What are the three functions of behavior maintained by positive reinforcement?
Attention, Access/Tangible, Automatic Positive SR
List two different categories of indirect assessments.
Structured Interviews, Checklists, Rating Scales, Questionnaires
List two different types of direct assessment methods.
ABC Narrative Recording; ABC Continuous Recording; Scatterplot Recording
How many conditions are in a traditional experimental functional analysis (EFA).
Four. (Contingent Attention; Contingent Escape; Alone; Play)
Note: Some EFAs include a fifth condition (Contingent Tangible)
When choosing an intervention based on an FBA, what is the most important consideration?
Functional Equivalence
What are the two functions of behavior maintained by negative reinforcement?
Escape; Automatic Negative SR
What is the primary difference between indirect and direct assessments?
Describe the difference between ABC Narrative Recording and ABC Continuous Recording.
ABC Narrative Recording: Each occurrence of the target behavior is recorded, with an open-ended description of any antecedent and consequent variables noted.
ABC Continuous Recording: Environmental events are selected and recorded, whether or not the target behavior occurs; events are coded rather than open-ended.
What are the two primary components of EACH condition in an EFA?
Motivating Operation (MO); Consequence
A timeout procedure is likely to be ineffective for which function(s)?
Escape; Automatic Negative SR
Describe the stimulus that is present in an escape contingency vs. an avoidance contingency.
Escape: Aversive Stimulus
Avoidance: Warning Stimulus (CMO-R)
Name two different rating scales you can use for an indirect assessment.
Motivation Assessment Scale (MAS), Motivation Analysis Rating Scale (MARS), Problem Behavior Questionnaire (PBQ), Functional Analysis Screening Tool (FAST), Questions About Behavioral Function (QABF)
Using the data below, calculate the conditional probability of the behavior occurring when access is denied.
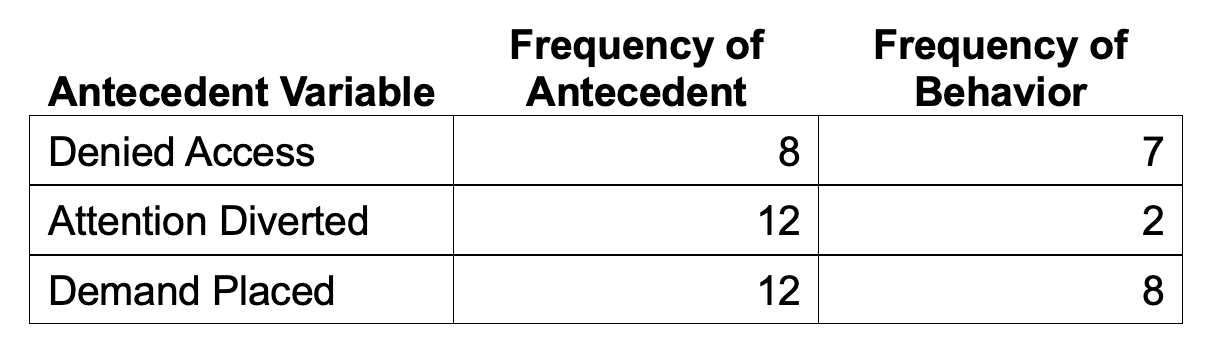
7 / 8 = 0.875
Name one limitation (or disadvantage) of a functional analysis.
Ignoring (Extinction); Planned Ignoring; NCR-Attention; DRA (Attention-Response); Timeout
Maggie is given dinner around 5pm every day. One evening, she lets out an excited bark right before the food is set down. A week later, Maggie is barking every evening around dinner time. Her behavior is likely an example of what?
Superstitious Behavior
Name one type of behavioral interview you can use for an indirect assessment.
Functional Assessment Interview; Behavioral Diagnosis and Treatment Information Form; Stimulus Control Checklist; Open-Ended Functional Assessment Interview
Given the graph below, what is the most likely function of the behavior?
