A type of assessment that happens after a client describes a symptom of pain ( ie abdominal pain
What is a Focused Interview/Assessment?
Vital signs are the first step in this hands on type?
What is Physical Assessment
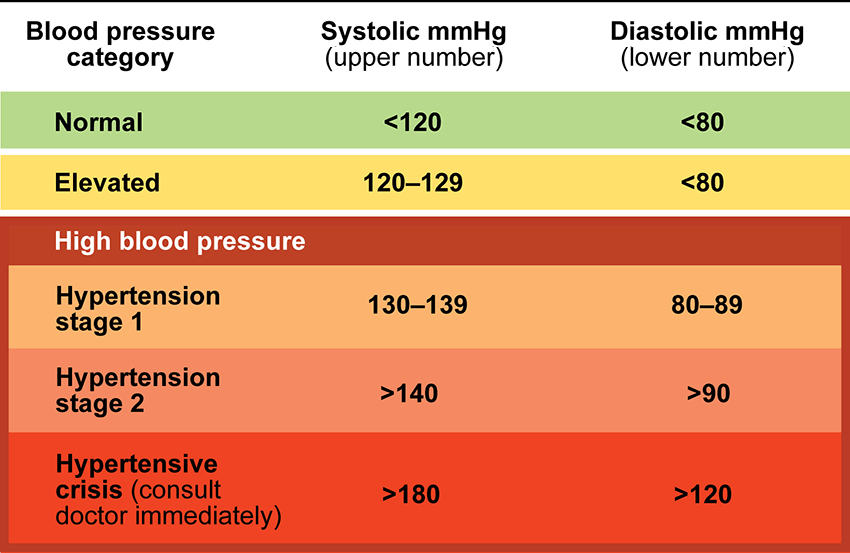
148/94 is this stage
What is Stage II Hypertension
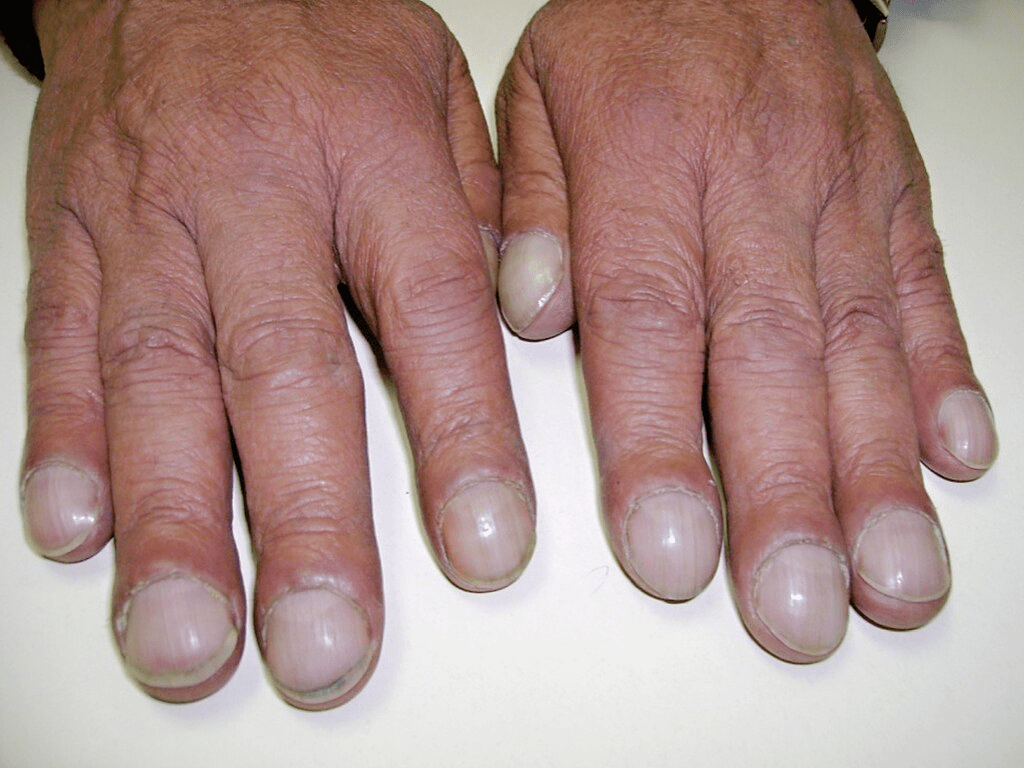
What is clubbing?
