Which number represents the ulna?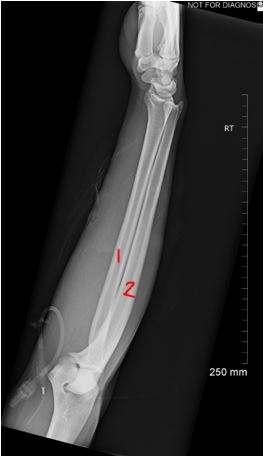
2
Which number represents the AC joint?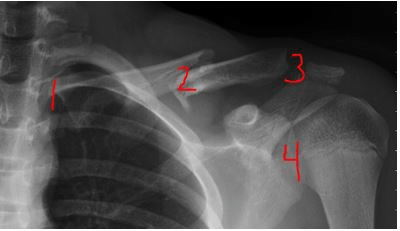
3
Approximately half of the patella should be seen free of superimposition by the femur in an AP oblique projection of the knee.
- True
- False
True
What anatomy would most likely be demonstrated if the patient is supine with knee flexed 40-45 degrees and the central ray is directed inferior-superiorly at 10-15 degrees from lower leg?
Patella in "sunrise" position
A radiograph of an AP pelvis reveals that the left obturator foramen is more open or elongated as compared with the right. What is the specific positioning error present on this radiograph?
- Left rotation
- Right rotation
Right rotation
Which number represents the MCP joint?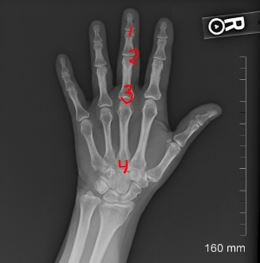
3
What is wrong with this PA hand image?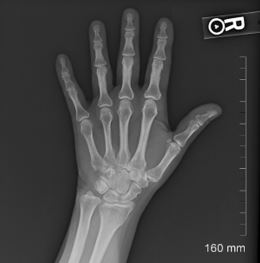
Wrong marker
The proximal tibiofibular joint should not be open in an AP oblique projection of the knee with medial rotation (internal rotation).
- True
- False
False
What anatomy would most likely be demonstrated with the patient is supine, knee flexed 40-45 degrees, CR perpendicular to lower leg, and centered ½ inch distal to apex of patella?
Intercondylar Fossa
By looking at this AP Pelvis, which way is the patient rotated?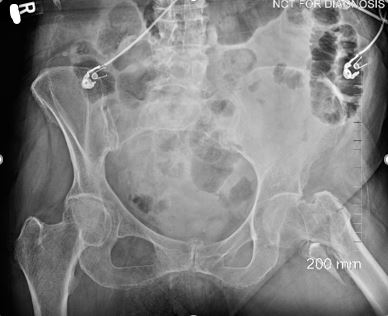
The patient is rotated towards the left.
Which number indicates an apice of the lung?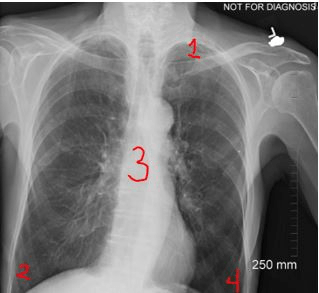
1
This is an AP Axial Clavicle image. Other than collimation what specifically is missing?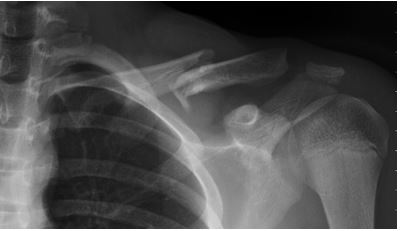
Marker
Regarding the anatomy of the knee, why is it important to angle the x-ray tube 5-7 degrees for a lateral knee?
- The medial condyle is longer
- The lateral condyle is longer
A
A radiograph of an AP pelvis reveals that the right iliac wing is foreshortened as compared with the left side. What specific positioning problem is present on this radiograph?
- Left rotation
- Right rotation
Left rotation
This is an AP Pelvis. Is all anatomy present that is required for this projection?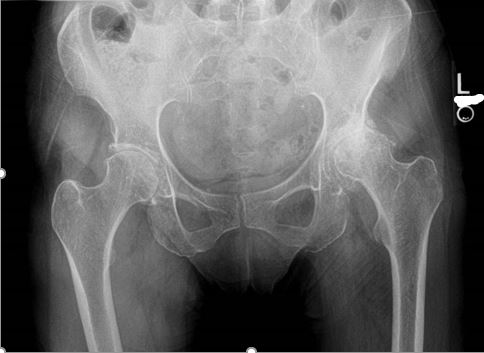
No, it needs repeated. Not all anatomy is present.