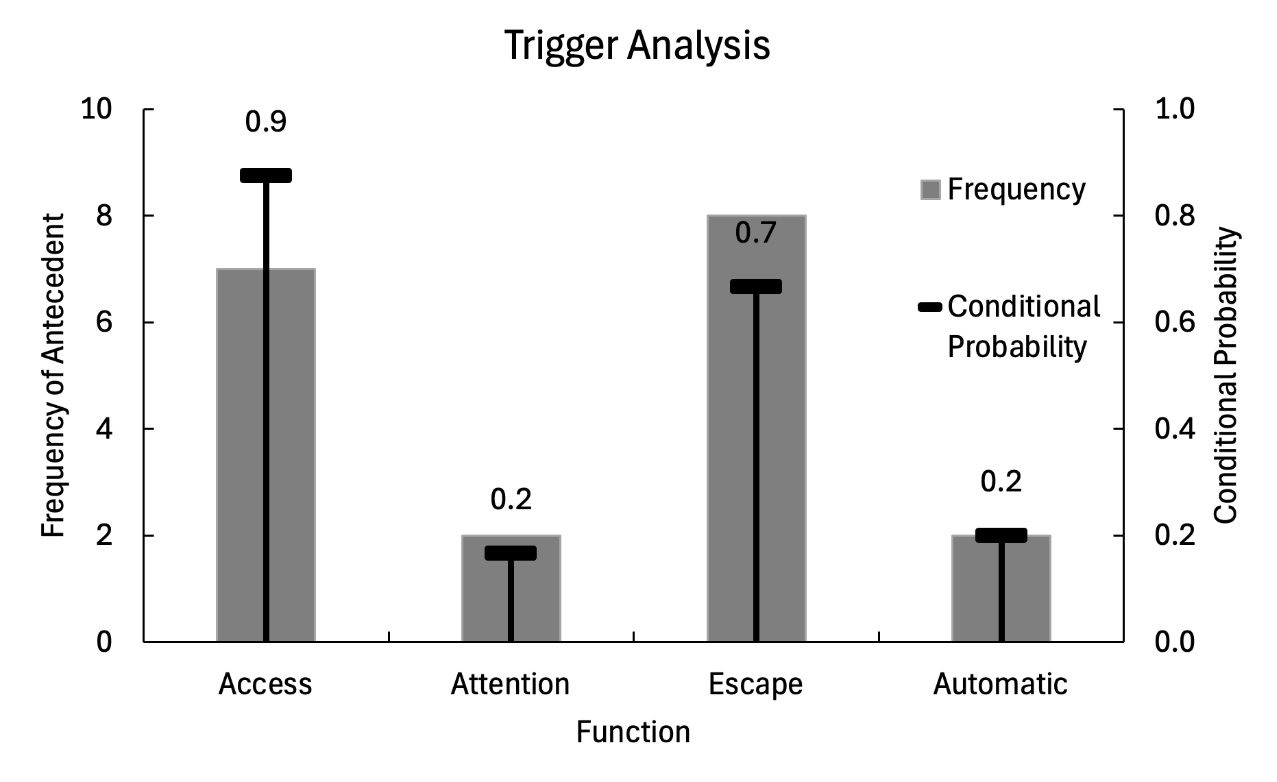
Access
Choose one condition in an EFA and describe a typical MO and consequence for that condition.
Play (Control): Low MO (reinforcement freely available); Behavior is ignored or neutrally redirected.
Contingent Attention: Attention is diverted or withheld; Mild attention is provided (e.g., soothing, or reprimand).
Contingent Escape: Task demand is placed; Demand withdrawn.
Alone: Low stimulation (no attention, no toys); Behavior is ignored or neutrally redirected.
Name two different interventions that might be appropriate (i.e., functionally equivalent) for aggression maintained by escape from task demands?
DRA (Requesting a Break; Help); Positive Practice; Overcorrection (or Restitutional Overcorrection); Escape Extinction; NCR Breaks; HPRS; Priming; Task Interspersal
After conducting a functional assessment, it's determined that Denise engages in problem behavior to escape from unwanted tasks in order to access attention and preferred activities. What kind of function is this?
Synthesized Contingency
List one strategy you can use to address the unreliability of indirect assessments.
Use in conjunction with direct assessments.
Test your hypotheses experimentally (e.g., PFA, EFA, TA).
Use multiple types of indirect assessments for comparison.
Have more than one person complete the same assessment independently.
An analysis that compares the probability a consequence will occur in the presence and absence of a particular behavior is called what?
Contingency Space Analysis
Name three variations of the experimental functional analysis.
Brief FA; FA in Natural Settings; Trial-based FA; IISCA; Latency FA; Precursor FA.
**Bonus: Describe the key differences between one of these and an EFA.**
Abhi engages in screaming behavior, often followed by severe SIB in the form of head-banging (both maintained by attention from others). What intervention(s) might be appropriate, given this information and considering Abhi's safety?
Reinforcing the screaming can function as an antecedent strategy for SIB (precursor intervention).