True or False:
The numerator or count is on the top of a fraction.
TRUE
The numerator is the number on the top of a fraction.

Which fraction is bigger?
 or
or 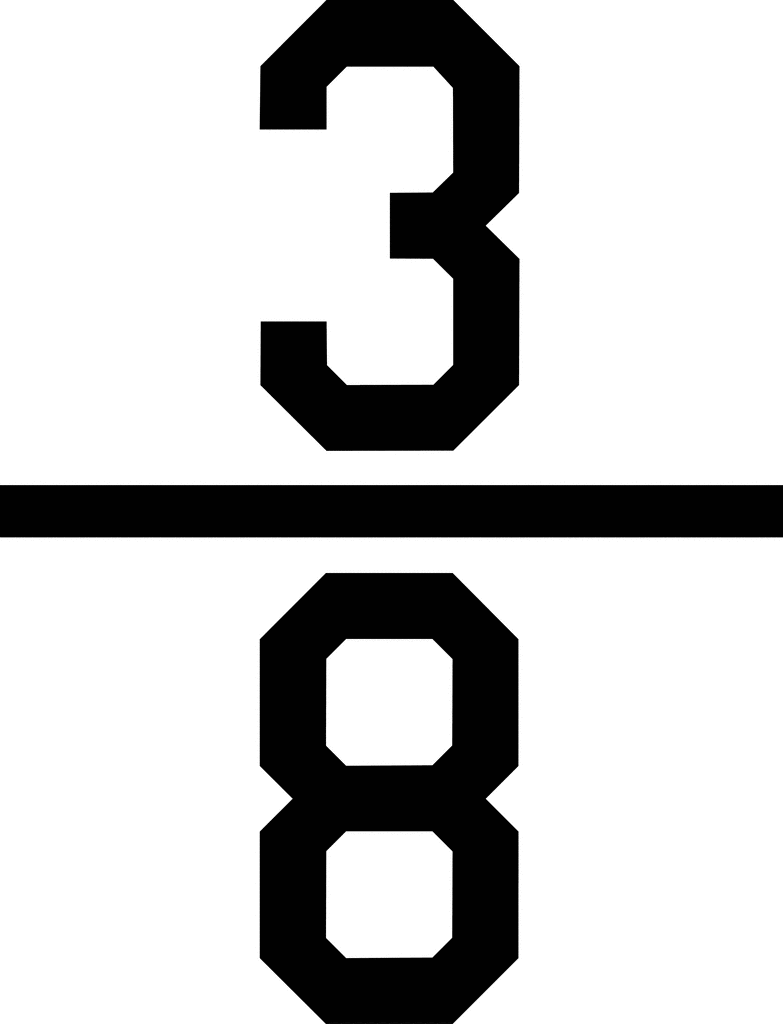
 >
> 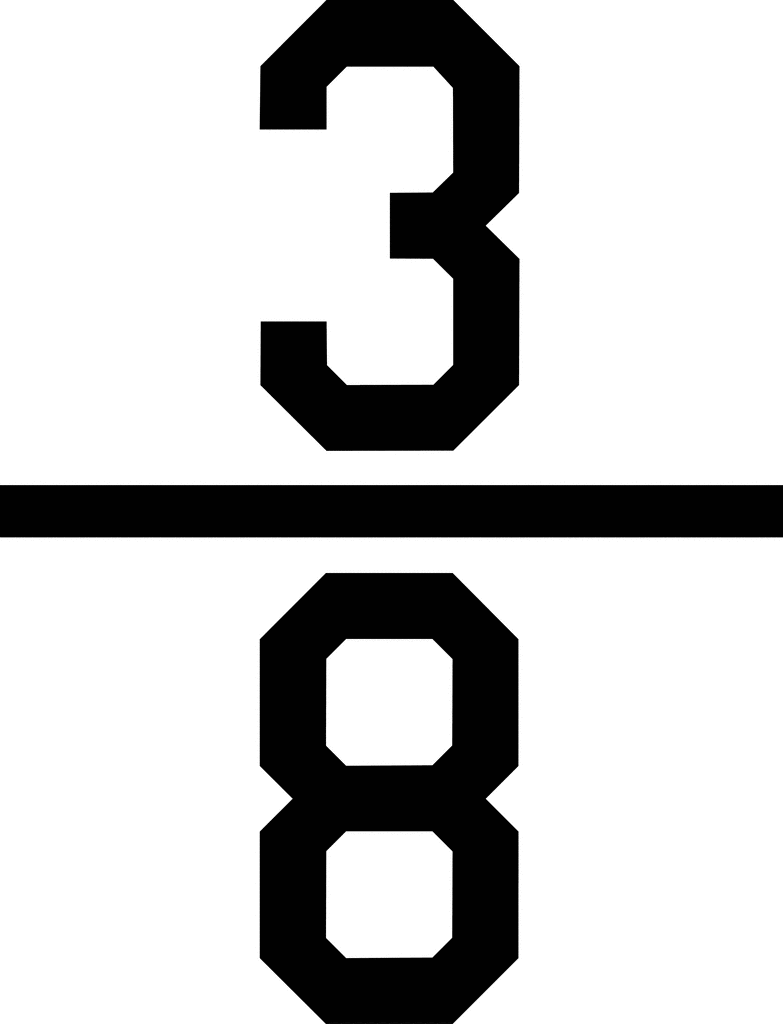
