Disorders/ Management
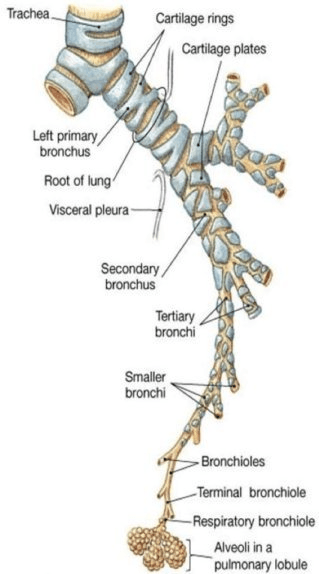
The structures transporting air into the lungs during breathing.
What is the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles?
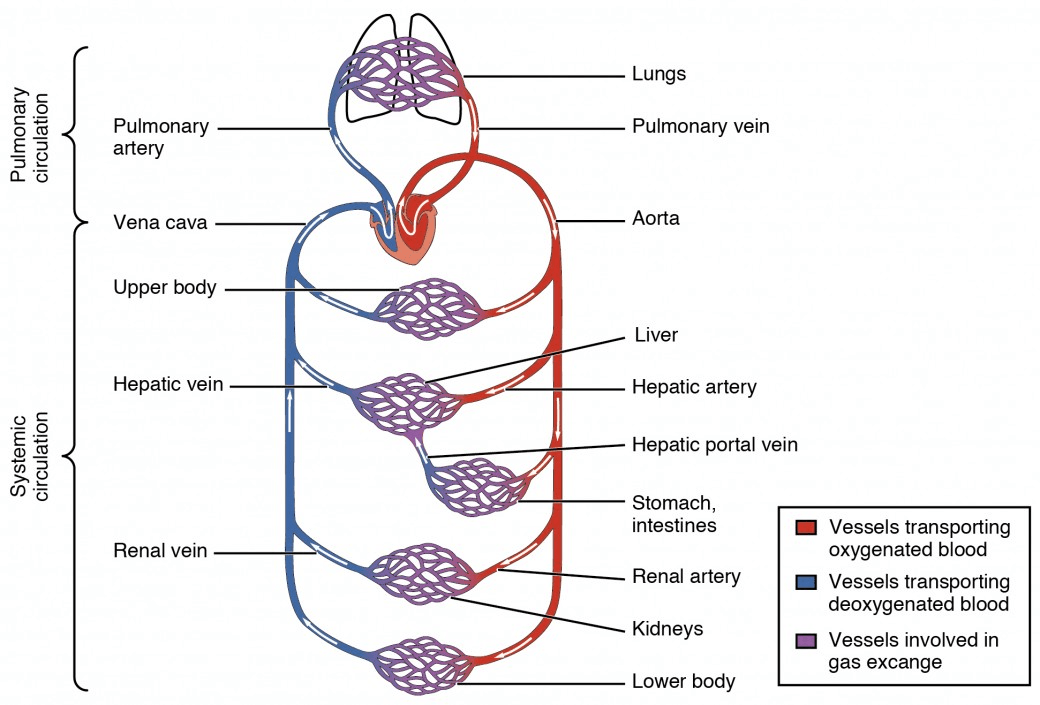
The structures transporting blood through the body.
What is the heart, arteries, veins and capillaries?
