Is there a short run and long run tradeoff in macroeconomic stabilization through sizable discretionary fiscal policy?
a. No, because short term macroeconomic stabilization would enhance long-term economic growth.
b. Yes, because expansionary fiscal policy to stabilize the economy in the short run increases fiscal deficits and debts, requiring larger financing in the future.
c. No, because the expansionary fiscal policy will be mostly financed by an increase in tax revenue during the economic recovery.
d. Yes, because large fiscal spending can send a signal to global investors that the country has weak fiscal discipline.
b. Yes, because expansionary fiscal policy to stabilize the economy in the short run increases fiscal deficits and debts, requiring larger financing in the future.
When a government decides to reduce its spending, it should:
a. Cut expenditure across the board
b. Protect core spending programs and eliminate specific inefficient programs.
c. Cut social safety nets, which are wasteful and excessive in most countries.
d. Replace targeted transfers with generalized subsidies
b. Protect core spending programs and eliminate specific inefficient programs.
Wild Card!!
Which ASEAN country is the largest economy by GDP?
a. Vietnam
b. Indonesia
c. Thailand
d. Philippines
b. Indonesia
Which of the following is a key source of fiscal risk?
a. Macroeconomic shocks
b. Contingent liabilities
c. Natural disasters
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
Recall the DDT “Input-Data” worksheet: which of the following variables used to populate the template does not require projections?
a. The total gross public debt-to-GDP ratio.
b. The primary balance-to-GDP ratio.
c. The foreign inflation rate.
d. Stock of uncalled guarantees, as a share of GDP.
a. The total gross public debt-to-GDP ratio.
Which one of the following statements best describes the Cyclically-adjusted Balance?
a. It is an estimate of the fiscal balance that would apply under current policies if the output gap were zero.
b. It is an estimate of the fiscal balance that would apply under current policies if the potential output were at its peak.
c. It is an estimate of the fiscal balance under Keynesian macro-stabilization policies to stabilize the economy.
d. It is an estimate of the fiscal balance that reflects economic upturns and downturns
a. It is an estimate of the fiscal balance that would apply under current policies if the output gap were zero.
Why would the headline fiscal balance be a misleading indicator to assess whether fiscal policy stance is expansionary, contractionary, or neutral?
a. Because of measurement errors in the statistics related to spending and revenues.
b. Because of the time lag between the planning and execution of the budget.
c. Because one would need to disentangle the effect of the economic cycle on revenue and spending due to automatic stabilizers.
d. Because one would need to exclude the interest payments.
c. Because one would need to disentangle the effect of the economic cycle on revenue and spending due to automatic stabilizers.
Suppose the initial debt-to-GDP ratio is 50 percent; the real interest rate is 8 percent; the real growth rate is 4 percent, and the primary surplus-to-GDP ratio is 1 percent. What will happen to the debt-to-GDP ratio over time?
a. It will explode.
b. It will stay at 50 percent.
c. It will shrink.
d. It will increase but then stabilize at a value above 50 percent.
a. It will explode.
Which of the following best describes fiscal transparency?
a. Keeping government financial information secret to protect national sec
b. Providing clear, reliable, timely, and relevant information about government fiscal operations to the public
c. Publishing financial reports only during election periods
d. Allowing only internal auditors to access fiscal data
b. Providing clear, reliable, timely, and relevant information about government fiscal operations to the public
In the event of a shrinking working-age population (and hence fewer contributors), what reform could work to balance cash flows in a defined benefit (typically pay-as-you-go) pension system?
a. Increase the replacement rate.
b. Decrease the contribution rate.
c. Introduce an indexation of pensions to wages.
d. Raise retirement age.
d. Raise retirement age.
Wild Card!!
Where is the world’s largest desert?
a. Asia
b. Africa
c. Latin America
d. Australia
e. Antarctica
e. Antarctica
Wild Card!!!
Which ASEAN country has one of the highest tax-to-GDP ratios?
a. Philippines
b. Indonesia
c. Singapore
d. Myanmar
c. Singapore
Which of the following statements is correct?
a. The debt/GDP ratio will continue to increase if a country runs permanent primary deficits.
b. As long as the primary fiscal balance is positive, the debt/GDP ratio will decrease.
c. The debt/GDP ratio can decrease in a country that runs permanent primary deficits as long as the growth rate is sufficiently high relative to the interest rate.
d. Solvency and the “no Ponzi Game condition” are always satisfied
c. The debt/GDP ratio can decrease in a country that runs permanent primary deficits as long as the growth rate is sufficiently high relative to the interest rate.