When the fractions have the same numerator, the smaller the size or denominator, the bigger the fraction.
(You are splitting the whole into less pieces)
Which models represent 1/2?
A. 
B. 
C. .png)
A. 2/4 = 1/2
B. 3/12 is not equivalent to 1/2
C. 3/6 = 1/2
True or False:
The denominator or size is on the top of the fraction.
FALSE!
The denominator or size is on the bottom of the fraction.

Which fraction is bigger?
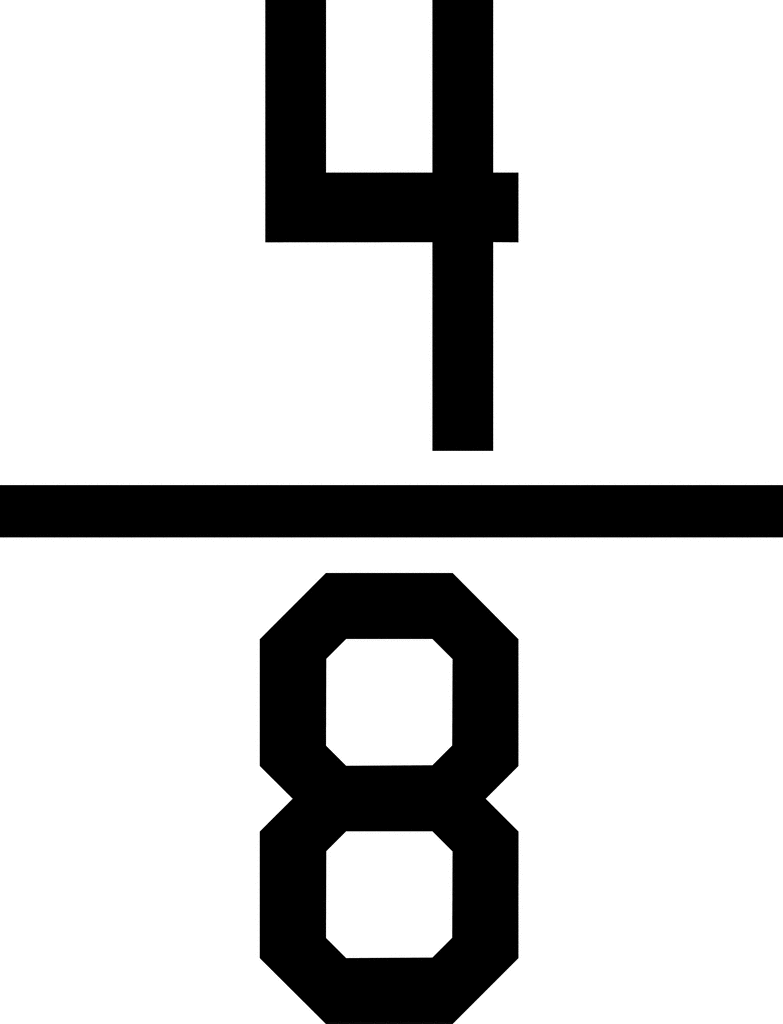 or
or 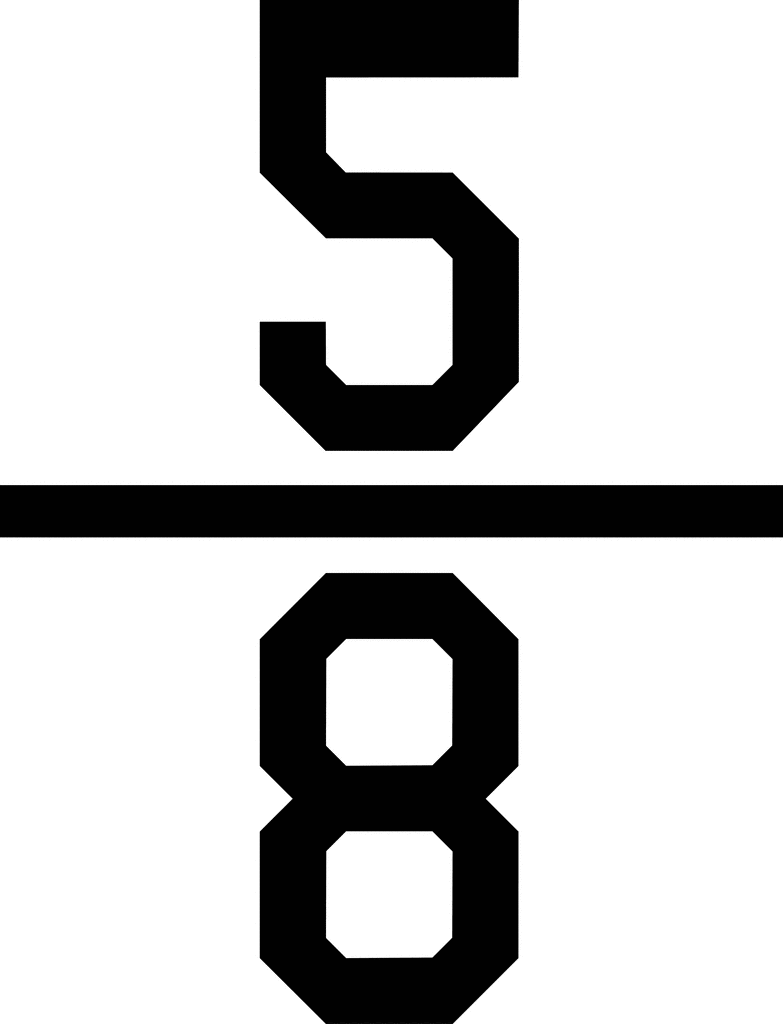