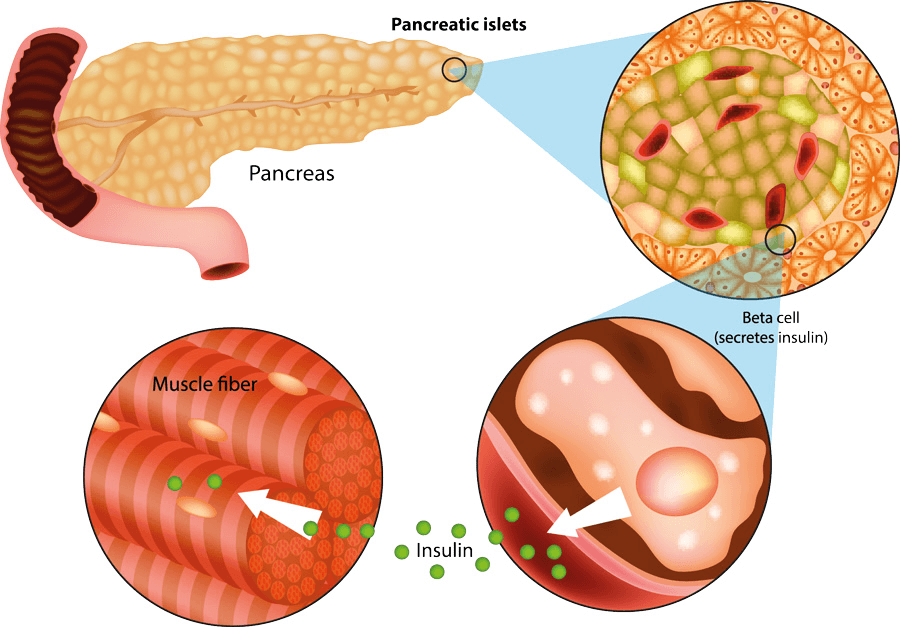
The organ and cells responsible for regulating blood glucose levels.
What is the pancreas and beta cells?
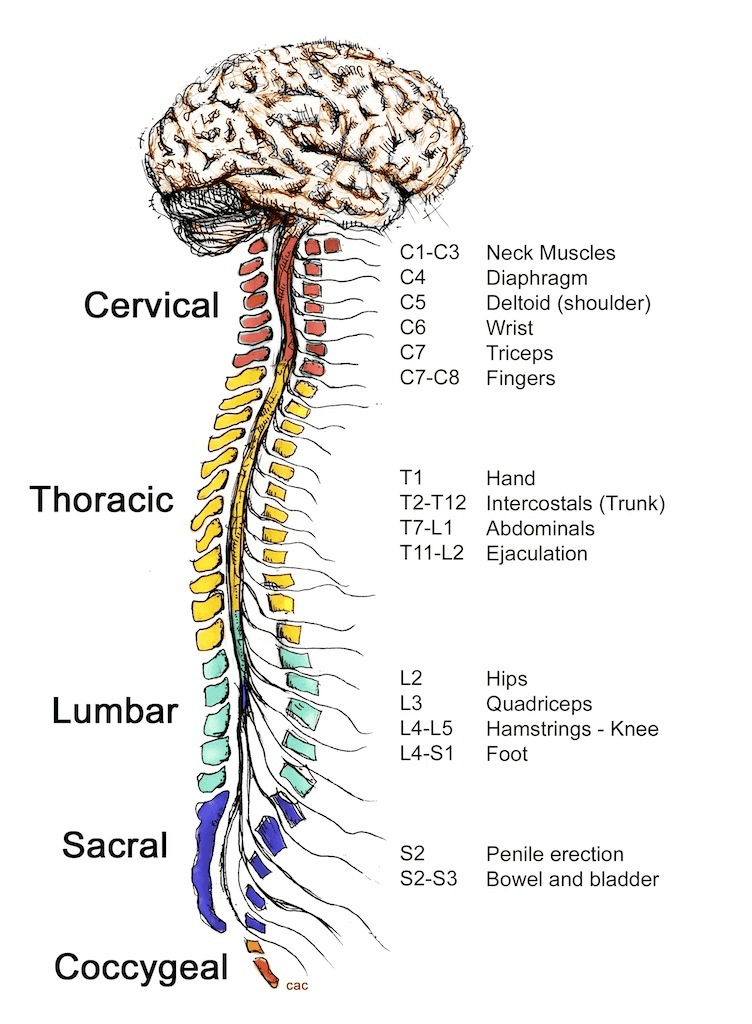
The structures responsible for transporting neural signals through the body.
What is the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves?
This standard guides nurses practice when communicating care with patients and providing an ISBAR handover to other health professionals.
What is Communicating for Safety Standard?

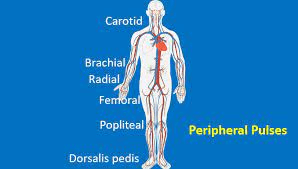
What are the sites where nurses can palpate pulse rate, rhythm and strength?

