Name
Causative organism
Black Piedra, caused by Piedra hortae
Firm adherent nonmobile stone-like concretions on shaft of hair, facial >> pubic hair, +breakage
Malassesia - curved septate hyphae, clusters of thick walled budding yeast
"ziti and meatballs"
Most common causes of tinea capitis
#1 US: Trichophyton tonsurans
#1 worldwide: Microsporum canis
An Indian patient with a foot injury presents with slowly progressive painless nodules with sinus tracts draining black grains. What is the disease process?
Eumycetoma
Madura foot- fungal and bacterial causes
- Eumycetoma (fungus): Pseudoallescheri boydii (white) most common
- Actinomycetoma (bacterial): Nocardia brasilensis (white) most common
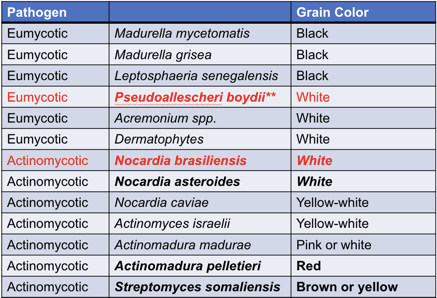
Black grains only seen in eumycetoma
Red grains only seen in actinomycetoma
Southeast-Asian man in stagnant water with eczematous plaque and olecranon bursitis
What would you expect to see on path?
Protothecosis, most common cause Prototheca wickerhamii
Path: Morula (soccer ball)
Name
Causative organism
Tinea Nigra, caused by Hortaea wernicki
Name the finding, the disease, and the causative organism
Chromonblastomycosis, caused by Fonsecaea pedrosoi
Microscopy: pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, granulomatous dermal inflammation with medlar bodies ("copper pennies")
Presentation: Slow growing verrucous plaques on the feet of shoeless tropical agricultural workers
Causative organisms, underlying disease?
A)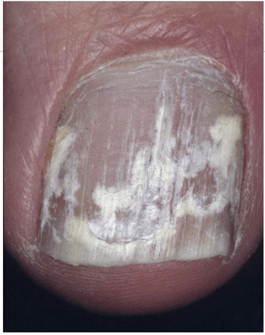
B)
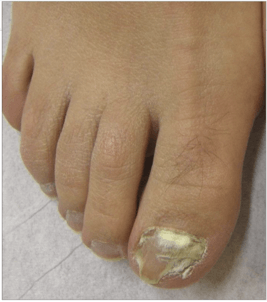
C)
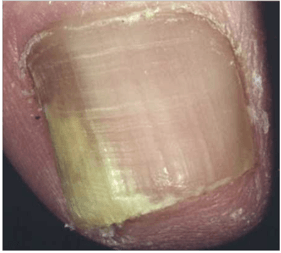
A) Superficial white- T. mentagrophytes (adults), T. Rubrum (children)
B) Proximal subungual- T. Rubrum, increased risk in HIV
C) Distal subungual- T. rubrum
Most common causative organism
Tinea barbae
T. verrucosum, T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans, T. rubrum
Most common fungus cultured in burn patients
Fusarium- Fusarium solani
What are the most common causes of:
- Tinea corporis
- Tinea cruris
- Tinea imbricatum
- Majocchi granuloma
- Tinea corporis: T. rubrum
- Tinea cruris: T rubrum > E. floccosum
- Tinea imbricatum: T. concentricum
- Majocchi granuloma: T. rubrum
Causative organism?
Treatment?
Sporotrichosis:
- Cigar shaped yeast in culture
- Histopath: asteroid body with eosinophilic fringle, Spendore-Heoppli phenomenom
Treatment: Itraconazole, SSKI
List the causes, most common?
