All medications given beneath the skin are administered via the _____. (chapter 35)
Parenteral route
Unintended effects that are more severe or harmful than side effects are called ____. (chapter 35)
Adverse effects
Which are included in the oral route of administration? (chapter 36)
A. Swallowing
B. Sublingual
C. Inhaling
D. Buccal
E. Nasal
A, B, D
Health-care provider's order: warfarin (Coumadin) 6 mg PO daily at noon. Drug on hand: warfarin 2 mg oral tablets. How many tablets will you administer per dose? (chapter 35)
3 tablets
To help distinguish between drugs that sound and look familar.
Medication that is administered under the tongue. (chapter 36)
Sublingual
The liquid portion of the blood is known as _______. (chapter 38)
Plasma
Before you can safely administer IV medications, there are several things you must know including: (chapter 38)
A. If the patient has ever had IV medications before
B. The patient's medication allergies
C. The patient's disease or condition
D. Sterile technique
B, C, D
Health-care provider's order: pravastatin sodium (Pravachol) 20 mg PO daily at bedtime. Drug on hand: Pravachol 40 mg oral tablets. How many tablets will you administer per dose? (chapter 35)
0.5 tablets
You are caring for a patient who has had a CVA. He is able to eat pureed foods but cannot swallow whole pills without choking. How will you administer his medications that are in tablet form? (chapter 36)
Crush each tablet separately and give with applesauce or pudding.
The exact ingredients of a medication. (chapter 35)
Chemical name
Another term for blood clot is _______. (chapter 38)
Thrombus
You are administering medication to a child. How can you ensure that you have calculated the correct dose before you administer it? (chapter 35)
A. Call a pharmacist and ask for the ranges for pediatric dosages of this medication.
B. Ask another nurse to check your calculations and verify that it is the correct dose.
C. Ask the child's parent how much of the medicine has been administered to the child in the past.
D. Determine half of the adult dose and administer that to the child.
B
The health-care provider's order reads as follows: Clindamycin 400 mg IM every 6 hours. The medication label reads: Clindamycin 155 mg/mL. How much medication will you administer? Round to the nearest hundredth. (chapter 37)
2.6 mg
Label B.
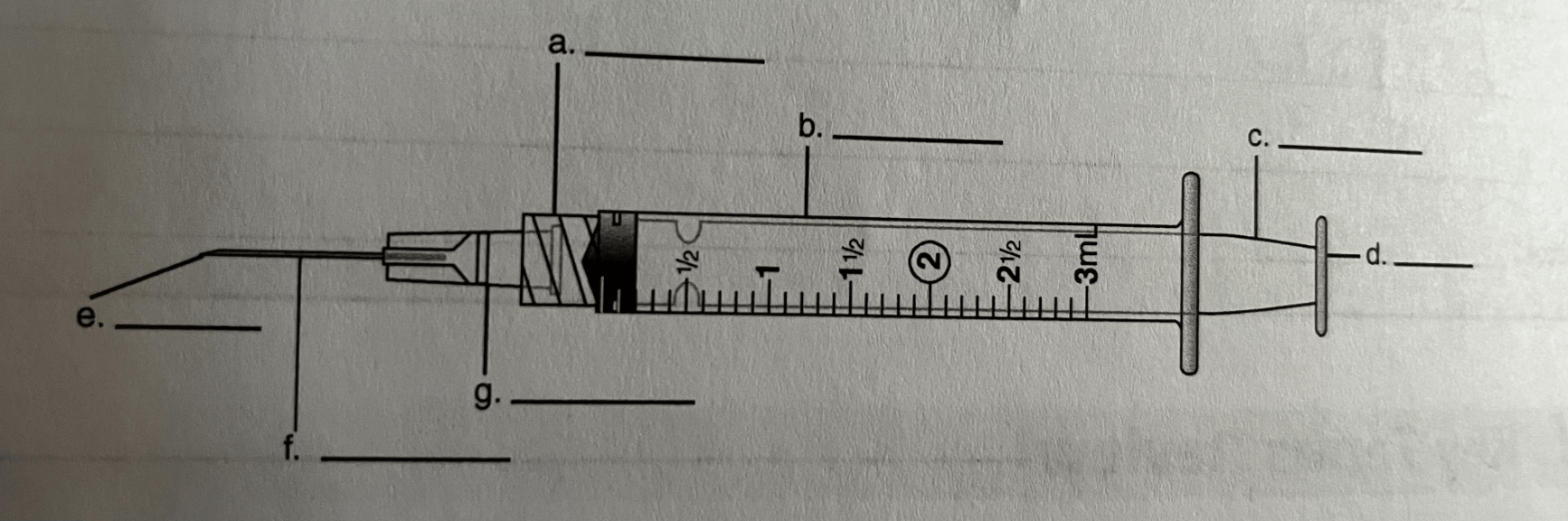
Barrel
A small, sealed glass drug container that must be broken to withdraw the medication. (chapter 37)
Ampule
An ________ tablet contains an outer coating that does not dissolve until the medication reaches the intestines. (chapter 36)
Enteric coated
Which of the following is the most important concept related to IV therapy? (chapter 38)
A. Maintain strict asepsis
B. Monitor IV infusion rate
C. Maintain fluid balance
D. Educate the patient about the IV therapy
A
The health-care provider's order reads: Ampicillin 175 mg IM every 6 hours. The medication label reads: Ampicillin 500 mg/2 mL. How much medication will you administer? Round to the nearest hundredth. (chapter 37)
0.7 mL
The interaction between the two drugs that causes a change in the activity or components of one or more of the drugs is known as a ________. (chapter 38)
Drug-drug interaction
Injection technique that closes the needle tract in the tissue, preventing seepage of medication. (chapter 37)
Z-track
A ______________ tablet is designed to slow the absorption of the drug. (chapter 36)
Sustained-release
When you prepare to administer medications through a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tube, it is important to determine: (chapter 36)