1. Breathing
2. Gas exchange
3. Transport of gases from the lungs into the circulating blood
4. Regulation of plasma pH
5. Sound/voice production
What are the functions of the respiratory system?
Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion.
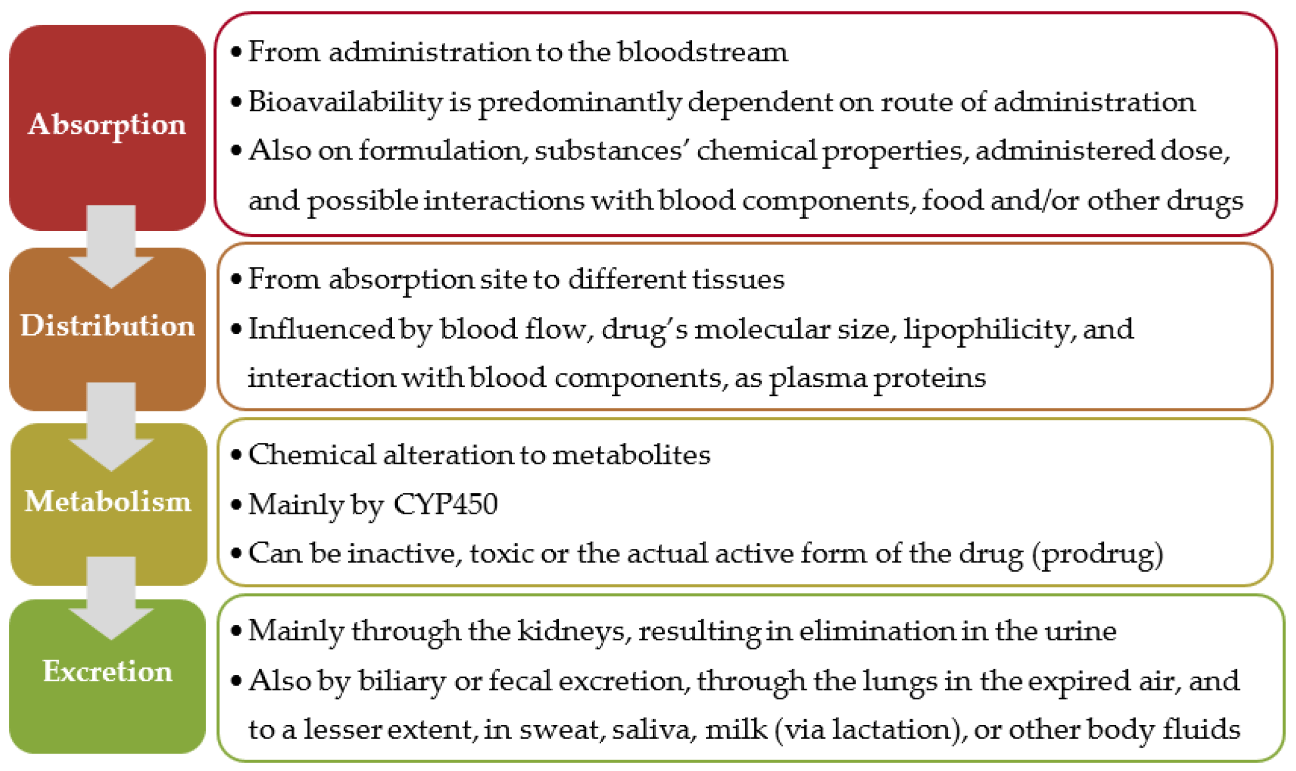 What is ADME?
What is ADME?
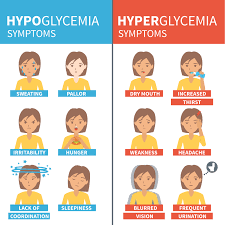
The blood glucose level measured at 2.8 mmol/L.
What is hypoglycaemia?
In general, signs and symptoms of hypoglycaemia may include:
- Confusion, fatigue, seizure, coma & potential death
- Tremors, palpitations & anxiety
- Hunger, diaphoresis & paraesthesia
FAST.
What is the Stroke Foundation resource used to provide education to the Australian population?
This standard guides nurses practice when providing care to patients.
What is the comprehensive care standard used for?

