What are the values for standard temperature and standard pressure?
1 atm or 101.3 kPa and
0°C or 273K
State the relationship between temperature and vapor pressure
As temperature increases, the vapor pressure increases
Under which conditions of pressure and temperature is a real gas most like an ideal gas?
High temperature and low pressure
The volumes of four samples of gaseous compounds at 298 K and 101.3 kPa are shown in the table below.
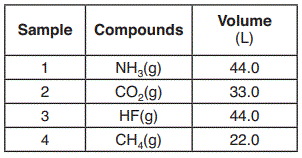
Which two samples contain the same number of molecules?
Sample 1 and 3
A balloon has a volume of 2.0 liters at 0.98atm. The pressure is increased to 2.5 atm. What is the new volume? Assume constant temperature.
0.78L
Which sample of argon gas has the same number of atoms as a 100.-milliliter sample of helium gas at 1.0 atm and 300. K?
50. mL at 1.0 atm and 300. K
50. mL at 0.5 atm and 300. K
100. mL at 0.5 atm and 300. K
100. mL at 1.0 atm and 300. K
D- 100. mL at 1.0 atm and 300. K
Two basic properties of the gas phase are
- a definite shape and a definite volume
- a definite shape but no definite volume
- no definite shape but a definite volume
- no definite shape and no definite volume
D) no definite shape and no definite volume
Based on Table H, state the vapor pressure of ethanol at 75ºC.
Approximately 86 kPa
Which statement describes the particles of an ideal gas, based on the kinetic molecular theory?
- There are attractive forces between the particles.
- The particles move in circular paths.
- The collisions between the particles reduce the total energy of the gas.
- The volume of the gas particles is negligible compared with the total volume of the gas.
D- The volume of the gas particles is negligible compared with the total volume of the gas.
A sample of helium gas is in a sealed, rigid container. What occurs as the temperature of the sample is increased?
- The mass of the sample decreases.
- The number of moles of gas increases.
- The volume of each atom decreases.
- The frequency of collisions between atoms increases.
D.) The frequency of collisions between atoms increases.
A sample of nitrogen inside a rigid, metal container at 293K is placed inside an oven whose temperature is 323K. The pressure inside the container at 293K was at 3.00 atm. What is the pressure of the nitrogen after its temperature is increased to 323K?
3.31 atm
A 10.0-gram sample of nitrogen is at STP. Which property will increase when the sample is cooled to 72 K at standard pressure?
- mass
- volume
- density
- temperature
C) density
Which element is a gas at STP?
- sulfur
- xenon
- potassium
- phosphorus
B) xenon
Which of the four liquids on Table H has the strongest forces of attraction?
ethanoic acid
Which phrase describes the motion and attractive forces of ideal gas particles?
- random straight-line motion and no attractive forces
- random straight-line motion and strong attractive forces
- random curved-line motion and no attractive forces
- random curved-line motion and strong attractive forces
A. random straight-line motion and no attractive forces
As the temperature of a given sample of a gas decreases at constant pressure, the volume of the gas
- decreases
- increases
- remains the same
A) decreases
A gas has a pressure of 0.370 atm at 323K. What is the pressure at standard temperature? Assume constant volume.
0.313 atm
A sample of oxygen gas is sealed in container X. A sample of hydrogen gas is sealed in container Z. Both samples have the same volume, temperature, and pressure. Which statement is true?
- Container X contains more gas molecules than container Z.
- Container X contains fewer gas molecules than container Z.
- Containers X and Z both contain the same number of gas molecules.
- Containers X and Z both contain the same mass of gas.
C) Containers X and Z both contain the same number of gas molecules.
When a sample of gas is cooled in a sealed, rigid, container the pressure the gas exerts on the walls of the container will decrease because the gas particles hit the walls of the container
- less often and with less force
- less often and with more force
- more often and with less force
- more often and with more force
A.) less often and with less force
At which temperature is the vapor pressure of ethanol equal to the vapor pressure of propanone at 35°C?
- 35°C
- 60.°C
- 82°C
- 95°C
B) 60.°C
At which temperature and pressure will a sample of neon gas behave most like an ideal gas?
- 300. K and 2.0 atm
- 300. K and 4.0 atm
- 500. K and 2.0 atm
- 500. K and 4.0 atm
C) 500. K and 2.0 atm
When the pressure exerted on a confined gas at constant temperature is doubled, the volume of the gas is
- halved
- doubled
- tripled
- quartered
A.) halved
A balloon with a volume of 2 liters and a temperature of 25oC is heated to 38oC. What is the new volume? Assume constant pressure
2.09L
Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, which of the following gases would behave most like an ideal gas?
- He(g)
- NH3(g)
- Cl2(g)
- CO2(g)
(A.) He(g)
What happens to the average kinetic energy of a gas when it is heated?
The kinetic energy increases
What is the normal boiling point of propanone?
Approximately 560C
The concept of an ideal gas is used to explain
- the mass of a gas sample
- the behavior of a gas sample
- why some gases are monatomic
- why some gases are diatomic
B) the behavior of a gas sample
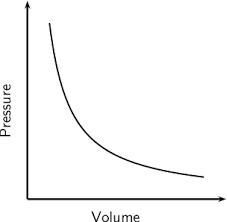
Draw the graph that shows the relationship between pressure and volume of a gas
When a sample of hydrogen is compressed to 240 mL, its pressure changes from 0.8 atmospheres to 2 atmospheres. What was the original volume of the sample?
600 mL
Determine the pressure of the helium gas in trial 4.
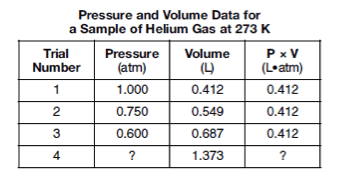
0.3 atm