard quantity used to express a physical property? What is what something is measured IN?
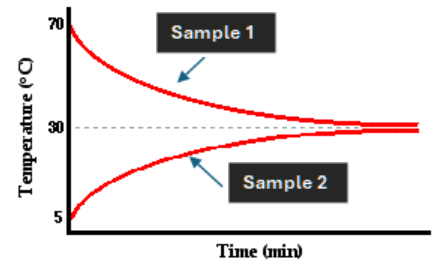
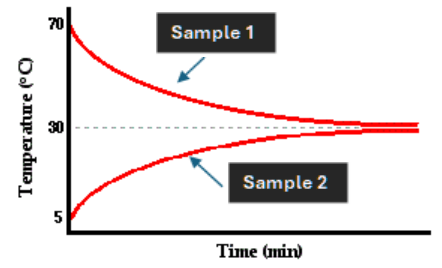
This sample (or neither of them) had a greater
Delta T.
What is sample one?
This is what the Eth column stands for.
What is thermal energy?
This is the side with a higher temperature.
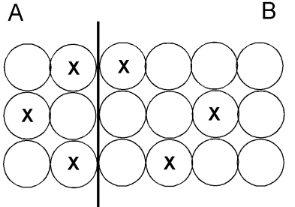
What is side A?
This is the type of energy transfer that happens when whipped cream is melting on a stack of waffles.
What is conduction?
Law of conservation of energy.
What is energy cannot be created nor destroyed?
This is a reason the lines are meeting at 30 degrees and not the middle point of 37.5 degrees.
What is the colder sample has more mass?
This is a representation of water at room temperature. The after chart would look this way if the water froze.
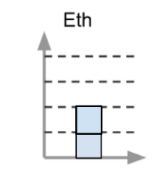
What is one block high?
This is the side with more thermal energy.
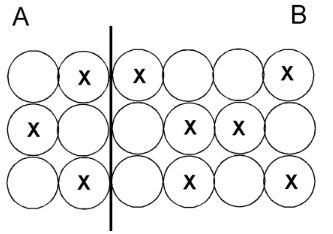
What is side B?
This is the order of substances from least to greatest of energy they would need for a 1000 g sample to increase by 50 degrees Celsius.
What is copper, iron, aluminum, ice, and water?
This is the specific definition for heat capacity. (Not how much energy a substance can store)
What is the amount of energy needed to raise an amount of a substance by 1 degree Celsius?
This is the final temperature you would get if a 50g iron block at -170 C and a 50g iron block at 3260 C were brought together.
What is 154.50 C?
Temperature is related to this, while heat is related to this.
What is temperature is related to particle speed, while heat is related to mass and speed?
This is the side with a higher temperature.
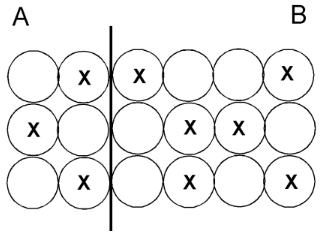
What is they are equal?