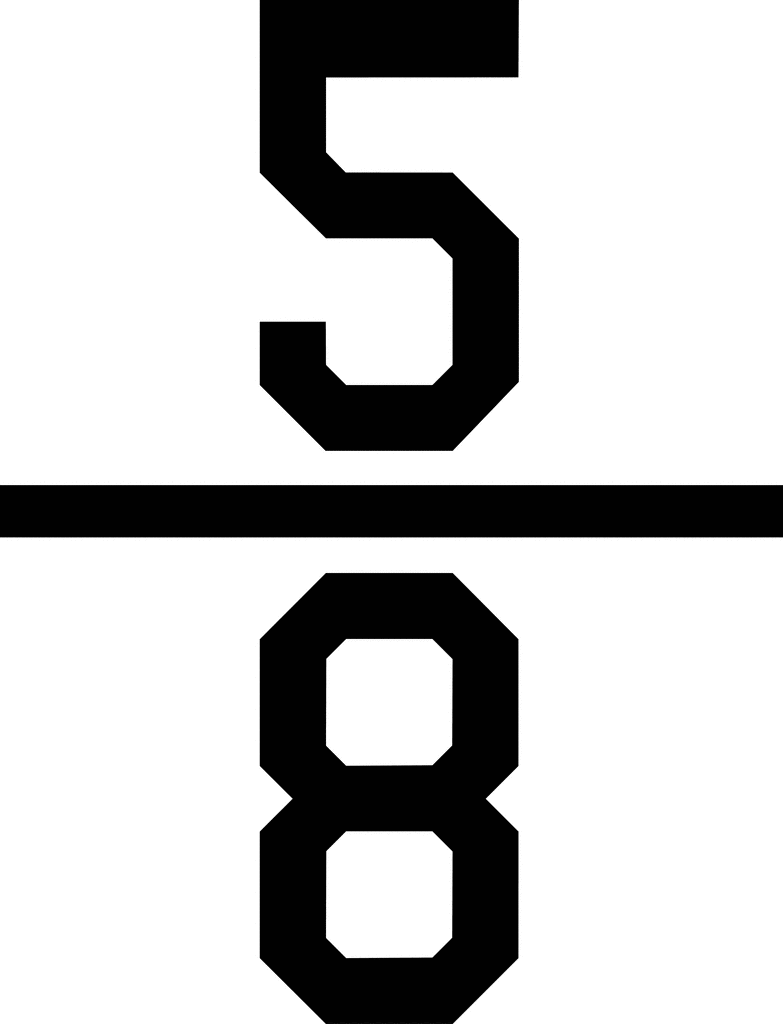 >
> 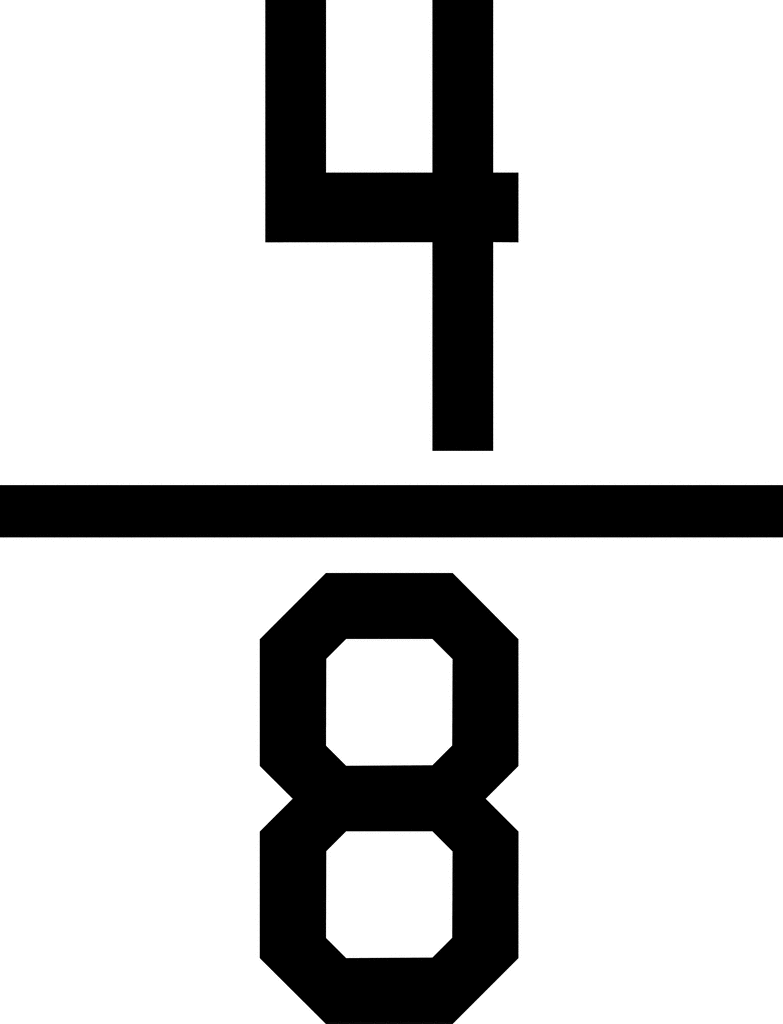
When the size or the denominator is the same, the fraction with the larger count is bigger because that means you are closer to one whole.