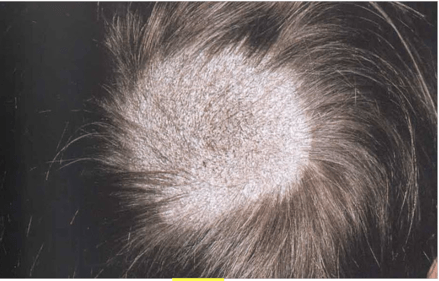
"Black dot" tinea capitus from Endothrix
T. rubrum (#1), T. gourvilli, T. yaounde, T. tonsurans, T. soudanese, T. violaceum
“Ringo Gave Yoko Two Squeaky Violins”
-------------------------
Ectothrix pattern
- Fluorescent: M. canis, M. audouinii, M. distortum, M. ferrugineum, M. gypseum, T. schoenleinii
"Cats And Dogs Fight and Growl Sometimes"
- Non-fluorescent: M. nanum, T. meginii, T. mentagrophytes, T. rubrum, T. verruocusum
Causative organisms in a locker room epidemic
Tinea cruris
Causes: T. rubrum > E. floccosum
E. floccosum is commonly associated with “epidemics” of tinea cruris in locker room, arthroconidia are viable in scale for long periods of time
A patient being treated for an invasive fungal infection develops blisters and erosions on the face and dorsal hands after a day out in the sun. What antifungal are they most likely receiving?
Voriconazole
Cutaneous adverse effects include:
- Severe phototoxicity, including pseudoporphyria and xeroderma pigmentosum-like changes
- Increased risk of SCC
Name the disease and the most common causative agents
A)
B)
C)
A) Moccasin: T. rubrum > E. floccosum
B) Interdigital: T. interdigitale, T. mentagrophytes
C) Ulcerative/vesicular/bullous: T. mentagrophytes
Name the disease and causative organism
Bonus: treatment?
Paracoccidiomycosis, most common cause Paracoccidiomycosis brasiliensis
Brazillian man who chews on sticks, with painful perioral ulcerative nodules and massive cervical and submandibular lymphadenopathy
Path: Mariner’s Wheel pattern
Treatment: Mild: bactrim; moderate: itraconazole; meningeal: fluconazole or voriconazole; severe: ampho B
What is the preferred treatment for:
1. Endothrix organisms
2. Ectothrix organisms
1. Endothrix: Terbinafine (highly effective against endothrix, most commonly T. tonsurans)
2. Ectothrix: Griseofulvin (more effective in tinea capitis aused by M. canis than terbinafine)
Central American man with painless ear nodules
1. What would you expect to see on path
2. Treatment
Lobomycosis, caused by Lacazia loboa, infects freshwater dolphins in South American rivers
Path: Bulbous chains of yeast-like thick-walled cells “brass knuckles” “pop beads”
Treatment: excision
50 year old male presents with these papulonodules on the hand, CD4+ lymphocyte count is 45.
1. What stains would you use to highlight the causative organism
Cryptococcus: Cryptococcus neomorphans
Histopath: single celled sphere with a double cell wall and thick capsule ("halo appearance"), collections of organisms look like soap bubbles
Stains: India ink, PAS, mucicarcine, GMS, Fontana-Masson
What is the cause of the hypopigmentation in this disease
Tinea versicolor- caused by Malassezia furfur and Malassezia globosa
Hypopigmenation is due to melanocyte inhibition by azalaic acid (dicarboxylic acid byproduct of Malassezia)
Lipophilic--> favors sebum rich areas
What is the treatment of choice for this biopsy finding
Rhinosporidiosis, most common cause Rhinosporidium (protozoa).
Geography: tropics (southern India and Sri Lanka)
Path: Giant sporangia with thousands of endospores
Treatment: excision
What is the MOA of terbinafine
Inhibits squalene epoxidase (which catalyzes conversion of squalene to lanosterol)--> decreased cell membrane synthesis
This organism causes a resistant tinea pedis that is clinically indistinguishable from dermatophytosis
Scytalidium hyalinum, Scytalidium dimidiatum
Patient walks into clinic with this verrucous plaque
1. What would you expect to see on path
2. What is the MOA of your preferred treatment
Blastomycosis (central healing)
1. Broad based buds
2. Intraconazole (Ampo B for severe disease):
Azole antifungals inhibit 14α demethylase (catalyzes conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol) → ↓ergosterol → ↓cell membrane synthesis, ↑ membrane rigidity/ permeability, growth inhibition, and cell death