PEARL
What is the nursing acronym for pupils equal and reacting to light?
RATES is used.
What is the respiratory assessment?
R – Respiratory Rate, Rhythm, and depth
A – check Airway, Auscultate lung sounds
T – Tracheal deviation
E – Effort of breathing, use of accessory muscles
S – oxygen Saturation
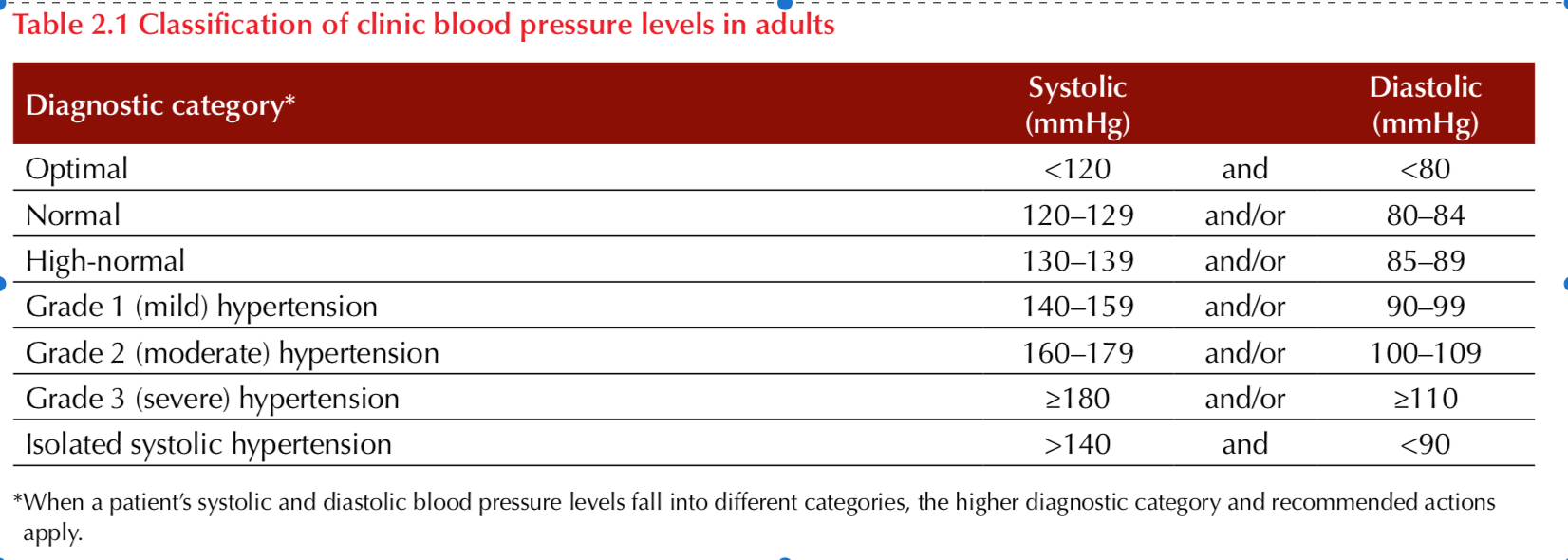
The Systolic blood pressure is 165/90 mmHg
What is hypertension?
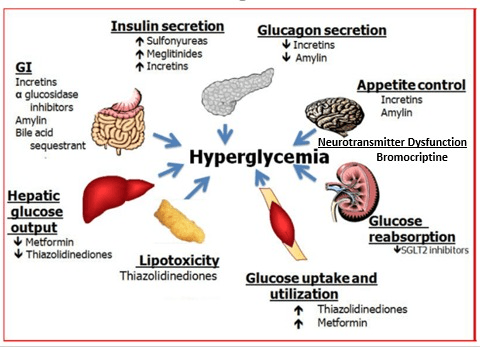
The condition that is treated with oral hypoglycaemic agents.
What is type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Falls history, functions in instrumental ADL and balance.
What does a falls risk screen assessment include?