Is this repeatable?
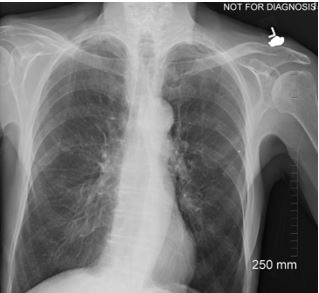
Yes
You have a patient for an elbow exam and they cannot straighten their arm completely (see below picture). How do you perform the AP elbow?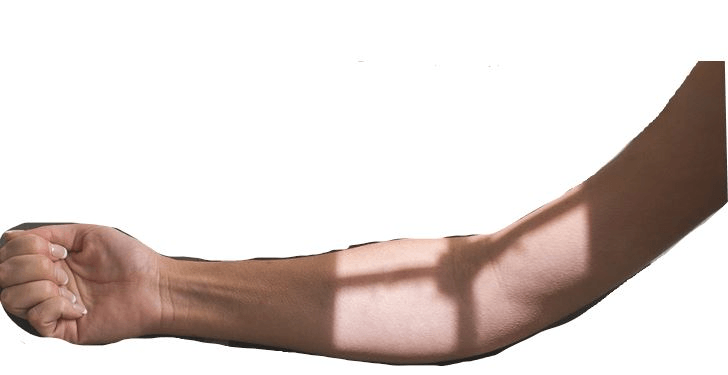
Take two images: one with the forearm parallel to the IR and one with the humerus parallel to the IR
If a patient is unable to separate their toes when positioning for a toe exam, what can you do to assist in proper positioning?
- Have the patient separate/hold their toes apart with their fingers.
- Use tape to separate toes.
- There is nothing you can do, the toes will be overlapping in the images.
What special projection is described as a Modified Axiolateral for patient who has limited movement in both lower limbs?
Clements-Nakayama Method
Please label the Pelvis.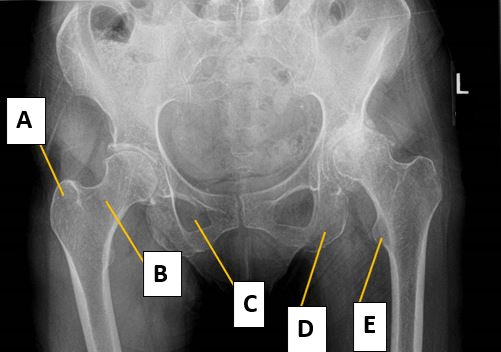
A Greater Trochanter
B Femoral Neck
C Obturator Foramen
D Ischial Tuberosity
E Lesser Trochanter
This is a lateral forearm. Other than collimation, what patient positioning modification needs to be used to make it a perfect lateral? 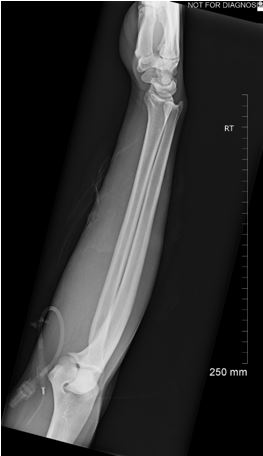
Elbow at 90° and wrist in true lateral
A patient has an obvious wrist deformity and they are unable to move their arm for a lateral position. How would you perform the lateral wrist?
Perform a x-table (horizontal beam) of the wrist, with minimal patient movement.
You performed a Leg (Tib/Fib) exam and the distal portion of the leg is clipped on both views. What should you do for the AP and Lateral to ensure all the anatomy is present?
- Obtain collimated views of the AP and Lateral knee.
- You only need to repeat the AP knee, even though the lateral is clipped.
- You only need to repeat the AP ankle, even though the lateral is clipped.
- Obtain collimated views of the AP and Lateral ankle.
Obtain collimated views of the AP and Lateral ankle.
What special projection is described as positioning the patient in posterior 45° obliques (upside and downside) to best visualize acetabulum and ilioiscial/iliopubic column?
Judet method
A patient comes into the ER with an obvious fractured right femur. They are unable to move their right leg, but they can move their left leg very well. The ER physician would like you to perform a right femur exam. How would perform the lateral proximal portion of the femur if the patient cannot turn on their side?