Thicker than water
Regurgilicious
When in doubt, SPU
Picture this
Potpurri
100
$100
Thickening feeds has been shown to cause this change in infants with reflux.
Thickening feeds has been shown to cause this change in infants with reflux.
What is a decrease in episodes of vomiting? It also causes reduced crying time. However, thickening formula does not improve index scores of GER and it may not reduce reflux episodes that are nonregurgitant.
100
$100
Transient relaxation of this structure is thought to be central to gastroesophageal reflux.
Transient relaxation of this structure is thought to be central to gastroesophageal reflux.
What is the lower esophageal sphincter?
TLESR (transient LES relaxation) occurs independently of swallowing and is regulated by vagovagal reflexes. It is stimulated by gastric distension and is more likely to occur during straining, increased intrabdominal pressure, and if the GE junction is positioned below the air-fluid level of the stomach.

TLESR (transient LES relaxation) occurs independently of swallowing and is regulated by vagovagal reflexes. It is stimulated by gastric distension and is more likely to occur during straining, increased intrabdominal pressure, and if the GE junction is positioned below the air-fluid level of the stomach.

100
$100
Upper endoscopy, which allows macroscopic and microscopic evaluation of the esophagus and UGI tract, can help rule out these other conditions that can be confused with GERD (name at least 2).
Upper endoscopy, which allows macroscopic and microscopic evaluation of the esophagus and UGI tract, can help rule out these other conditions that can be confused with GERD (name at least 2).
What are eosinophilic esophagitis, pill esophagitis, Crohn disease, Peptic Ulcer disease, and Celiac disease?
Example of eosinophilic esophagitis

Example of eosinophilic esophagitis

100
$100
The information age has brought about a wireless 48-hour version of this gold standard study for gastroesophageal reflux.
The information age has brought about a wireless 48-hour version of this gold standard study for gastroesophageal reflux.
What is intraesophageal pH monitoring?
pH monitoring documents esophageal exposure to refluxed contents over a prolonged period of time and can be useful when deciding whether to pursue Nissen fundoplication. The traditional method is the "pH probe," a catheter-based 24-hour continuous study. However, two new technologies are available, including the wireless 48-hour monitor and a 24-hour catheter that combines impedance and pH monitoring with a multichannel probe (sensors all along the esophagus).
Prior to conducting this study, H2 blockers should be held for 72 hours, PPIs for 1 week.
The wireless pH monitor is thought to be more tolerable for children, provides prolonged monitoring, and allows activity. At this point it is only being used in children 4-18 years of age, at least 30 lb in weight.
pH monitoring documents esophageal exposure to refluxed contents over a prolonged period of time and can be useful when deciding whether to pursue Nissen fundoplication. The traditional method is the "pH probe," a catheter-based 24-hour continuous study. However, two new technologies are available, including the wireless 48-hour monitor and a 24-hour catheter that combines impedance and pH monitoring with a multichannel probe (sensors all along the esophagus).
Prior to conducting this study, H2 blockers should be held for 72 hours, PPIs for 1 week.
The wireless pH monitor is thought to be more tolerable for children, provides prolonged monitoring, and allows activity. At this point it is only being used in children 4-18 years of age, at least 30 lb in weight.
100
$100
These agents are first-line recommended pharmacotherapy for gastroesophageal reflux.
These agents are first-line recommended pharmacotherapy for gastroesophageal reflux.
What are Histamine-2 receptor antagonists (cimetidine, famotidine, nizatidine, and ranitidine)?
They are effective for mild-moderate symptoms. They have an excellent safety profile. They act by selectively inhibiting histamine receptors on the parietal cells of gastric mucosa.
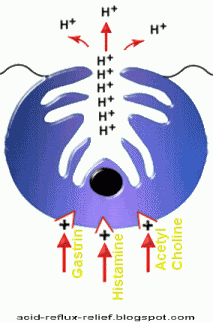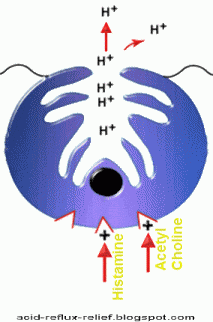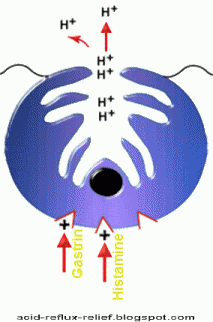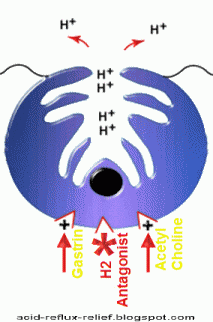
They are effective for mild-moderate symptoms. They have an excellent safety profile. They act by selectively inhibiting histamine receptors on the parietal cells of gastric mucosa.
200
$200
Current recommendations for formula thickening in this ratio increases caloric density of regular infant formula to 30 kcal/ounce.
Current recommendations for formula thickening in this ratio increases caloric density of regular infant formula to 30 kcal/ounce.
What is 1 tablespoon of rice cereal to 1 ounce formula?


