An ipad is an example of this.
 What is a tablet?
What is a tablet?
I _________ help you with your homework tomorrow, I promise.
What is will?
In this case, this is a promise so we use will.
____________ The stairs are slippery.
What is watch out!?
In this sentence, "watch out" is used as a warning to be cautious of the slippery stairs, suggesting the person should pay attention to avoid slipping or getting hurt.
My parents told me I ______ finish my homework before I go out.
What is must?
A modal verb used when we are 100% sure that something IS true.
What is this shoe is made of? Name two using a complete sentence.
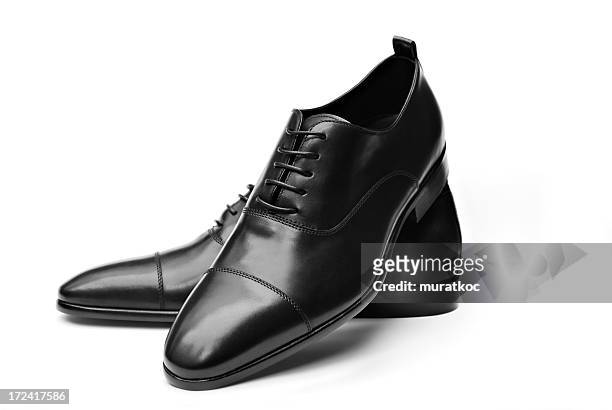

This shoe is made of leather and the sole is made of rubber.
I need to buy new _________ for my flashlight because the current ones have run out of power.
What are batteries?
I promise I ______ forget your birthday.
What is won't/will not?
"Won't" is the contracted form of "will not", and in this sentence, it’s used to express a promise or a firm intention not to do something (forgetting the birthday). The speaker is assuring the listener that they will not forget the event.
If you said, "I’m not going to forget your birthday", it would imply a future plan or intention to avoid forgetting the birthday, but it doesn't feel as strong or assuring as a promise. "Won't" makes it clear that you are committed to not forgetting, whereas "going to" just refers to the idea that it's something you're planning or intending to avoid, without the same level of certainty or commitment.
So, "won't" is used here because it emphasizes a promise, whereas "going to" would focus more on intention without the same strong commitment.
She __________ her phone all morning before realizing it was in her bag.
What is looked for?
In this sentence, "looked for" means to search or try to find the phone. An effort was made to find the phone, but it was only discovered after some searching.
I ______ go to the park later if the weather improves.
a) must
b) might
c) may not
d) cannot
What is b) might?
a. "Must" shows a strong obligation or certainty, but we are not certain the weather will improve.
b. "Might" indicates a possible action, "may not" indicates the possibility of not doing the action, which doesn't make sense in this case because we are saying the the weather could improve.
d. "Can't" doesn't fit here because it implies something is impossible or not allowed. You're not saying it's impossible to go to the park, just that it depends on whether the weather gets better.
To show:
past: _____
past participle: _______To show: show, shown (mostrar)
This machine can be programmed to perform tasks automatically, often used in factories or as assistants in homes
What is a robot?
Look at those dark clouds! It _____ rain soon
What is is going to/'s going to?
"Will" is typically used for spontaneous decisions, promises, or when something is certain, but not based on evidence.
If we said, "It will rain soon," it sounds like a decision or a statement of certainty without considering the signs (the dark clouds). The use of "will" would not reflect the evidence or signs leading to the prediction.
In this case, "going to" emphasizes that the speaker is making a prediction based on something observed (the dark clouds), while "will" would make it sound more like a general statement or an immediate decision rather than a prediction based on evidence.
So, "going to" fits here because it shows that the prediction is made based on signs or evidence, while "will" is more often used for things that are certain or decided in the moment, without reliance on external clues.
When you actively search for specific information or a fact on the internet or in a book.
What is look up?
- Look up is used when actively searching for specific, often factual information.
- Find out is used when discovering or uncovering information, often with a sense of discovery.
You ______ park your car here; it's a no-parking zone.
What is can't?
What is musn't/must not?
In this sentence, "can't" is a modal verb used to express prohibition or something that is 100% not allowed. It indicates that parking your car in that location is not permitted, and it's an explicit rule or restriction.
"Mustn't" is the contracted form of "must not", and it is also used to express prohibition or something that should notbe done. It's typically a stronger, more formal way of saying that something is not allowed.
Name the infinitive, past, and past participle of "dibujar"
To draw: drew, drawn
The veterinarian implanted a _________ in the dog's collar to help identify it if it gets lost."
What is a microchip?
I think________have the pizza for dinner because I’m too tired to cook.
What is I'll/I will?
In this case, "will" is used for an instant decision made in the moment, while "going to" would imply a prior plan, which doesn't fit here since the decision was made on the spot.
I _______ that she’s moving to a new city next month
What is found out?
In this case, "found out" is used because it's about discovering a piece of personal information that you didn’t actively search for (like in a conversation or by accident), and it wouldn't make sense to use "look up" here.
You ______ leave early today if your work is finished.
What is may?
What is might?
What is could?
"May" is used to express permission or possibility. In this sentence, it is used to give permission for someone to leave early if they meet the condition (finishing their work). It indicates that leaving early is allowed, but it is not a strict requirement. It’s optional and depends on the situation (whether the work is finished).
"Could" also expresses possibility, but it often implies more of an ability or potential. It suggests that, if the work is finished, leaving early is within the realm of possibility, but it may not necessarily happen. It implies a slightly greater chance or opportunity to leave early than "might."