Bolded Steps to Assessing Lips, Gums, and Tongue for Head to Chest and an Priority 1 abnormal finding you may find for each
Inspection for color and moisture of lips, gum, tongue
cyanosis of lips, swollen tongue and abscess in gums
ineffective perfusion or ineffective airway
This type of Assessment identifies client's higher risks
What is Family history or Genogram
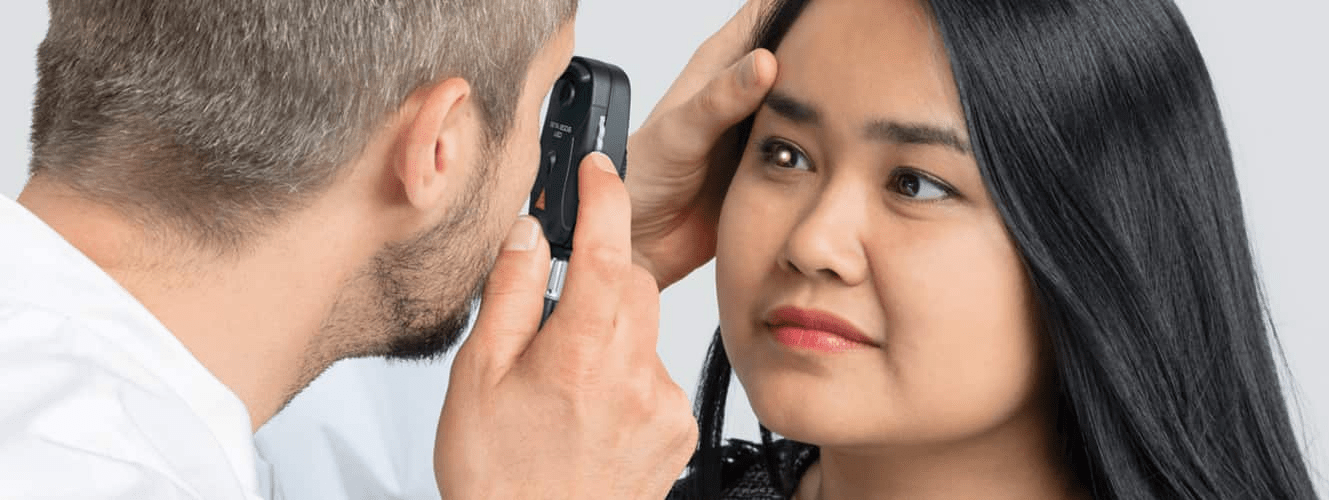

This Tool and Six parts of the Eye
What is Ophthalmoscope?
Five parts - Cornea, Iris, Sclera, Retina, Pupil , Conjunctiva
Heart Rate 98,RR 12,Temp. 99.1 F, BP 112/62
What is normal VS?
Cyanosis- decreased tissue perfusion
Pallor - lack of superficial capillaries
Jaundice- byproduct of bilirubin
Erythema- redness- superficial capillaries
Best location _lips, tongue, gums, nails and eyes.
Risk Level of Braden Score of 9 and interventions for this score
What is severe risk and Regularly changing a person's lying or sitting position is the best way to prevent pressure ulcers. Special mattresses and other aids can help to relieve pressure on at-risk areas of skin. Most pressure ulcers (bedsores) arise from sitting or lying in the same position for a long time without moving.
Vision/Hearing, Mobility, Home environment, social support, Activities of Daily Living
What are the components of a Functional Assessment
The interpretation of 20/60 vision
What is you must be at 20 feet to see what a person with normal vision can see at 60 feet.
Cap Refill >5 seconds and what it means in nursing terms
What is abnormal cap refill and A CRT longer than 2 seconds suggests poor perfusion due to peripheral vasoconstriction. 5. Peripheral vasoconstriction is an appropriate response to low circulating blood volume and reduced oxygen delivery to vital tissues.
The WRONG way and RIGHT Way to measure respirations in adults and infants
Adults Right- measure after pulse Wrong - tell patient you are measuring
Infants -Right full minute / try when they are sleeping Wrong - count while crying
Possible cause for Increased BP, Increased HR , Increased RR, Increased Temperature, Decreased Pulse Oximetry
What is Pain, Sepsis, Asthma, Infection, Exacerbation of COPD
- Multiply your weight in pounds by 703.
- Divide that answer by your height in inches (there are 12 inches in 1 foot).
- Divide that answer by your height in inches again.
What is BMI?
Ethnic background, religious preference, family patterns, food preferences, eating patterns, and health practices
What are cultural considerations in a nursing assessment?
3 Changes in Vital Signs for aging adults
What is faster HR, Slower HR , irregular HR, Atrial Fibrillation
This occurs due to inadequate oxygenation secondary to conditions that lead to an increase of deoxygenated hemoglobin or abnormal hemoglobin.
What is cyanosis?
The next thing to do when the UAP hands you abnormal HR of 142 from her vital signs task
Reassess by RN
Stature, nutrition, symmetry, posture, position, build
What is Body Structure assessment
Physical appearance, body structure, mobility, and behavior ***** Double Jeopardy*****
What are the four components of the General Survey?
Techniques to Assess skin temperature and turgor
What is use dorsal part of the hand and pinch forearm and sub-clavicular region for tenting
ABCDEF , IPPA , and PQRSTU definitions *****Double Jeopardy*****
 What is
What is 

What is lice?