Red current jelly sputum, lobar pneumonia in alcoholics and diabetics. Common a nosocomial aspiration pneumonia, and is becoming increasingly multi-drug resistant.
What is klebsiella.
This treatment should be given always when they present with urethritis/PID or you are suspicious of the clap.
Ceftriaxone + doxycycline.
What is the number 1 cause of UTI's in women and men.
What is E. Coli.
This Gram negative bacilli is not able to ferment lactose, but is oxidase positive and catalase positive.
What is Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Patient comes in with this very common type of UTI, with fever flank pain and dysuria, and it looks like this after urine cultures on MacConkey agar.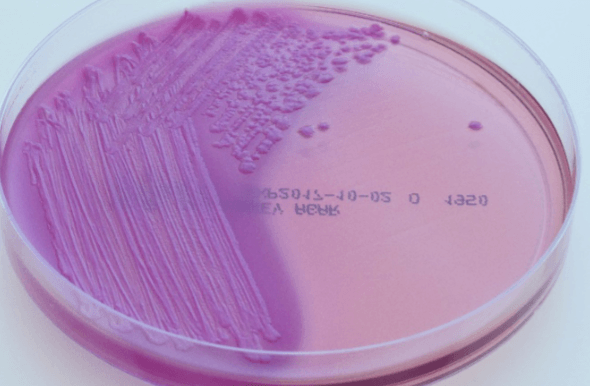
What are E. Coli, klebsiella and enterobacter.
This is represented by the water truck's title in the back.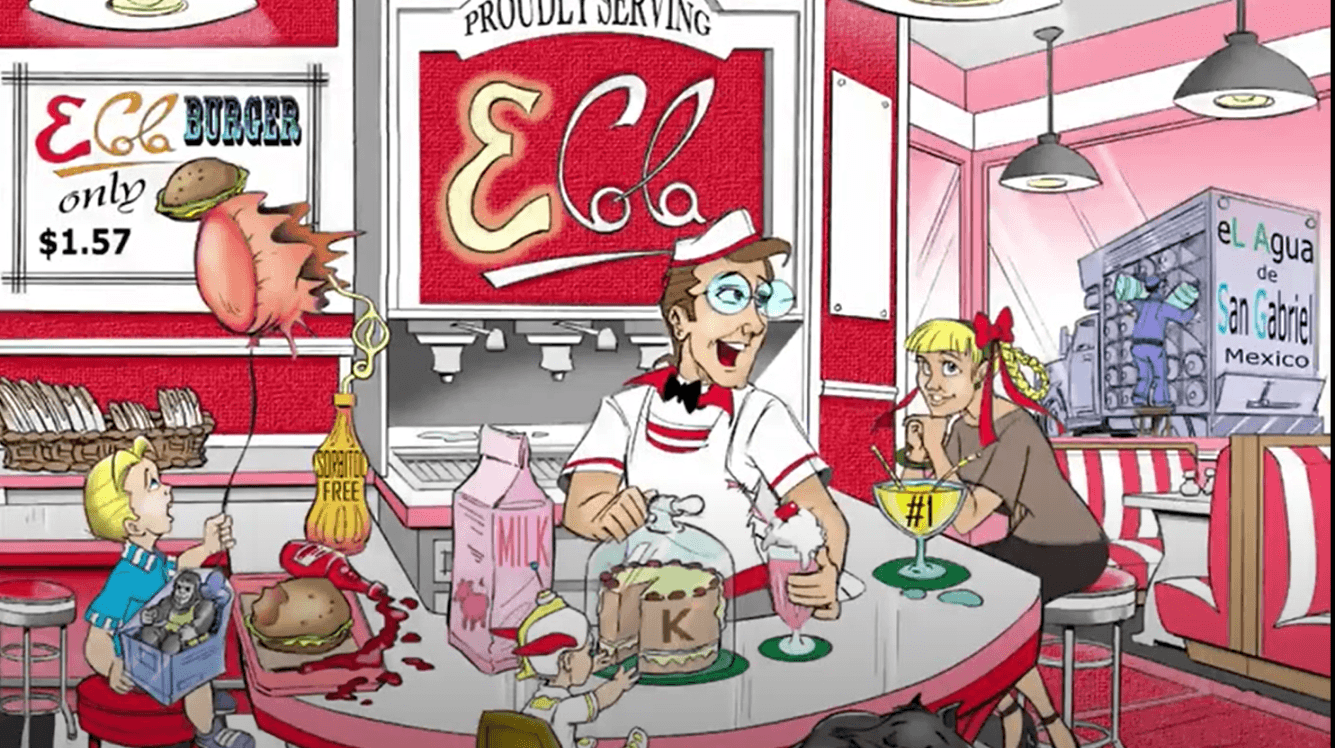
What are the two enterotoxins produced by E. Coli (heat labile with cAMP, and Heat stabile with cGMP)
This comma shaped bug grows in alkaline media and releases an enterotoxin that increases cAMP, causing rice water diarrhea.