1. Number of falls in the past 12 months: 0 to 3 or more
2. Prior to today, how much assistance was the individual requiring for ADLs: 0 Completely independent, 1 Supervision needed, 2 Some assistance required & 3 Completely dependent
3. When walking or turning, does the person appear unsteady or at risk of losing their balance: 0 No unsteadiness observed, 1 Minimally unsteady, 2 Moderately unsteady & 3 Consistently and severely unsteadyOR unable to observe walking
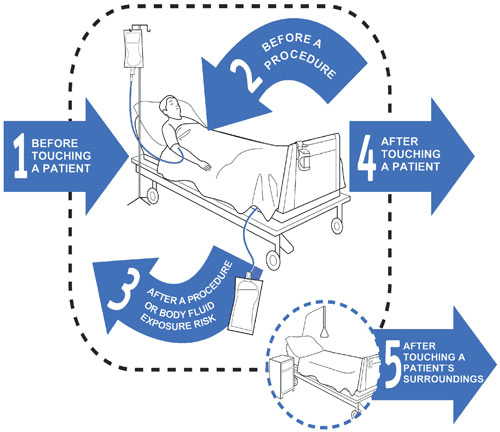
This standard guides nurses practice when performing the 5 moments of hand hygiene.
What is the preventing and controlling infections standard used for?
- Obtain a cardiovascular health history
- Inspect the skin (Colour, Warmth, Movement & Sensation) + Capillary refill
- Palpate for peripheral pulses (Rate, Rhythm, and Strength), skin turgor & oedema
- Palpate and auscultate blood pressure
- Auscultate for heart sounds (Aortic, Pulmonary, Tricuspid and Mitral valves)
What are the components of the focused cardiovascular assessment?
The use of accessory muscles, sternal recession, tracheal tug, intercostal recession, nasal flaring and pursed lip breathing.
What are the signs of respiratory distress?
This syndrome encompassing several different
types of cardiac dysfunction that result in inadequate perfusion of tissues with oxygen and blood-borne nutrients.
What is heart failure?
Type 1 diabetes mellitus signs and symptoms.
What is weight loss, frequent urination, irritability, blurry vision and fruity breath?
- Confirm patient details
- Obtain a patient history of neurological system
- Assess mental health status & level of consciousness
- Assess 12 Cranial nerves
- Assess motor strength and sensation
- Document findings
- Report out of range values
- Answer any patient questions
What is a focused neurological assessment?
This standard guides nurses practice when including the patient in the care decision making.
What is the partnering with consumers standard used for?

- Obtain a respiratory health history
- Inspect the thorax
- Palpate the thorax
- Palpate for tactile and vocal fremitus
- Percuss the thorax
- Auscultate for breath sounds
- Repeat Steps 2 to 6 on both the anterior and posterior thorax
What are the components of a focused respiratory system assessment?
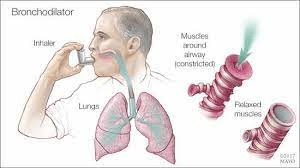
The respiratory medications beta-adrenoceptor agonist, short acting beta2-agonist (relievers) & long-acting beta2-agonist (controllers).
What are bronchodilators?
ABCDD medications.
What is the acronym for cardiovascular system medications for heart failure?