200
$200
By this age, you can expect most infants to outgrow their symptoms of GER.
By this age, you can expect most infants to outgrow their symptoms of GER.
What is 12 months?
50% of 0-3 month olds and 67% of 4 month olds experience vomiting at least once daily. By 12 months, only 5% of healthy twelve-month olds experience vomiting.
50% of 0-3 month olds and 67% of 4 month olds experience vomiting at least once daily. By 12 months, only 5% of healthy twelve-month olds experience vomiting.
200
$200
This procedure is considered effective therapy with children who have intractable GERD.
This procedure is considered effective therapy with children who have intractable GERD.
What is Nissen Fundoplication?
It is especially effective in chidlren with refracotry esophagitis, structures, or those at risk for morbidity from chronic pulmonary disease. Fundoplication doescarry the risk of being too tight (dysphagia) or too loose (incompetent - which occurs frequently as seen in long term studies of fundoplications).
It is especially effective in chidlren with refracotry esophagitis, structures, or those at risk for morbidity from chronic pulmonary disease. Fundoplication doescarry the risk of being too tight (dysphagia) or too loose (incompetent - which occurs frequently as seen in long term studies of fundoplications).
200
$200
This is one of the most important indications for a pH probe study.
This is one of the most important indications for a pH probe study.
What are pulmonary symptoms in the absence of clinical GERD (e.g. evaluate apnea with pH probe and pneumogram)? Other acceptable responses include: assessing the efficacy of acid suppression during treatment, and to evaluate atypical GERD.
200
$200
Extraesophageal symptoms are common in GERD. This common disease has a prevalence in 13.2% of patients with GER symptoms versus 6.8 % of controls.
Extraesophageal symptoms are common in GERD. This common disease has a prevalence in 13.2% of patients with GER symptoms versus 6.8 % of controls.
What is asthma?
Additional extraesophageal symptoms to look for include pneumonia, ALTE, bronchiectasis, general respiratory symptoms, ENT symptoms, and dental erosion.
Significantly, studies have been inconsistent in showing the relationship between pharmacologic treatment of GERD and extraesophageal symptoms. Short term studies have shown no improvement with prokinetics, H2 blockers, and PPI ( studies with cisapride and ranitidine) over placebo. However, 1 six-month study reports significant improvements in asthma sx in patients receiving PPI compared to controls.
El Serag, et. al. Prevalence of symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux during childhood: a pediatric practice-based survey. Pediatric Practice Research Group. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2000; 154: 150-4.
Additional extraesophageal symptoms to look for include pneumonia, ALTE, bronchiectasis, general respiratory symptoms, ENT symptoms, and dental erosion.
Significantly, studies have been inconsistent in showing the relationship between pharmacologic treatment of GERD and extraesophageal symptoms. Short term studies have shown no improvement with prokinetics, H2 blockers, and PPI ( studies with cisapride and ranitidine) over placebo. However, 1 six-month study reports significant improvements in asthma sx in patients receiving PPI compared to controls.
El Serag, et. al. Prevalence of symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux during childhood: a pediatric practice-based survey. Pediatric Practice Research Group. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2000; 154: 150-4.
300
$300
Although this type of positioning has been shown to be helpful in GERD, it is not recommended by the AAP for this reason. (Name the positioning and the reason)
Although this type of positioning has been shown to be helpful in GERD, it is not recommended by the AAP for this reason. (Name the positioning and the reason)
What is prone positioning, not recommended because of SIDS risk?
While awake the patient can be placed in prone position and upright carried position. There is also some evidence to show benefit to left side positioning. Additionally, elevation of the head of the bed during sleep (note, elevate head of bed, not excess pillows) can help in avoiding abdominal flexion and compression that could worsen reflux.
While awake the patient can be placed in prone position and upright carried position. There is also some evidence to show benefit to left side positioning. Additionally, elevation of the head of the bed during sleep (note, elevate head of bed, not excess pillows) can help in avoiding abdominal flexion and compression that could worsen reflux.
300
$300
The Rome III criteria judges infant regurgitation (GER) as having the following frequency.
The Rome III criteria judges infant regurgitation (GER) as having the following frequency.
What is regurgitation greater than or equal to 2 times a day for greater than or equal to 3 weeks?
ADDITIONALLY: There is no retching, hematemesis, aspiration, apnea, FTT, feeding or swallowing difficulties, or abnormal posturing
The infant must be 1-12 months of age and otherwise healthy. There is no evidence of metabolic, gastrointestinal, or CNS disease to explain the symptoms.
ADDITIONALLY: There is no retching, hematemesis, aspiration, apnea, FTT, feeding or swallowing difficulties, or abnormal posturing
The infant must be 1-12 months of age and otherwise healthy. There is no evidence of metabolic, gastrointestinal, or CNS disease to explain the symptoms.
300
$300
The finding of these types of cells on BAL are helpful in evaluating for silent aspiration when using laryngotracheobronchoscopy in GERD.
The finding of these types of cells on BAL are helpful in evaluating for silent aspiration when using laryngotracheobronchoscopy in GERD.
What are lipid-laden macrophages?