How should the Medium-Term Fiscal Framework (MTFF) guide the annual budget process?
a. By developing 3-5 year budget allocations for each Line Ministry
b. By setting the aggregate expenditure ceiling to guide budget preparation
c. It doesn’t, it should be prepared after the budget is approved.
b. By setting the aggregate expenditure ceiling to guide budget preparation
What is the main product of the Low Income Country Debt Sustainability Framework (LIC DSF)?
a. A stress map indicating the risks associated with the level and profile of debt, and financing needs.
b. The probability of default.
c. Type 1 and type 2 errors for predicting debt crises.
d. A rating of the risk of external debt distress.
d. A rating of the risk of external debt distress.
Country X is a commodity exporter, and its fiscal revenue depends on commodity exports. What is the relationship between its cyclically adjusted balance and its structural balance during a large increase in global commodity prices (assuming that the economy is at its potential)?
a. The structural balance should be more deteriorated than the cyclically adjusted balance.
b. The structural balance should be less deteriorated than the cyclically adjusted balance.
c. The structural balance should be the same as the cyclically adjusted balance.
d. It is impossible to predict how the structural balance compares to the cyclically adjusted balance.
a. The structural balance should be more deteriorated than the cyclically adjusted balance.
Which one of the following is one of the reasons fiscal multipliers tend to be smaller in emerging market and developing economies (EMDEs) than in advanced economies (AEs)?
a. The monetary policy is less accommodative in EMDEs than in AEs.
b. The share of informal sector is higher in EMDEs than in AEs.
c. The share of cash constrained households is higher in EMDEs than in AEs.
d. The exchange rate regimes in EMDEs are less flexible than in AEs.
b. The share of informal sector is higher in EMDEs than in AEs.
What is the primary debt stabilizing balance (approximate) in the following scenario:
Initial level of debt/GDP ratio = 100%
Real interest rate (cost of debt) = 1%
Real GDP growth rate = 6%
Primary fiscal balance is -3%?
a. -5%
b. -3%
c. 3%
d. 5%
a. -5%
Which is not a key component of a Medium-Term Fiscal Framework (MTFF)?
a. Macroeconomic and fiscal forecasts
b. Fiscal strategy
c. Expenditure performance indicators
d. Fiscal risk assessment
c. Expenditure performance indicators
What type of tax is a major source of revenue for most ASEAN governments?
a. Wealth tax
b. Corporate income tax
c. Value-Added Tax (VAT)
d. Capital gains tax
c. Value-Added Tax (VAT)
The government delayed interest payments that were due in the fiscal year 2022 to fiscal year 2023. What is the consequence of such interest arrears on the fiscal balances in 2022 and 2023, compared to the case where the government honored the payments in 2022?
a. Under accrual-based accounting (GFSM2001/14), the fiscal balance in FY2022 improves while that of FY2023 deteriorates.
b. Under cash-based accounting (GFSM1986), the fiscal balance in FY2022 deteriorates while that of FY2023 improves.
c. Under accrual-based accounting (GFSM2001/14), the fiscal balances in FY2022 and FY2023 are unchanged.
d. Under cash-based accounting (GFSM1986), the fiscal balance in FY2022 and FY2023 are unchanged.
c. Under accrual-based accounting (GFSM2001/14), the fiscal balances in FY2022 and FY2023 are unchanged.
Under which of the economic conditions below is fiscal multiplier expected to be smaller?
a. There is a large output gap.
b. The monetary policy of the (regional) central bank is accommodative.
c. The economy has high propensity to import.
d. The households have high propensity to consume.
c. The economy has high propensity to import.
Suppose the interest rate-growth differential is positive (r>g) and the starting debt ratio is below the target debt ratio. Assume that the primary surplus-to-GDP ratio is set at the value such that if the debt ratio were equal to the target debt ratio, the debt ratio will stay constant going forward (i.e. debt-stabilizing value at the debt target ratio). What can you say about the debt dynamics in this economy?
a. The debt ratio will explode.
b. The debt ratio will fall.
c. The debt ratio will stay constant.
d. The debt ratio will fall to zero
b. The debt ratio will fall.
Wild card
How many countries can attend courses at Singapore Regional Training Institute?
a. 31
b. 35
c. 38
d. 41
c. 38
For the fan chart below, what is the probability of the debt-to-GDP ratio remaining above 40 percent of GDP in period d( t+3)?
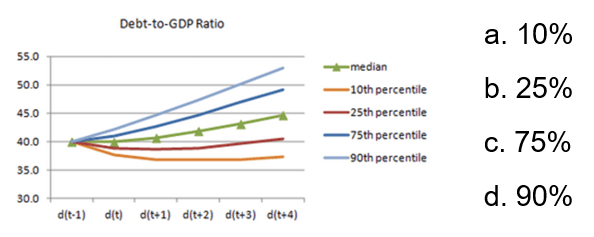
b. 25%