What is Boyle’s Law?
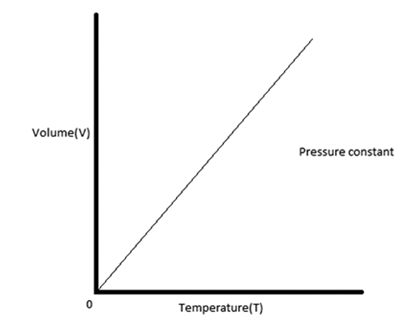
What is Charles’ Law?
This law states that pressure and temperature are directly proportional when volume is constant.
What is Gay-Lussac’s Law?
This law states that equal volumes of gases contain equal numbers of molecules at the same temperature and pressure.
What is Avogadro’s Law?
This gas law states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each gas.
What is Dalton’s Law?
The equation for the ideal gas law is this.
What is PV = nRT?
According to Boyle’s Law, if the volume of a gas decreases, this happens to the pressure.
What is increase?
The temperature in Charles’ Law must always be measured in this unit.
What is Kelvin?
If a gas at 1.0 atm and 300 K is heated to 600 K at constant volume, the new pressure is this.
What is 2.0 atm?
Avogadro’s Law states that volume is directly proportional to this quantity.
What is the number of moles (n)?
The pressure exerted by a single gas in a mixture is called this.
What is partial pressure?
In PV = nRT, the variable ‘R’ represents this.
What is the ideal gas constant?
A gas has a pressure of 2.0 atm and a volume of 4.0 L. If the volume increases to 8.0 L at constant temperature, what is the new pressure?
What is 1.0 atm?
A gas at 300 K and 2.0 L is heated to 600 K at constant pressure. The new volume is this.
What is 4.0 L?
The relationship between temperature and pressure in Gay-Lussac’s Law is called this type of proportionality.
What is direct?
A 2.0 L container holds 1.0 mole of gas. If 3.0 more moles are added, the new volume is this.
What is 8.0 L?
A container holds oxygen at 2.0 atm and nitrogen at 3.0 atm. The total pressure in the container is this.
What is 5.0 atm?
A sample of gas has a volume of 5.0 L, pressure of 2.0 atm, and 0.5 moles. Solving for temperature, this is the result using R = 0.0821 L·atm/mol·K.
What is 244 K?
Boyle’s Law is mathematically expressed as this equation.
What is P₁V₁ = P₂V₂?
Charles’ Law is mathematically expressed as this equation.
What is V₁/T₁ = V₂/T₂?
Gay-Lussac’s Law is mathematically expressed as this equation.
What is P₁/T₁ = P₂/T₂?
The standard molar volume of a gas at STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure) is this.
What is 22.4 L?
Dalton’s Law is mathematically expressed as this equation.
What is Ptotal=P1+P2+P3+...P?
The conditions of 0°C (273 K) and 1 atm pressure are known as this.
What is Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)?
If a balloon at 3.0 atm and 6.0 L is placed in a vacuum chamber where pressure decreases to 1.0 atm, the balloon’s new volume is this.
What is 18.0 L?
If a balloon at -23°C has a volume of 5.0 L, its volume at 277°C will be this.
What is 10.0 L?
If a sealed container is placed in an oven, and the temperature is doubled, this happens to the gas pressure inside.
What is it doubles?
This scientist’s hypothesis led to the understanding that gases of different types, at the same conditions, have the same number of molecules in equal volumes.
Who is Amedeo Avogadro?
A gas is collected over water at 25°C, where the vapor pressure of water is 23.8 mmHg. If the total pressure in the container is 760 mmHg, the pressure of the dry gas is this.
What is 736.2 mmHg?
A gas sample has a pressure of 3.0 atm, a volume of 10.0 L, and a temperature of 400 K. Using R = 0.0821 L·atm/mol·K, the number of moles of gas in the sample is approximately this.
What is 0.91 moles?