A "bronch" can also look at other extraesophageal manifestations of GERD, such as posterior laryngeal inflammation, and vocal cord nodules.

A "bronch" can also look at other extraesophageal manifestations of GERD, such as posterior laryngeal inflammation, and vocal cord nodules.
300
$300
In this study (see image) of a 12-year old boy with dysphagia, this structure was identified in the distal esophagus. (Name the study and the structure)
In this study (see image) of a 12-year old boy with dysphagia, this structure was identified in the distal esophagus. (Name the study and the structure)
 |
| From GER |
What is an Upper GI series and Schatzki's ring?
The upper GI series (using barium) is used to rule out anatomic abnormalities of the upper GI tract, including malrotation. For diagnosing reflux its sensitivity and specificity are very inconsistent and are inferior compared to the gold standard of 24-hour intraesophageal pH monitoring.
The upper GI series (using barium) is used to rule out anatomic abnormalities of the upper GI tract, including malrotation. For diagnosing reflux its sensitivity and specificity are very inconsistent and are inferior compared to the gold standard of 24-hour intraesophageal pH monitoring.
300
$300
These are two ways in which GERD is thought to induce respiratory symptoms.
These are two ways in which GERD is thought to induce respiratory symptoms.
What are:
(1) direct contact of refluxed gastric contents with respiratory tract AND
(2) reflexive interactions between the esophagus and respiratory tract.
(1) direct contact of refluxed gastric contents with respiratory tract AND
(2) reflexive interactions between the esophagus and respiratory tract.
400
$400
While it is good to try empiric therapy in children with reflux, these indications warrant prompt diagnostic evaluation (name 3).
While it is good to try empiric therapy in children with reflux, these indications warrant prompt diagnostic evaluation (name 3).
What are emesis, failure to thrive, dysphagia, and severe respiratory complications?
400
$400
These must be present to put the "Disease" in GERD.
These must be present to put the "Disease" in GERD.
What are complications?
Infant reflux turns into reflux disease when the pattern of emesis and regurgitation turns to irritability, back arching, and feeding aversion - and can present as chest or epigastric pain in older children. Esophagitis can occur and lead to stricture formation. It can also lead to failure to thrive, respiratory presentations, apnea, and stridor.
Infant reflux turns into reflux disease when the pattern of emesis and regurgitation turns to irritability, back arching, and feeding aversion - and can present as chest or epigastric pain in older children. Esophagitis can occur and lead to stricture formation. It can also lead to failure to thrive, respiratory presentations, apnea, and stridor.
400
$400
This complication encountered after fundoplication can occur especially if the edges of the dilated esophageal hiatus are not approximated well.
This complication encountered after fundoplication can occur especially if the edges of the dilated esophageal hiatus are not approximated well.
What is a paraesophageal hernia?