"Might" expresses a possibility. It suggests that leaving early is an option, but it’s not guaranteed. There is some uncertainty about whether the person will actually leave early, depending on their work completion.
Must - If we replaced "may" with "must," the sentence would imply that leaving early is required if the work is finished, which isn’t the case here.
Can't - "Can't": This modal verb indicates prohibition or something that is not allowed. If we used "can't," the sentence would say that leaving early is forbidden, regardless of whether the work is finished. For example:
"You can't leave early today, even if your work is finished." This would imply that leaving early is not permitted at all.
Form the question and answer.
The garage floor / made of ?
The garage floor ___ _____ ____ _____.
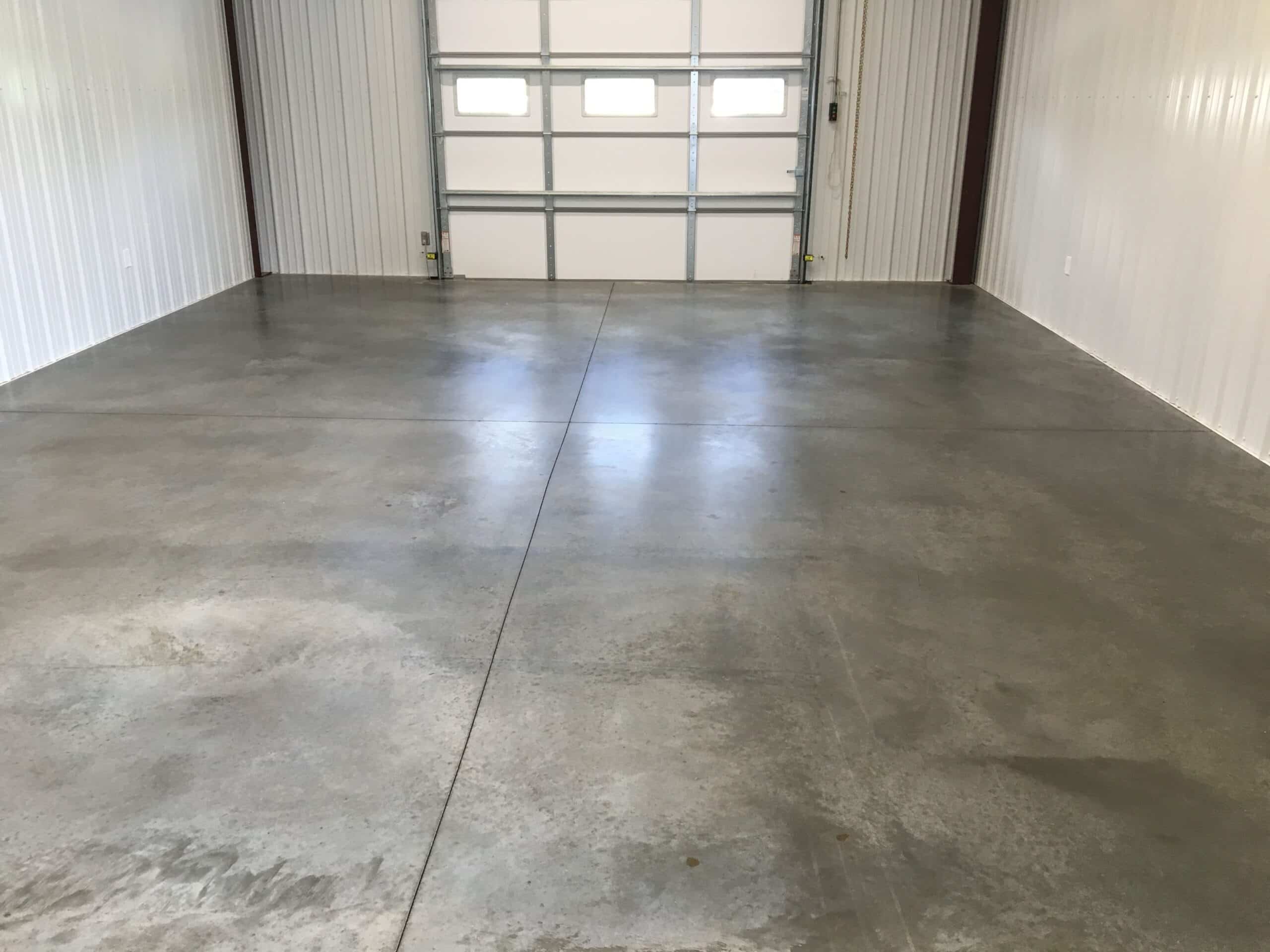

What is the garage floor made of?
The garage floor is made of concrete.
He used a _____ over the park to take aerial photos.
What is a drone?
I _______ visit my grandparents this weekend
What is am going to/'m going to?
In this case, "going to" is used for a planned action, whereas "will" would typically be used for a spontaneous decision or future promise.
She ________ at the party even though she wasn’t invited.
What is turned up?
In this case, "turned up" means to arrive or show up unexpectedly.
"If you finish your homework, you ____ go to the movies."
D) B and C are both true
A) must
B) may
C) could
D) can't
E) B and C are both true
What is E?
A) must: This would indicate an obligation or necessity. If you say, "You must go to the movies," it would mean it’s required or mandatory, which is not the intended meaning in the sentence.
B)/C) may: This indicates permission, suggesting that it is allowed to go to the movies, but "could" works better here to express a possible outcome, not just permission. Both work in this case.
E) can't: This would indicate a prohibition or something that is not allowed. It’s the opposite of what we want to say in this context, where going to the movies is a possibility.
Name the infinitive, past, and past participle of "volar"
To fly: flew, flown