- A – Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (Antihypertensive Medication)
- B – Beta blockers (Slows Heart Rate)
- C – Calcium Channel blockers (Slows Heart Rate and Lower Blood Pressure)
- D – Digoxin (Strengthens Contractility of Cardiomyocytes and Slows Heart Rate)
- D – Diuretics (Loop or Thiazide, Reduce blood plasma volume)
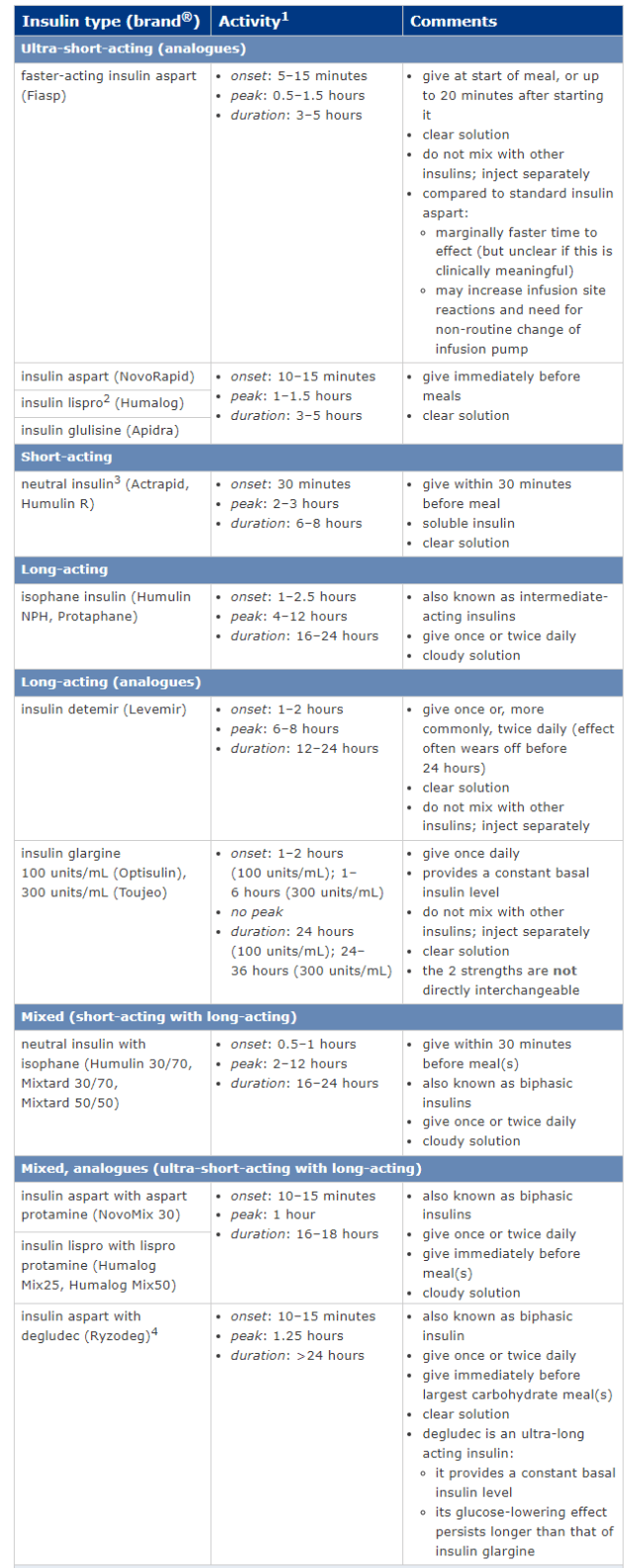
Increase or restore ability to metabolise glucose by enhancing cellular glucose uptake; inhibit endogenous glucose output and lipolysis.
What is the mode of action of insulin?
Stroke, intracranial infection, cardiac arrhythmias, hypoxia, hypo/hyperglycaemia, alcohol and blood loss.
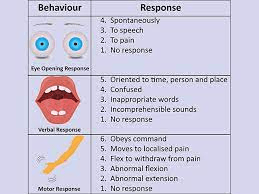
What are the common reasons for a drop in GCS and require emergency team to be called?
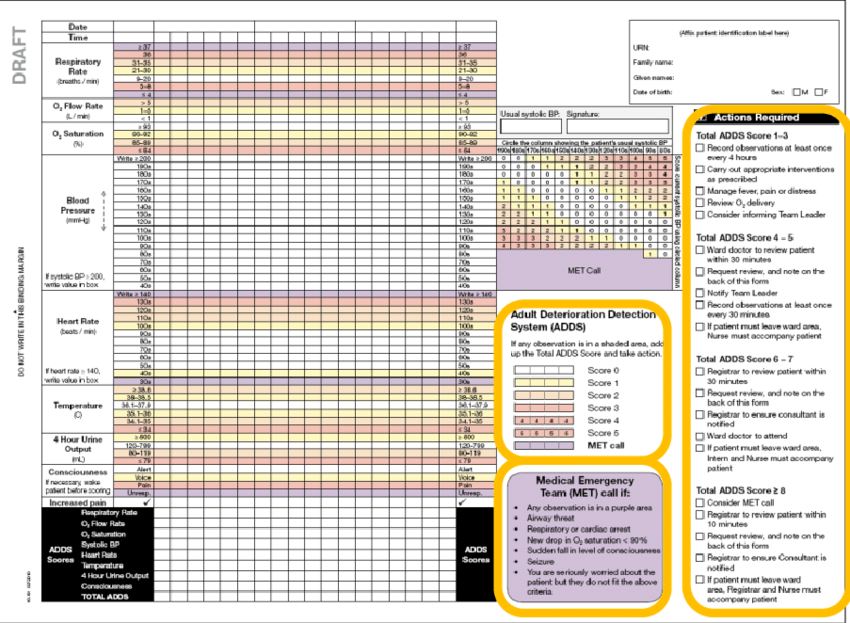
This standard guides nurses practice when a nurse calls a MET call after assessing the patients' blood pressure and heart rate reaching the purple zone on the RADAR chart.