Name the fraction where the arrow is pointing.
1/8
True or False:
Equivalent means the same.
TRUE
Equivalent = Equal or the same

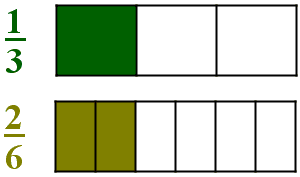
Use a number line and bar model to prove 1/3 and 2/6 are equivalent.

Joe and Betsy are both eating the same size chocolate bar. Betsy ate 2/4 of the bar. Joe ate 4/8 of his. Use a bar model or number line to show much both people ate.
Did they eat the same amount?
 Yes they ate them same amount!
Yes they ate them same amount!
True or False:
The opening of the symbol should be facing the smaller number.
FALSE
The opening should be facing the greater number. Remember BIG!
Which fraction is bigger? 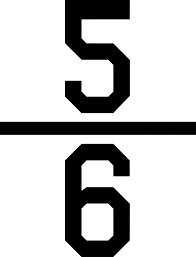 or
or 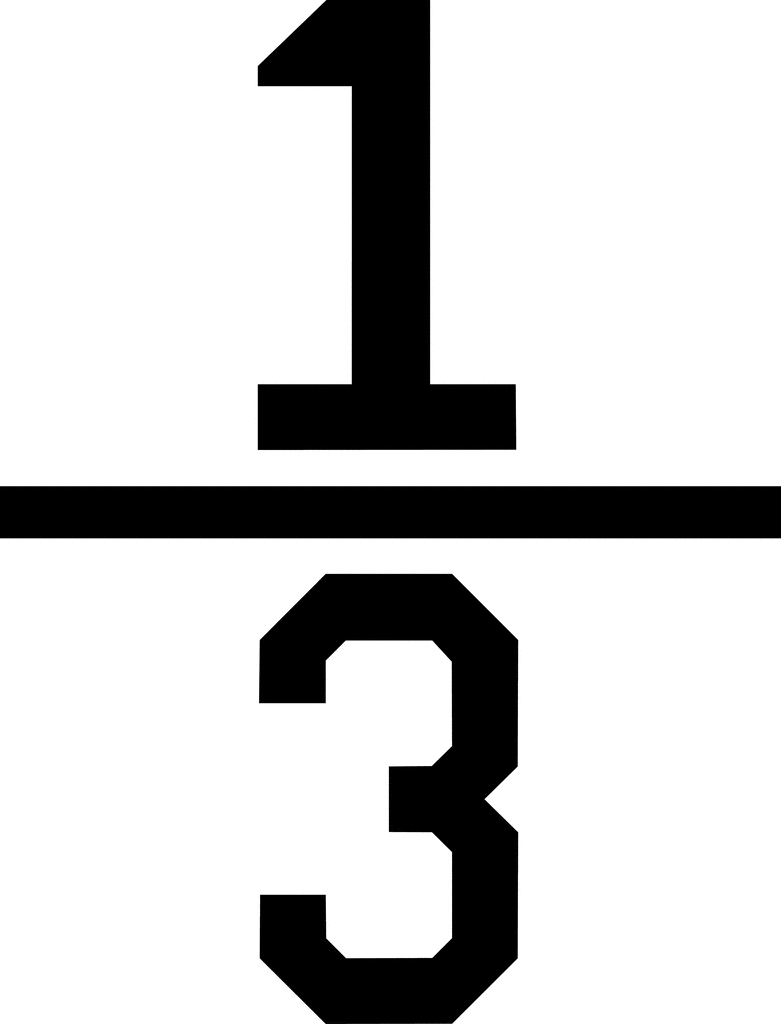
 >
> 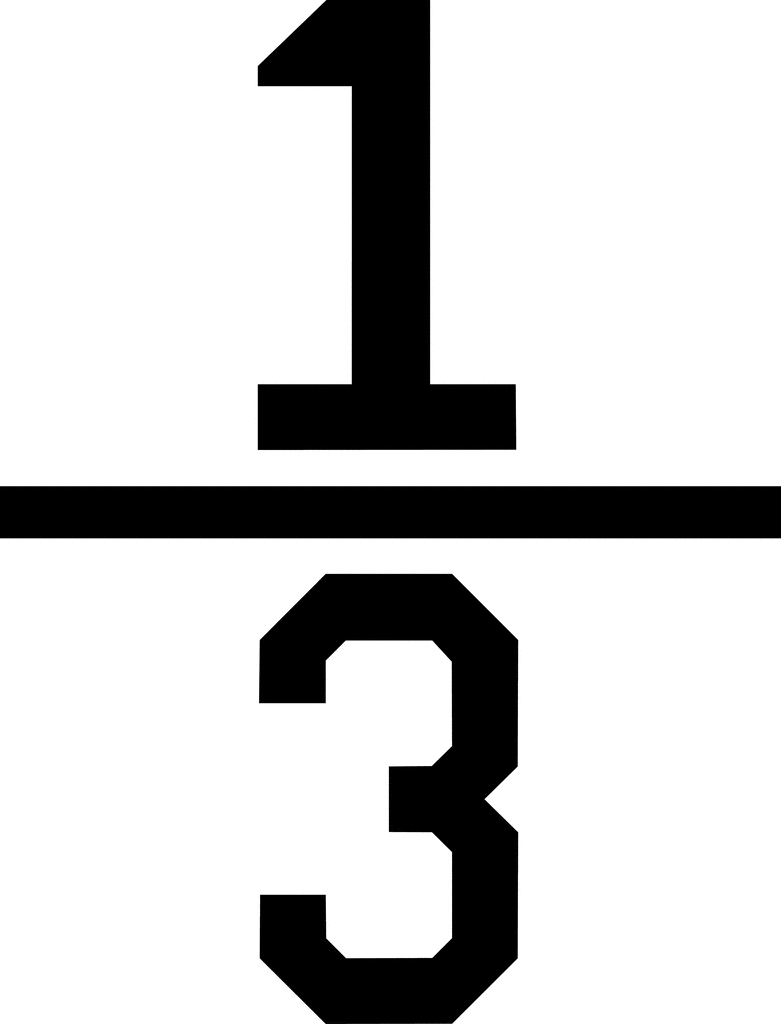
How much more does Joe have to eat of his candy bar?
How much more does Betsy have to eat?
Joe has 4/8 left to eat:

Betsy has 2/4 left to eat.

True or False:
When comparing two fractions with the numerator of one, the fraction with the bigger denominator is greater.
Example: 1/8 > 1/4
FALSE
When the numerator is the same, the bigger the denominator, the smaller the fraction because you are splitting the whole into more pieces.
Draw one bar model that represents both 1/4 and 2/8
Whiteboard demonstration
Use a bar model AND number line to show 3/4 and 6/8 are equivalent!