What is vibrio cholerae.
The most common gram negative meningitis should be treated with this medication.
What is ceftriaxone, with rifampin prophylaxis for close contacts.
This strain of a bug produces heat labile and heat stabile enterotoxins that produce a watery diarrhea. It is noninflammatory as well as noninvasive, however other strains of the same bug are quite nasty.
What is ETEC.
This gram negative bacilli can ferment lactose and has fimbriae and a k capsule. In addition, it has multiple different strains leading to different presentations.
What is Escherichia coli.
This bug caused wrist/ankle swelling and pain, a fever and presents with a small tender lesion. Synovial fluid shows cloudy fluid with G- diplococci. 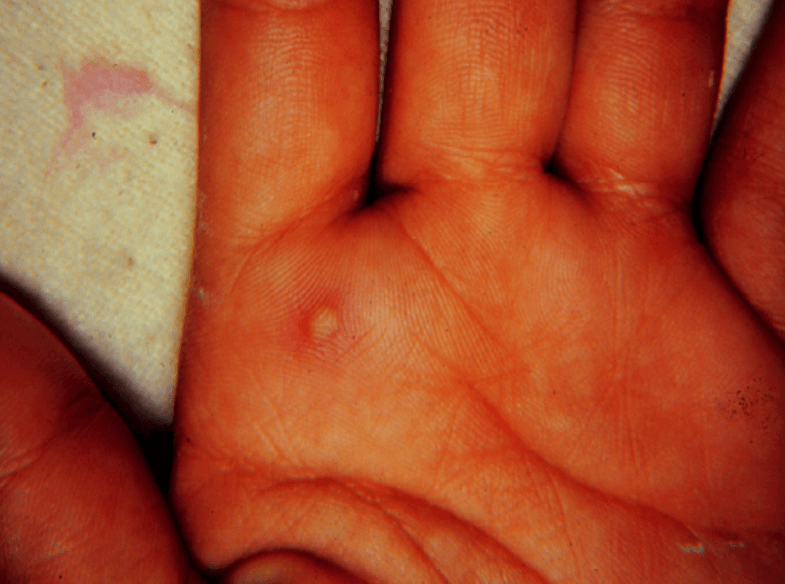
What is N. Gonorrheaa
The two suitors on the left (not the accordion player) represent this about pseudomonas.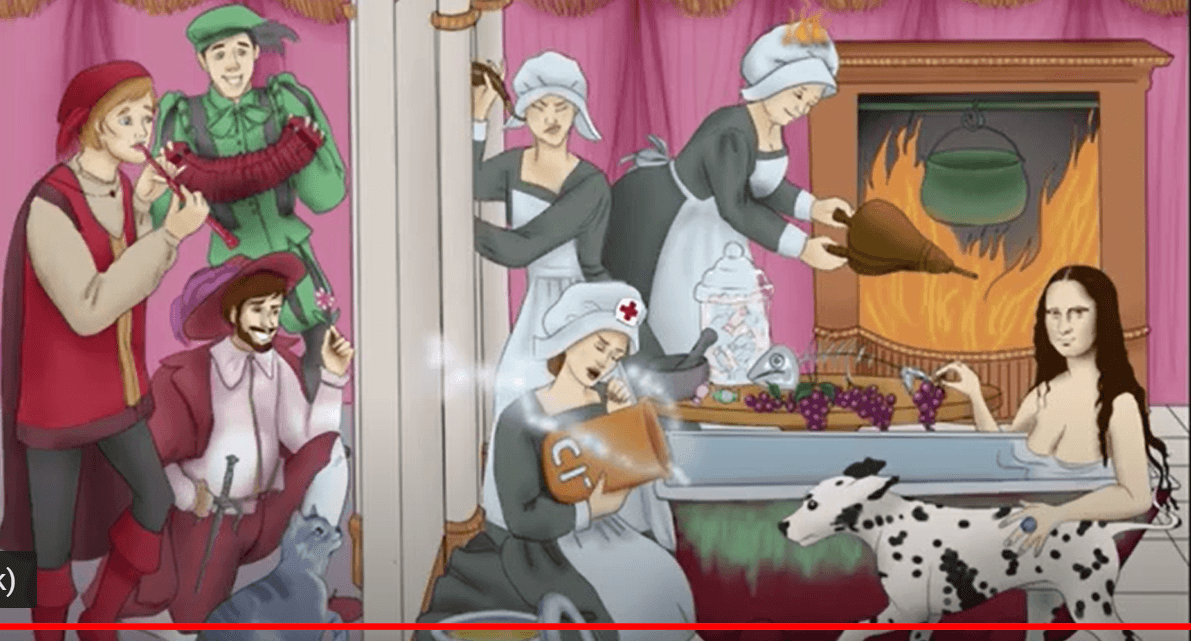 
What is that they can be treated with piperacillin as well as fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides.