400
$400
Although this study can give information about gastric emptying and may help in detection of GER and aspiration episodes, it has poor sensitivity, its technique is difficult to standardize, and there is a lack of age-normative data behind the study.
Although this study can give information about gastric emptying and may help in detection of GER and aspiration episodes, it has poor sensitivity, its technique is difficult to standardize, and there is a lack of age-normative data behind the study.
What is gastric scintigraphy? (milk scan)
This is a nuclear medicine study in which radiolabeled formula is fed to the patient and swallowing and reflux episodes are tracked with imaging.
This is a nuclear medicine study in which radiolabeled formula is fed to the patient and swallowing and reflux episodes are tracked with imaging.
400
$400
Dental erosions secondary to GERD are found on this surface of the teeth.
Dental erosions secondary to GERD are found on this surface of the teeth.
What is the lingual surface?


500
$500
Erythromycin is sometimes used for cases of reflux because it does this.
Erythromycin is sometimes used for cases of reflux because it does this.
What is act as a prokinetic?
Additional prokinetic agents include metochlopramide (working by blocking D2 and 5HT3 receptors), bethanechol (cholinergic). Erythromycin functions as a motilin receptor agonist.
Prokinetic agents can improve gastric emptying and often increase LES pressure. The frequency of TLESRs is not reduced with prokinetics.
Additional prokinetic agents include metochlopramide (working by blocking D2 and 5HT3 receptors), bethanechol (cholinergic). Erythromycin functions as a motilin receptor agonist.
Prokinetic agents can improve gastric emptying and often increase LES pressure. The frequency of TLESRs is not reduced with prokinetics.
500
$500
This set of pathophysiologic changes -- which can occur in GERD -- is termed Barrett Esophagus, which is a precursor of esophageal adenocarcinoma.
This set of pathophysiologic changes -- which can occur in GERD -- is termed Barrett Esophagus, which is a precursor of esophageal adenocarcinoma.
What is the metaplastic transformation of normal esophageal squamous epithelia into intestinal epithelium?

500
$500
These infectious complications have been associated with GERD. (name 3)
These infectious complications have been associated with GERD. (name 3)
What are aspiration pneumonia, otitis media, sinusitis, laryngitis?
Noninfectious complications include vocal cord nodules, lymphoid hyperplasia, hoarseness, laryngeal edema, chronic cough, voice fatigue.
Noninfectious complications include vocal cord nodules, lymphoid hyperplasia, hoarseness, laryngeal edema, chronic cough, voice fatigue.
500
$500
A new type of monitoring, MII-pH monitoring uses esophageal impedance to overcome this disadvantage of traditional pH monitoring.
A new type of monitoring, MII-pH monitoring uses esophageal impedance to overcome this disadvantage of traditional pH monitoring.
What is the inability to detect nonacid reflux?
In this type of study, sensitivity is increased over pH alone because 50% of reflux episodes in infants can be nonacid. Symptomatic reflux - including irritability and apnea, can occur with both acid and nonacid reflux.
In this type of study, sensitivity is increased over pH alone because 50% of reflux episodes in infants can be nonacid. Symptomatic reflux - including irritability and apnea, can occur with both acid and nonacid reflux.
500
$500
This syndrome is used to describe the series of stereotypic back arching and stretching movements present in patients with GER, which can be mistaken for dystonia or atypical seizures.
This syndrome is used to describe the series of stereotypic back arching and stretching movements present in patients with GER, which can be mistaken for dystonia or atypical seizures.
What is Sandifer Syndrome?