Chargaff's rule says that ____ pairs with T and _____ pairs with G.
A, C
U stands for...
Uracil
Transcription turns ___________ into _________.
DNA, mRNA
The amino acid carrier molecule and the molecule that does the translation
tRNA, ribosome
What the "A" stands for in DNA and RNA.
Acid
The weakest bond in DNA
Hydrogen
The number of strands in mRNA
1
Where transcription takes place in eukaryotes
The nucleus
The type of covalent bond between amino acids.
peptide
Thymine and Uracil both pair with ____________.
Adenine
The type of sugar in DNA
RNA is made up of repeating nucleotides. This makes it a ______________.
Nucleic Acid
Transcription always reads the _________ strand of DNA, which goes from __' to ___'.
template strand; 3' to 5'
Outline the steps of translation
- The ribosome (small and large subunits) assembles on the mRNA, usually at the start codon (AUG).
- tRNA carrying the first amino acid (methionine) binds to the start codon.
- The ribosome moves along the mRNA, one codon at a time.
- tRNA molecules, each carrying a specific amino acid, bind to the ribosome and match their anticodon to the mRNA codon.
- Peptide bonds form between adjacent amino acids, adding them to the growing polypeptide chain.
- The ribosome continues to move along the mRNA, bringing in new tRNAs and adding more amino acids to the chain.
- When the ribosome encounters a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA), the translation process stops.
- The ribosome releases the completed polypeptide and the mRNA.
The term for DNA's backbone running 5' -> 3' on one side and 3' -> 5' on the other.
Antiparallel
The scientist that took the x-ray crystallography photo that showed DNA was a double-helix
Rosalind Franklin
The type of sugar in mRNA
ribose
If the DNA coding strand is ATG GGC TTA CCG, the the mRNA will be:
AUG GGC UUA CCG
The mutation causes a different amino acid to be used in the hemoglobin protein. This causes hemoglobin to fold incorrectly, causing the red blood cell to be full of rods of hemoglobin. This makes the red blood cell sticky and misshapen, causing clots in the blood vessels.
The building block of proteins.
Amino Acids
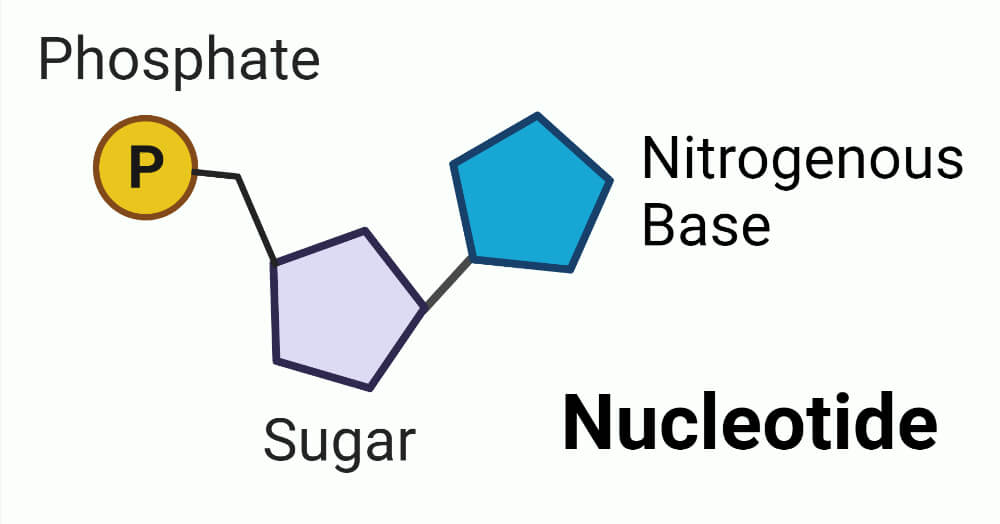
This is the structure of a nucleotide
Where RNA would be made in prokaryotes
The cytoplasm (they do not have a nucleus)
If the mRNA sequence is AUGAACGGUAC, then the coding strand of the DNA must have been...
ATGAACGGTAC
Translate this template strand of DNA into a polypeptide:
TAC CCT GAT ATT CCC
Met - Gly - Leu - STOP
Notes:
- no amino acid after STOP
- DNA coding strand: ATG GGA CTA TAA GGG)
- mRNA: AUG GGA CUA UAA GGG)
3 nucleotides on tRNA
anti-codon