A. The compatibility of the tube feeding formula with the ordered medications
B. Whether the medications can be crushed for administration through a PEG
C. Whether to mix the crushed medications with water or with just juice
D. The brand and length of the PEG tube that is in place.
A, B, C
The health-care provider's order reads: Heparin 15,000 units subcut every 12 hours. The medication label reads: Heparin 20,000 units per mL. How much medication will you administer? Round to the nearest thousandths. (chapter 37)
0.75 mL
Label E.
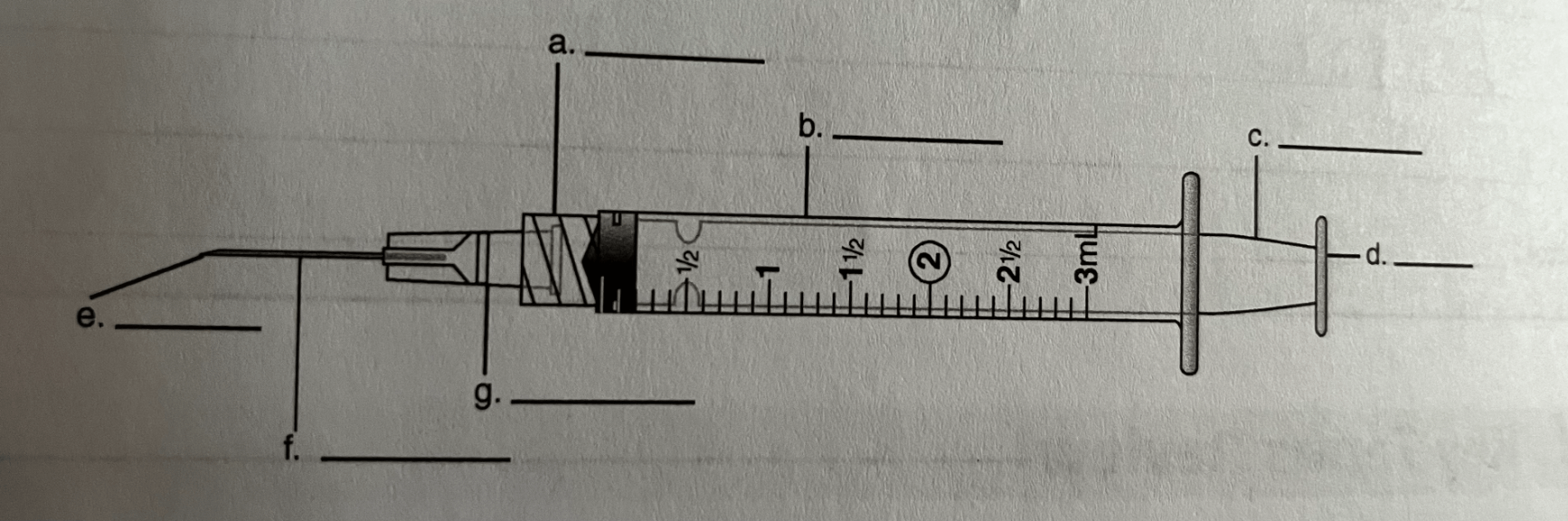
Bevel
Leakage of nonvesicant IV fluid or medication into the tissue surrounding the IV insertion site. (chapter 38)
Infiltration
The subcutaneous connective tissue layer contains _____ tissue and larger _______ _______ and _______. (chapter 37)
Fatty, blood vessels, nerves
Which of the following drugs requires a second and third nurse to verify the dosage? (chapter 37)
A. Insulin
B. Epinephrine
C. Heparin
D. Purified protein derivative
A, C
The health-care provider's order reads: Lantus insulin 17 units subcut daily at 0730. The medication label reads: Lantus (insulin glargine [rDNA origin] injection) solution for subcutaneous injection. How much insulin will you draw up?
17 units
You are administering omeprazole (Prilosec) via a PEG tube. Explain how this will be different from administering metoprolol (Lopressor), and list the reason for the differences. (chapter 36)
Mix omeprazole with apple juice or orange juice instead of water. Flush the tube with the juice also to prevent clumping of the granules and to preserve their enteric coating. Metoprolol can be crushed and mixed with a small amount of water for administration. The tube can be flushed with water too.