This bug loves water, and produces a grape like odor when grown, and makes a blue-green pigment. Commonly associated with pneumonia, sepsis, ecthyma gangrenosum, UTIs, osteomyelitis, Otitis externa, and hot tub folliculitis.
What is Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
A common water-loving nosocomial infection that causes pneumonia, sepsis, UTIs osteomyelitis and otitis externa could be treated with these medications.
What are Carbapenems, aminoglycosides, monobactams, fluoroquinolones, 3rd/4th gen cephalosporins and extended spectrum PCNs such as piperacillin and ticarcillin.
What is Haemophilus influenzae.
This gram negative bacilli can't ferment lactose and is oxidase negative, but dose produce H2S on TSI agar. They have to major different presentations depending on the specific strain, but both have flagella, require large inoculum to be infectious and produce endotoxin.
What is salmonella.
A patient comes in with this infection that they got after eating undercooked meat. They present with anemia, thrombocytopenia and acute kidney injury after a bout of hemorrhagic dysentery notably absent of any fever.
What is EHEC, most likely O157:H7
This is represented by balloons and plates in this sketch. 
What is hemolytic uremic syndrome.
This gram negative diplococci can cause neonatal conjunctivitis, septic arthritis, PID and fits-hugh-curtis syndrome. It is often co-infected with another bug.
What is Neisseria gonorheae
A disease that presents with undulant fevers, night sweats and arthralgias that survive in macrophages in the reticuloendothelial system, obtained from contaminated animal products should be treated with this medication
What are doxycycline and rifampin.
This bug is acid-labile, and produces and endotoxin causing constipation then diarrhea. It can progress to a feverish syndrome with rose spots on abdomen, fever and GI ulceration and hemorrhage. It is able to maintain a carrier state within the gallbladder.
This bug is a gram negative diplococci, which can metabolize glucose and produces IgA proteases. There are two main strains, which cause two wildly different, but both troubling presentations.
A child comes in with an extensive cough, followed by intense inspiration and post-tussive vomiting. They state that they have been like this for over a month. This used to be common, but has been mostly stopped by vaccinations.
What is bordetella pertussis.
This bug is commonly found infecting bite wounds from both cats and dogs.
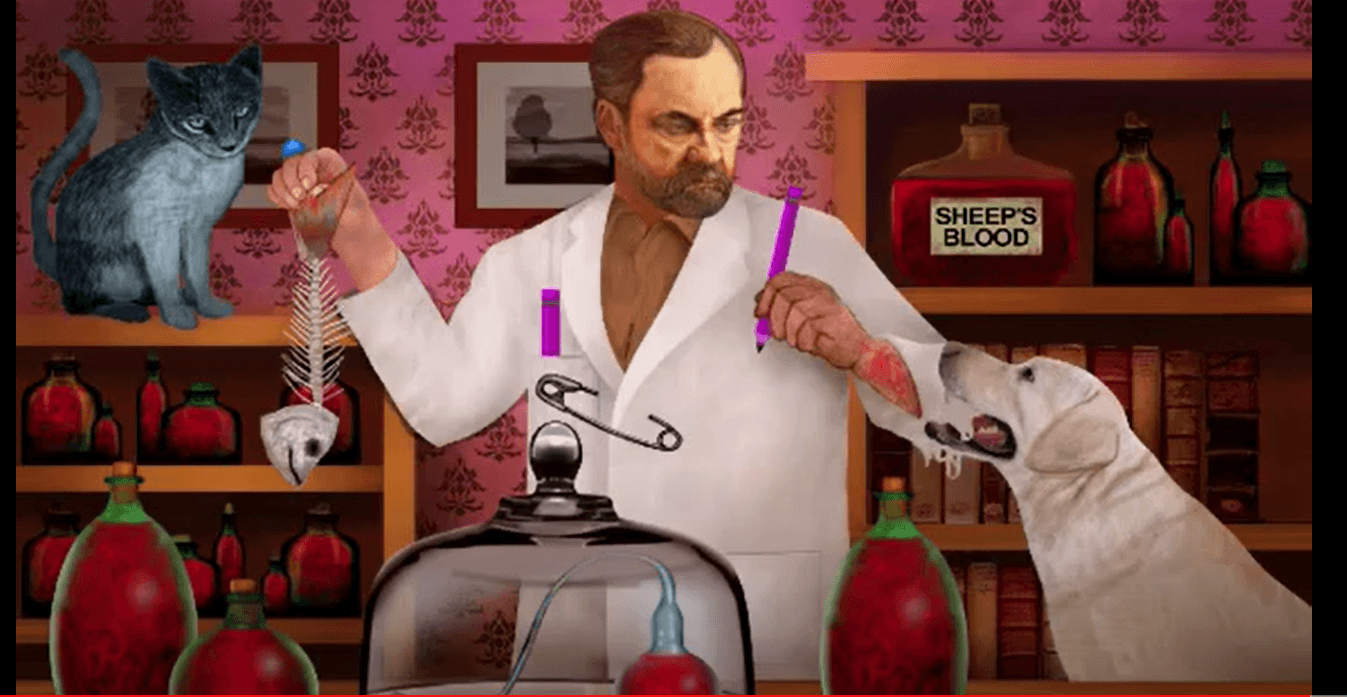

What is Pasteurella
This bug requires the use of silver stain and charcoal yeast extract plus cysteine in order to be grown/visualized. Labs commonly show hyponatremia as well as pneumonia.
