What hemoglobin level is an indication for transfusion in a GI bleed?
<7
In the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy, aside from lactulose, what other medications can be administered to help reduce ammonia levels?
Rifaximin
When should oral feeding be resumed in acute pancreatitis?
When nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain resolve
What type of hepatitis is usually associated with aminotransferase levels >1000?
HAV
What is the recommended treatment for a 50-year-old male presenting with dysphagia and odynophagia, given the findings shown below?
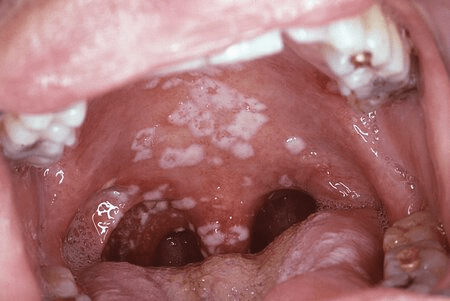
Oral fluconazole
Based on the endoscopy image below, what is the source of the upper GI bleed?
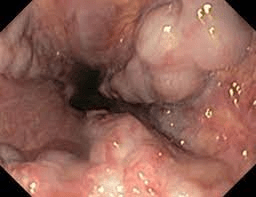
Varices- due to increased portal hypertension
What class of antibiotics is the first choice for treating spontaneous bacterial peritonitis?
Third generation cephalosporins (eg. Cefotaxime)
If feeding is not tolerated in the setting of acute pancreatitis, within how many hours should you consider starting enteral feeding?
72 hours
Non-immunized persons recently exposed to HAV should receive the HAV vaccine within ____ weeks of exposure
2
What is the recommended treatment for gallstones that are discovered incidentally and are asymptomatic?
Clinical observation
When is it appropriate to resume anticoagulation in a patient who has recently experienced a gastrointestinal bleed and achieved hemostasis?
Within one week of discontinuation
What blood pressure medications should be stopped in patients with cirrhosis/portal hypertension?
ACE inhibitors, ARBs.
Note: non-selective beta blockers are not necessarily contraindicated, but should be used with caution
What is the treatment of choice for type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis?
high-dose prednisone
What is the definitive diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis?
Liver biopsy
Which disorder is associated with the presence of anti-mitochondrial antibodies?
Primary biliary cirrhosis
What would be the treatment of choice for a patient with recent GI bleeding who needs to be continued on NSAIDs?
Celecoxib+PPI
Name one condition associated with a SAAG >1.1 and ascitic fluid protein >2.5
Right-sided heart failure, Budd Chiari syndrome
1.5 mL/kg/hr
45-year-old male with history of HCV presented with the palpable purpura shown below. What is your primary DDx?
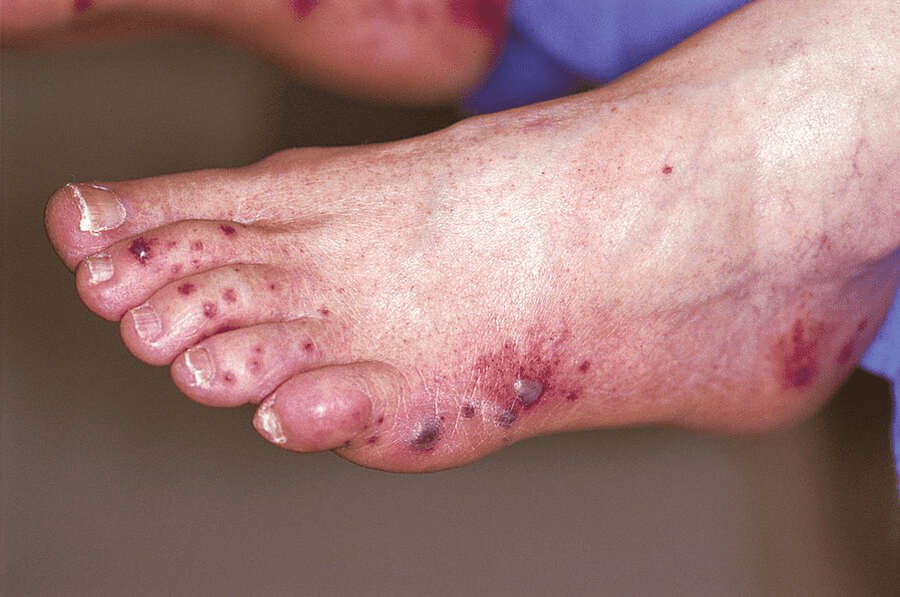
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis consistent with HCV-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia
Other than endoscopy, what test can be used to confirm the diagnosis of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth?
glucose breath test
What test should be considered for stable patients with small bowel bleeding if endoscopy and colonoscopy results are normal?