What is the recognising and responding to acute deterioration standard used for?

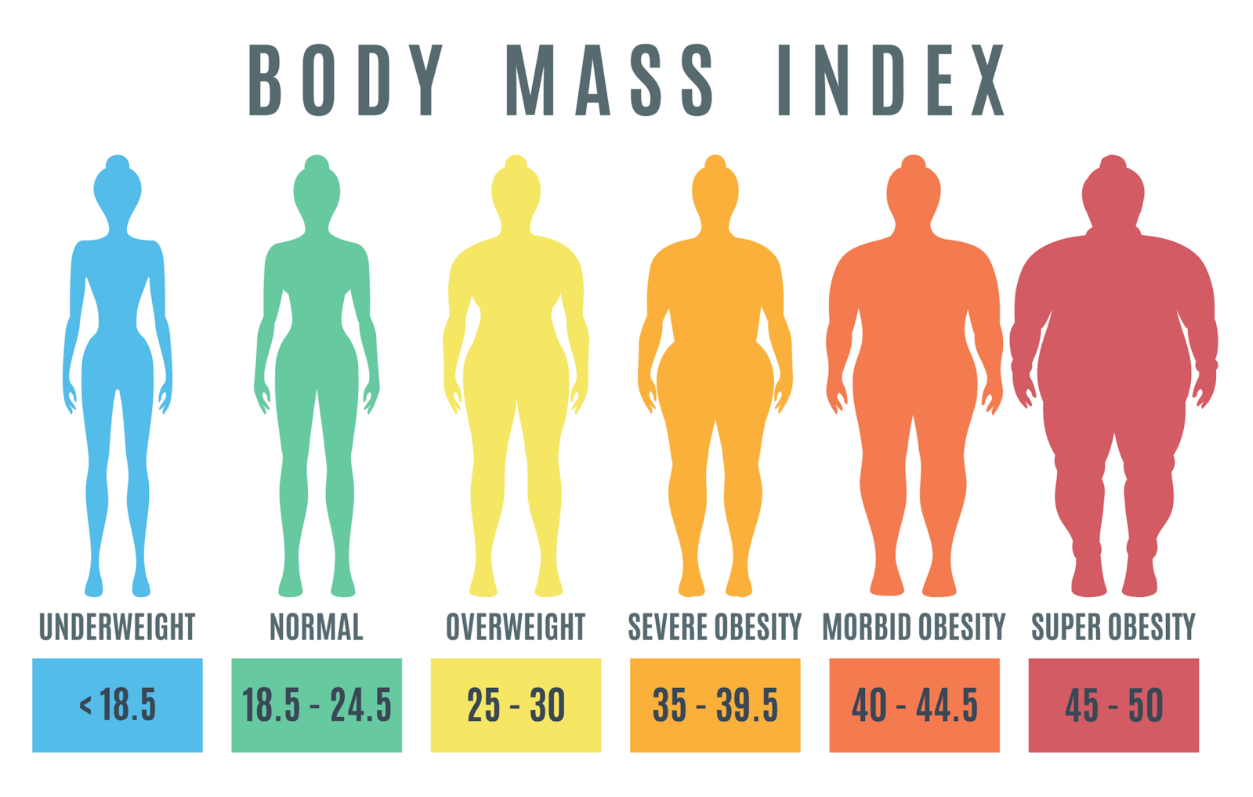
The BMI >30 kg/m2
What is obesity?