What is Legionella pneumophila
What are macrolides.
This triple positive (catalase, oxidase, and urease), bug is able to survive in acidid mucosa, and is a treatable cause of peptic ulcers, and adenocarcinoma/lymphoma.
This gram negative curved rod has a polar flagella, and is oxidase positive. One of its more unique properties is that it grows at 42 degrees celsius.
A patient comes in complaining of neuropathy in hands and feet after a bout of bloody diarrhea. They believe they got the diarrhea after some bad chicken.
What is Campylobacter jejuni.
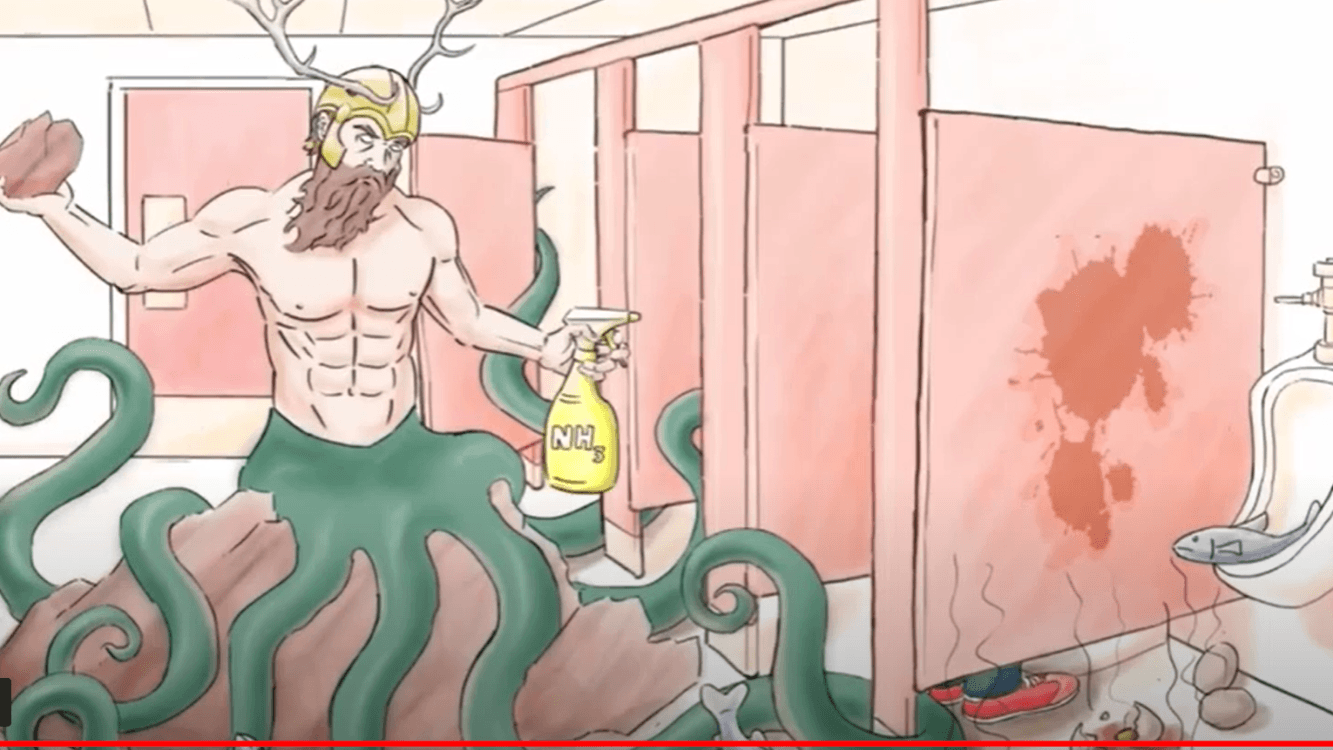 What is represented by the tentacles and the hat in this image.
What is represented by the tentacles and the hat in this image.
The ability for the bug to swarm and from struvite stones.