Capsule endoscopy
Name one condition associated with a SAAB <1.1 and ascitic fluid protein >2.5
Malignancy or TB
What complications associated with pancreatitis may require a surgical consultation, aside from those necessitating cholecystectomy?
Pancreatic necrosis, infected pseudocysts
What antiviral medication is usually used for the treatment of acute hepatitis B infections?
Entecavir or Tenofovir
Note: In patients co-infected with HIV and who have not yet been treated for either disease, emtricitabine-tenofovir is typically used as part of ART.
What is the treatment of choice for mild-to-moderate ulcerative proctitis?
5-Aminosalicylate suppositories
Based on the endoscopy image, what is the source of the upper GI bleed?
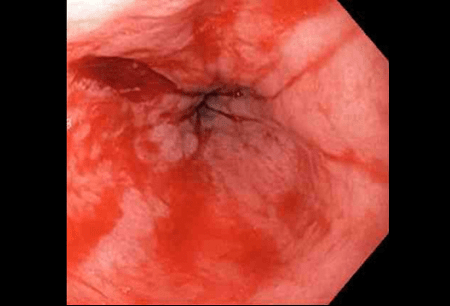
Mallory-Weiss tear
What are the two primary screening modalities recommended for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis?
Abdominal ultrasonography and AFP screening every 6 months
What is the recommended size at which uninfected, asymptomatic pancreatic cysts need to be drained?
Pancreatic pseudocysts do NOT require drainage unless they cause significant symptoms or are infected, regardless of size.
What is the recommended follow-up test if an anti-HCV antibody test returns positive for Hepatitis C infection?
HCV RNA- to determine the presence of active infection
What combination treatment should be added for Crohn disease patients resistant to glucocorticoids?
Infliximab+azathioprine
What diagnosis should be considered in someone with GI bleed and a crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur at the right upper sternal border?
Heyde syndrome (triad of aortic stenosis, GI bleed due to angiodysplasia, and acquired vWF syndrome)
What is the indication for albumin infusion in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis?
Bilirubin level >5 mg/dl
CT reveals parenchymal swelling (“sausage-shaped” pancreas). IgG4 positive. What is your diagnosis?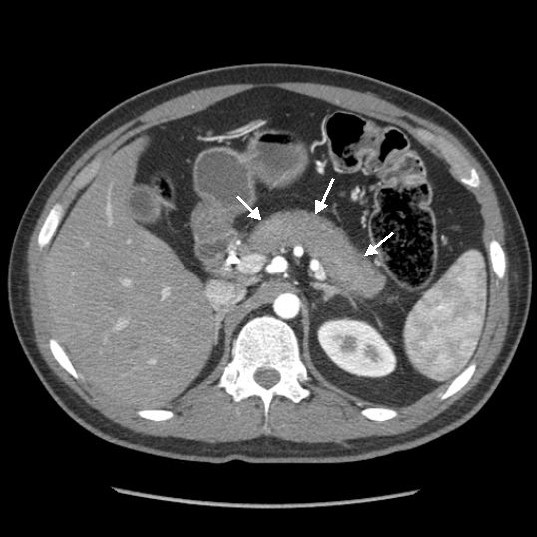
Autoimmune pancreatitis
For patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis, as defined by a MELD score of greater than 20, prednisolone and ________ are the recommended treatments.
N-acetylcysteine
27-year-old male with a history of celiac disease and the rash shown below, consistent with dermatitis herpetiformis. What is the treatment of choice?

Dapsone
Note: testing for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency is required before initiation of therapy.